Using index notation, show that the trace is cyclic, i.e. that for any number m of N × N matrices M(1), M(2),..., M(m), the following holds true: Tr ( M (1) M (²) ... M(m)) = Tr (M(m) M(¹) M (²) ... M(m−1)) (1)
Using index notation, show that the trace is cyclic, i.e. that for any number m of N × N matrices M(1), M(2),..., M(m), the following holds true: Tr ( M (1) M (²) ... M(m)) = Tr (M(m) M(¹) M (²) ... M(m−1)) (1)
Elements Of Modern Algebra
8th Edition
ISBN:9781285463230
Author:Gilbert, Linda, Jimmie
Publisher:Gilbert, Linda, Jimmie
Chapter2: The Integers
Section2.2: Mathematical Induction
Problem 46E: Use generalized induction and Exercise 43 to prove that n22n for all integers n5. (In connection...
Question
Please answer this question in detail with examples
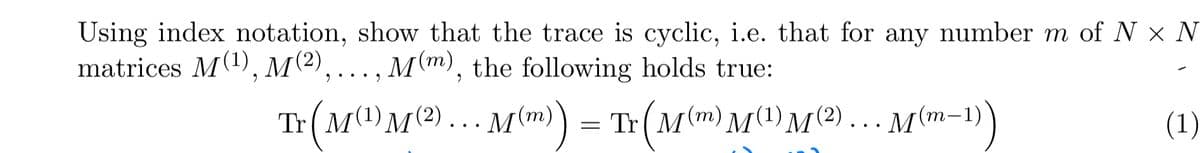
Transcribed Image Text:Using index notation, show that the trace is cyclic, i.e. that for any number m of N × N
matrices M(1), M(2),..., M(m), the following holds true:
Tr ( M (1) M (²) ... M(m)) = Tr (M(m) M(¹) M (²) ... M(m−1))
(1)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Elements Of Modern Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463230
Author:
Gilbert, Linda, Jimmie
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage


Elements Of Modern Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463230
Author:
Gilbert, Linda, Jimmie
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage


Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning