Using the indicial notation, show that: a. (āx b) a = 0 b. c. div(curl v) = 0 curl Vu = 0 for any continuously differentiable u.
Using the indicial notation, show that: a. (āx b) a = 0 b. c. div(curl v) = 0 curl Vu = 0 for any continuously differentiable u.
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter6: The Trigonometric Functions
Section6.1: Angles
Problem 38E
Related questions
Question
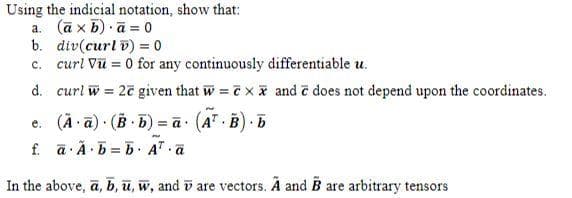
Transcribed Image Text:Using the indicial notation, show that:
a. (āx b) ā= 0
b. div(curl v) = 0
c. curl Vũ = 0 for any continuously differentiable u.
d. curl w = 2ē given that w = cx
e. (A·ā). (Bb)=ā. (AT B). b
F
f. a Abb. A a
.
In the above, a, b, u, w, and are vectors. A and B are arbitrary tensors
and e does not depend upon the coordinates.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305071742
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305071742
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning