vhere the constants A vertically scales the function. (negative A reflects the function about the x-axis.) B horizontally scales the function. (negative B reflects the function about the y-axis.) • H horizontally shifts the function. K vertically shifts the function. Transform f(x) into g(a) where the transformation is g(x) = f(x -3) – 1 The function f (x) is shown below in red. Graph the transformed function g(x) by first placing a dot at each end point of the new transformed function and then click on the "line segment" button and connect the two blue dots. (Hint: Transform the function by applying the constants in this order: H, B, A, K.) -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 3 4 -2 -3 -4 -5- -6- Clear All Draw: Dot Line Segment
vhere the constants A vertically scales the function. (negative A reflects the function about the x-axis.) B horizontally scales the function. (negative B reflects the function about the y-axis.) • H horizontally shifts the function. K vertically shifts the function. Transform f(x) into g(a) where the transformation is g(x) = f(x -3) – 1 The function f (x) is shown below in red. Graph the transformed function g(x) by first placing a dot at each end point of the new transformed function and then click on the "line segment" button and connect the two blue dots. (Hint: Transform the function by applying the constants in this order: H, B, A, K.) -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 3 4 -2 -3 -4 -5- -6- Clear All Draw: Dot Line Segment
ChapterP: Prerequisites
SectionP.4: Factoring Polynomials
Problem 84E: The rate of change of an autocatalytic chemical reaction is kQxkx2 where Q is the amount of the...
Related questions
Question
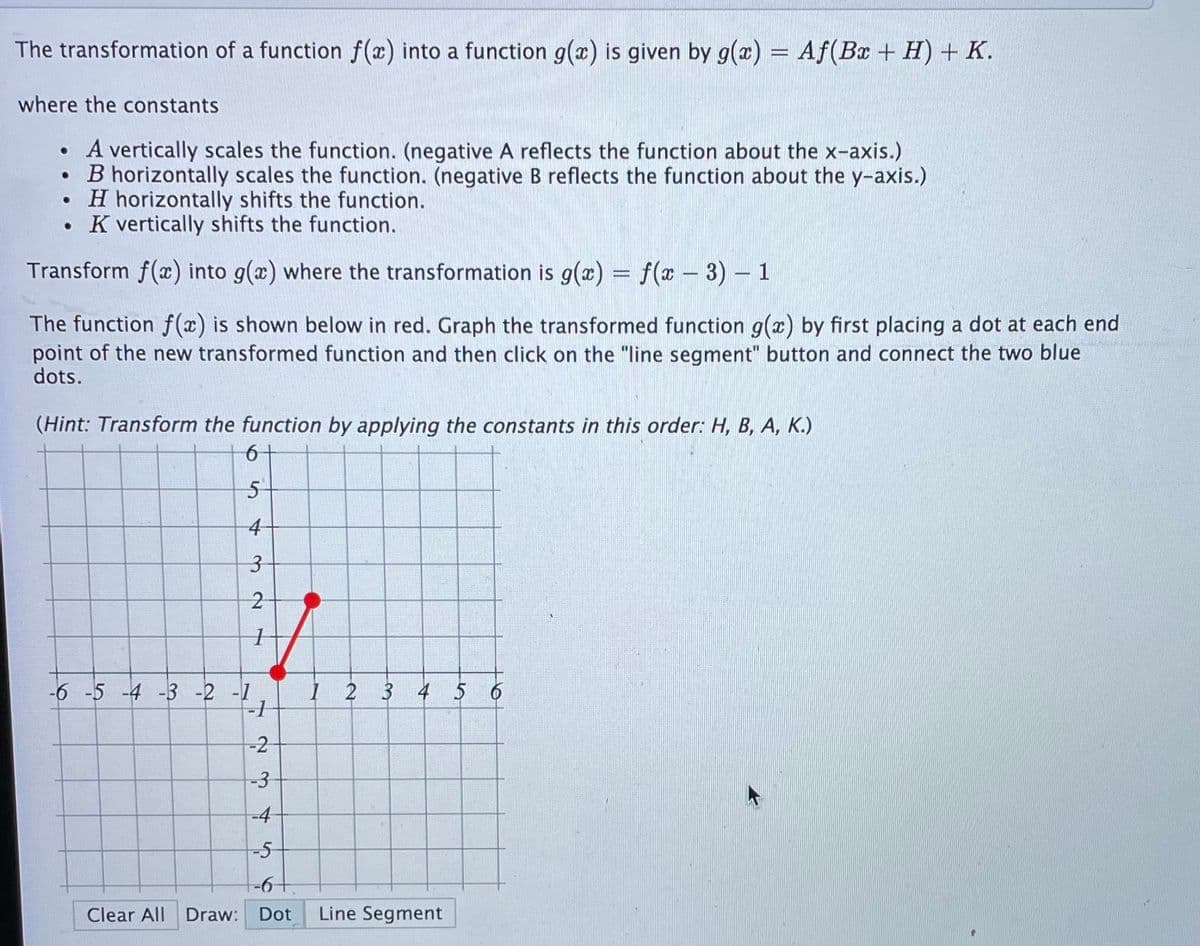
Transcribed Image Text:The transformation of a function f(x) into a function g(x) is given by g(x)
= Af(Bx + H) + K.
where the constants
• A vertically scales the function. (negative A reflects the function about the x-axis.)
B horizontally scales the function. (negative Breflects the function about the y-axis.)
• H horizontally shifts the function.
• K vertically shifts the function.
Transform f(x) into g(x) where the transformation is g(æ) = f(x – 3) – 1
The function f (x) is shown below in red. Graph the transformed function g(x) by first placing a dot at each end
point of the new transformed function and then click on the "line segment" button and connect the two blue
dots.
(Hint: Transform the function by applying the constants in this order: H, B, A, K.)
4
2
-6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1
-1
I 2 3 4 5 6
-2
-3-
-4
-5-
Clear All Draw: Dot
Line Segment
3.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, algebra and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage



Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage


Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305071742
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning