Volume/cm³ 60 55 50 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 50 75 100 125 150 175 200 225 100 150 200 230 270 300 250 275 300 325 350 Pressure/kPa It is suggested that if the temperature is constant, the pressure, P, of a fixed mass of gas is inversely proportional to the volume, V, that is = kx P where k is a constant. To test whether the relationship applies in this case, read off values of V from the graph to complete the table below. Calculate the corresponding values of Pressure, P/ kPa Volume, V/cm³ cm³
Volume/cm³ 60 55 50 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 50 75 100 125 150 175 200 225 100 150 200 230 270 300 250 275 300 325 350 Pressure/kPa It is suggested that if the temperature is constant, the pressure, P, of a fixed mass of gas is inversely proportional to the volume, V, that is = kx P where k is a constant. To test whether the relationship applies in this case, read off values of V from the graph to complete the table below. Calculate the corresponding values of Pressure, P/ kPa Volume, V/cm³ cm³
Related questions
Question
100%
Transcribed Image Text:WEEK 4
LESSON 2 Worksheet
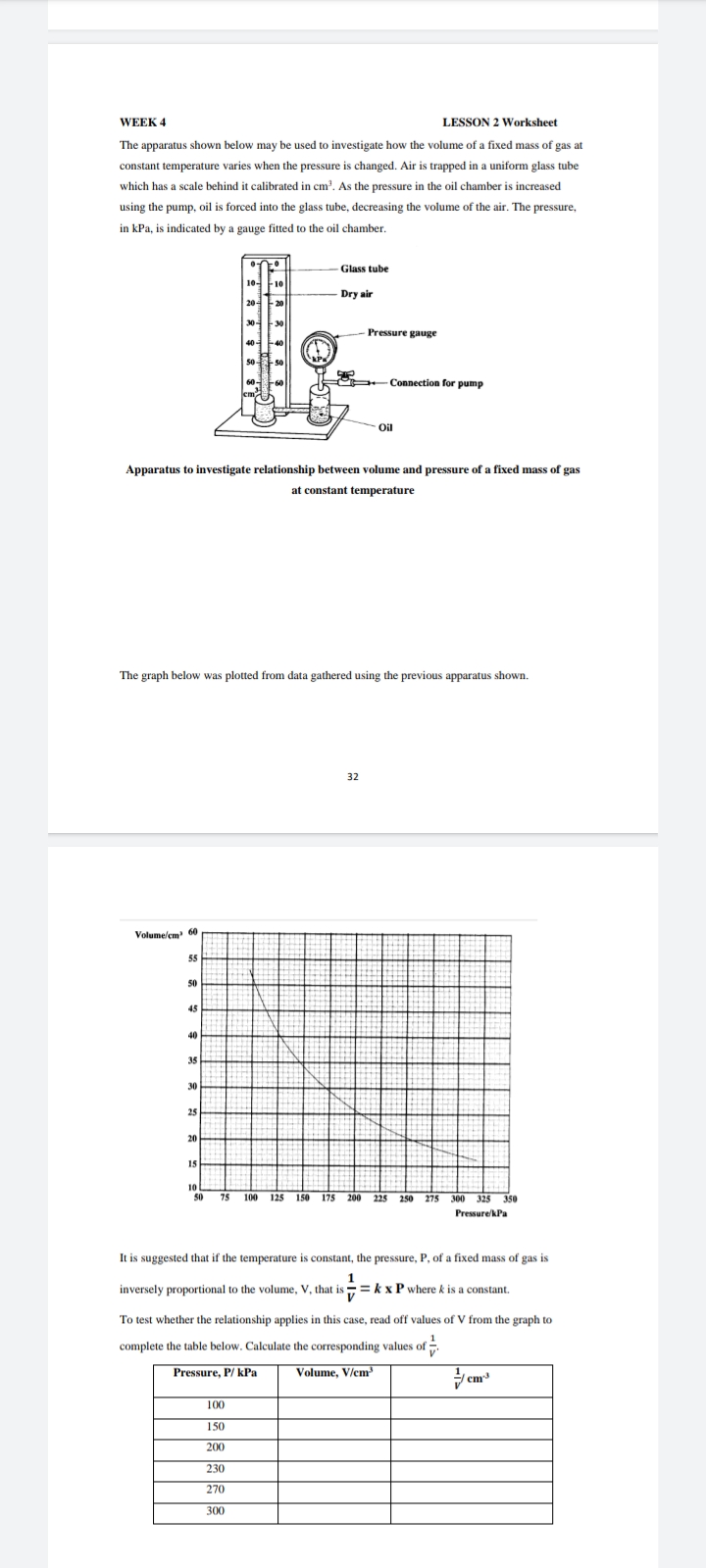
The apparatus shown below may be used to investigate how the volume of a fixed mass of gas at
constant temperature varies when the pressure is changed. Air is trapped in a uniform glass tube
which has a scale behind it calibrated in cm³. As the pressure in the oil chamber is increased
using the pump, oil is forced into the glass tube, decreasing the volume of the air. The pressure,
in kPa, is indicated by a gauge fitted to the oil chamber.
Volume/cm³ 60
55
50
45
40
35
30
25
20
15
10
10-
Apparatus to investigate relationship between volume and pressure of a fixed mass of gas
at constant temperature
50 75
30-
The graph below was plotted from data gathered using the previous apparatus shown.
40-
50-
100
150
200
230
270
300
60
cm
-10
20
30
-Glass tube
Dry air
100 125
125 150
Pressure gauge
-Connection for pump
32
Oil
175 200 225 250 275 300 325 350
Pressure/kPa
It is suggested that if the temperature is constant, the pressure, P, of a fixed mass of gas is
1
inversely proportional to the volume, V, that is = kx P where k is a constant.
To test whether the relationship applies in this case, read off values of V from the graph to
complete the table below. Calculate the corresponding values of
Pressure, P/ kPa
Volume, V/cm³
cm3
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps
