What is the Reynolds’s number for the fluid exiting the device at 23 degrees celsius for the same mass flow rates as in Part A)
What is the Reynolds’s number for the fluid exiting the device at 23 degrees celsius for the same mass flow rates as in Part A)
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Chapter1: Introduction
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1P
Related questions
Question
What is the Reynolds’s number for the fluid exiting the device at 23 degrees celsius for the same mass flow rates as in Part A)

Transcribed Image Text:One can has your teeth cleaned professionally using
Problem 1: Reynold's number
a rotating brush or with a jet stream oi a baking soda slurry. For baking soda slurries, the dentist
uses a device similar to the device shown in HD Figure 8.24 to remove plaque. The fluid used
in the device is a baking soda slurry. Baking soda slurry is 3.0% baking soda (sodium
bicarbonate) in water, where 0.90% is the saturation limited of baking soda in water. If the inlet
velocity is 0.24 m/s with inlet diameter of 5.4 mm at 23°C. The nozzle tip has a diameter of 0.51
mm. Assume no frictional effects. See page 4 for sodium bicarbonate-viscosity graph.
State any other assumption needed.
FIGURE 8.24
Inlet
Flow
Outlet
Q
Flow
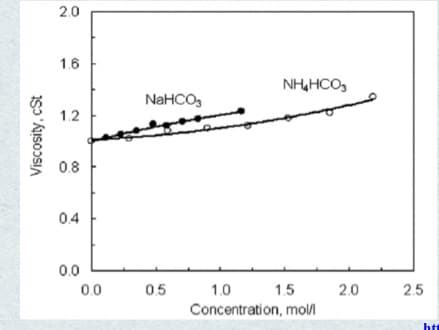
Transcribed Image Text:2.0
1.6
NH,HCO,
NaHCO,
1.2
0.8
0.4
0.0
0.0
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
2.5
Concentration, mol/l
ht
Viscosity, cSt
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259696527
Author:
J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133887518
Author:
H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:
Prentice Hall

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259696527
Author:
J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133887518
Author:
H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:
Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781285061238
Author:
Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:
Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780072848236
Author:
Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Companies, The