When I first studied hominin evolution, they had found "Lucy", an Australopithecus afarensis, and everyone thought her species was an early ancestor of Homo sapien. The picture is much more complicated, with lots of hominins living in close proximity for millions of years...much different than our now singular species. Look at the phylogenetic tree and use it as a guide to briefly describe hominin lines in Africa up to Homo. Do not discuss Homo.Just discuss a sense that you generally can grasp what was going on in Africa with our Genus for 6 or 7 million years!
When I first studied hominin evolution, they had found "Lucy", an Australopithecus afarensis, and everyone thought her species was an early ancestor of Homo sapien. The picture is much more complicated, with lots of hominins living in close proximity for millions of years...much different than our now singular species. Look at the phylogenetic tree and use it as a guide to briefly describe hominin lines in Africa up to Homo. Do not discuss Homo.Just discuss a sense that you generally can grasp what was going on in Africa with our Genus for 6 or 7 million years!
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (MindTap Course List)
5th Edition
ISBN:9781305117396
Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Chapter12: Processes Of Evolution
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 4CT
Related questions
Question
When I first studied hominin evolution, they had found "Lucy", an Australopithecus afarensis, and everyone thought her species was an early ancestor of Homo sapien. The picture is much more complicated, with lots of hominins living in close proximity for millions of years...much different than our now singular species.
Look at the phylogenetic tree and use it as a guide to briefly describe hominin lines in Africa up to Homo. Do not discuss Homo.Just discuss a sense that you generally can grasp what was going on in Africa with our Genus for 6 or 7 million years!
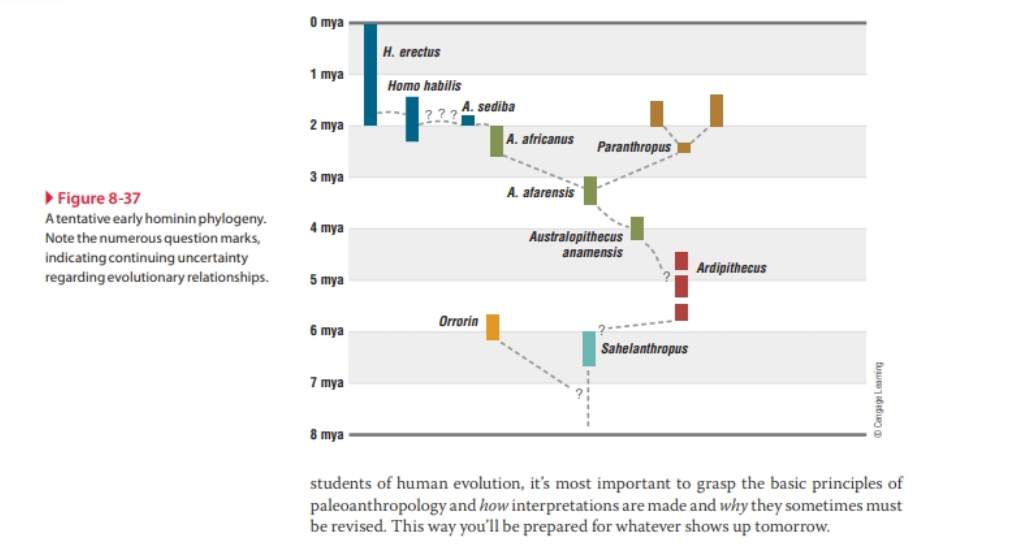
Transcribed Image Text:▶ Figure 8-37
Atentative early hominin phylogeny.
Note the numerous question marks,
indicating continuing uncertainty
regarding evolutionary relationships.
0 mya
1 mya
2 mya
3 mya
4 mya
5 mya
6 mya
7 mya
8 mya
H. erectus
Homo habilis
???
A. sediba
Orrorin
A. africanus
A. afarensis
Paranthropus
Australopithecus
anamensis
Sahelanthropus
Ardipithecus
Cengage Leaming
students of human evolution, it's most important to grasp the basic principles of
paleoanthropology and how interpretations are made and why they sometimes must
be revised. This way you'll be prepared for whatever shows up tomorrow.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305117396
Author:
Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap…
Biology
ISBN:
9781337408332
Author:
Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305117396
Author:
Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap…
Biology
ISBN:
9781337408332
Author:
Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:
Cengage Learning