Which one of the these primary protein structures is most likely to form an alpha helix that would would cross a plasma membrane from the extracellular side to the cytoplasmic side? The N terminus is outside the cell and the C terminus is inside the cell in this example. Use the diagram provided to decode the one letter amino acid abbreviations.
Which one of the these primary protein structures is most likely to form an alpha helix that would would cross a plasma membrane from the extracellular side to the cytoplasmic side? The N terminus is outside the cell and the C terminus is inside the cell in this example. Use the diagram provided to decode the one letter amino acid abbreviations.
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Chapter1: The Human Body: An Orientation
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ: The correct sequence of levels forming the structural hierarchy is A. (a) organ, organ system,...
Related questions
Question
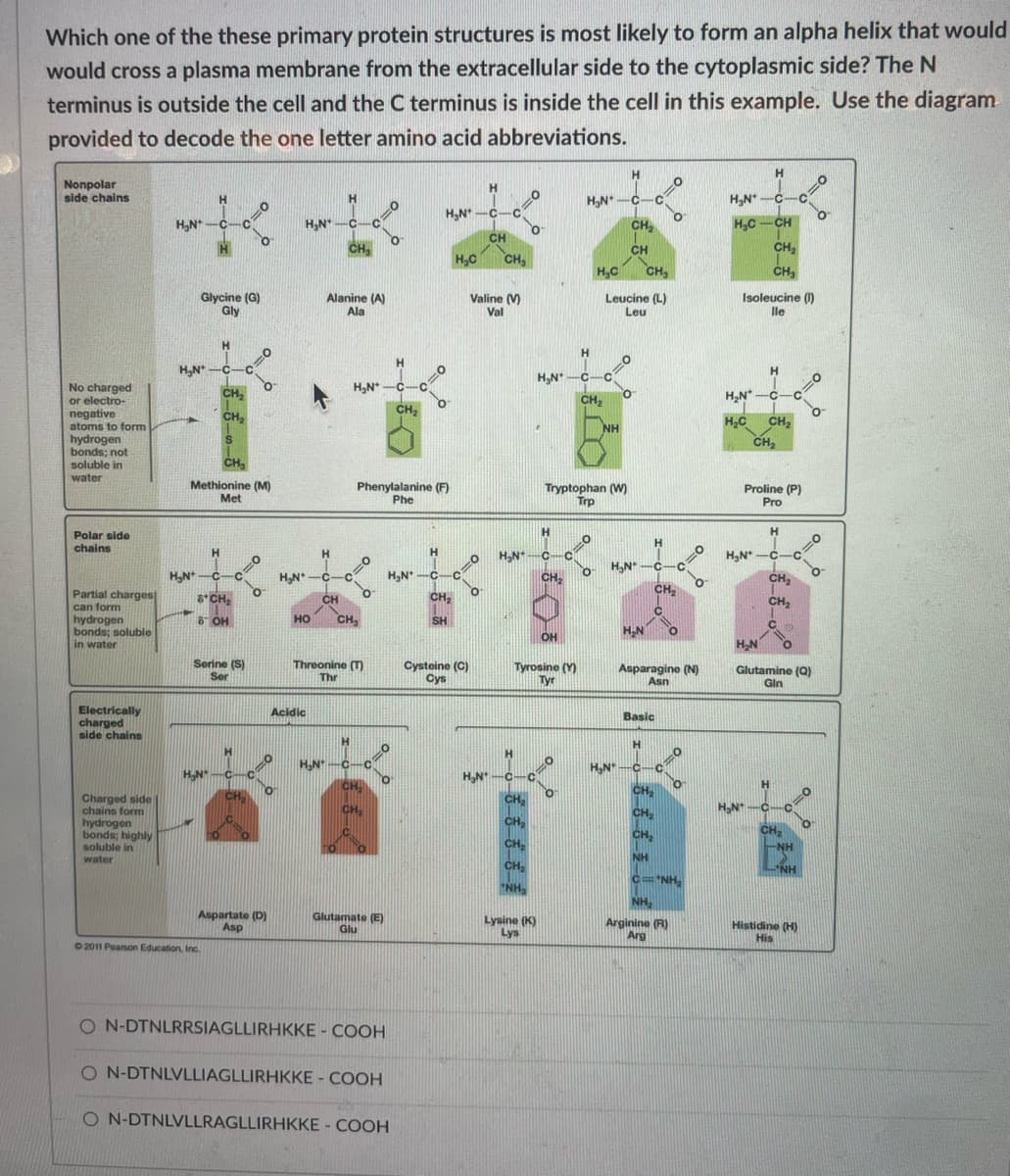
Transcribed Image Text:Which one of the these primary protein structures is most likely to form an alpha helix that would
would cross a plasma membrane from the extracellular side to the cytoplasmic side? The N
terminus is outside the cell and the C terminus is inside the cell in this example. Use the diagram
provided to decode the one letter amino acid abbreviations.
Nonpolar
side chains
No charged
or electro-
negative
atoms to form
hydrogen
bonds; not
soluble in
water
Polar side
chains
Partial charges
can form
hydrogen
bonds; soluble
in water
Electrically
charged
side chains
Charged side
chains form
hydrogen
bonds; highly
soluble in
water
H
H₂N-C-C
H₂N-C-
H₂N+
Glycine (G)
Gly
H
H
H₂N*
Methionine (M)
Met
C
8*CH₂
6 OH
2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
CH₂
CH₂
S
CH₂
=0
Serine (S)
Ser
c=0
O
O
Aspartate (D)
Asp
20
H₂N-C- с
CH₂
H₂N*
HO
Acidic
Alanine (A)
Ala
H
L
CH
C
H₂N-C C
CH₂
CH₂
Threonine (T
Thr
H₂N C
Phenylalanine (F)
Phe
O
0=0
CH₂
CH₂
Glutamate (E)
Glu
ON-DTNLRRSIAGLLIRHKKE - COOH
H₂N+
ON-DTNLVLLIAGLLIRHKKE-COOH
ON-DTNLVLLRAGLLIRHKKE - COOH
H
H₂N-C-
CH₂
SH
H₂C
C
Cysteine (C)
Cys
H
0
H₂N
CH
C
Valine (V)
Val
CH₂
H₂N*
O
O
H₂N+
H
C C
CH₂
CH₂
CH₂
CH₂
NH₂
Lysine (K)
Lys
Tyrosine (Y)
Tyr
C
CH₂
OH
20
H₂N-C C
H
Tryptophan (W)
Trp
C
CH₂
O
H₂C CH₂
Leucine (L)
Leu
NH
H
CH₂
CH
H₂N
H₂N-
H
H₂N-C-C
Basic
H
O
O
CH₂
C
Asparagine (N)
Asn
CH₂
CH₂
CH₂
NH
=0
Arginine (R)
Arg
O
010
10
CNH,
NH₂
H₂N* C-
H₂CCH
Isoleucine (1)
lle
CH₂
CH₂
H
H₂N* -C-
с
H₂C
CH₂
CH₂
H₂N
Proline (P)
Pro
H₂N-C-
H
H₂N-C
-C-C
CH₂
CH₂
C
C
CH₂
Glutamine (Q)
Gin
=0
C
NH
=0
NH
Histidine (H)
His
O
o
=0
O
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:
9780134580999
Author:
Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:
PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:
9781259398629
Author:
McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:
Mcgraw Hill Education,

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:
9780134580999
Author:
Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:
PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:
9781259398629
Author:
McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:
Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:
9780815344322
Author:
Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:
W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:
9781260159363
Author:
Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:
9781260231700
Author:
Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:
McGraw Hill Education