With what initial velocity must an object be thrown upward (from a height of 2 meters) to reach a maximum height of 800 meters? Step 1 We want to find the initial velocity, v(0) of an object thrown upward such that the maximum of the height function f(t) is 800. We also assume the acceleration due to gravity is a(t) = -9.8 meters per second. First, we must find an equation for the velocity and height functions. Recall that the derivative of the velocity function is acceleration, or v'(t) = a(t). This also means that v(t) is the antiderivative of the constant function a(t). Find v(t). v(t) = [a(t) dt - S- -9.8 dt = -9.8 -9.8 t + C The initial velocity is the velocity at time t = 0. Find the initial velocity by substituting 0 for t in the equation above. v(0)= 9.8(0) + C Step 2 We have found that the velocity of the object thrown upward has the general solution v(t) = -9.8t + C, and the initial velocity is v(0) = C. Substituting v(0) for the constant C to find the particular solution for the velocity gives us the following. v(t) = -9.8t + v(0) Now recall that the derivative of the height function is the velocity, or s'(t) = v(t). This also means that s(t) is the antiderivative of v(t). Find s(t). s(t) = /v(t) dt - [o = (-9.8t + v(0)) dt x )t² + v(0)t + C₁ Submit Skip (you cannot come back)
With what initial velocity must an object be thrown upward (from a height of 2 meters) to reach a maximum height of 800 meters? Step 1 We want to find the initial velocity, v(0) of an object thrown upward such that the maximum of the height function f(t) is 800. We also assume the acceleration due to gravity is a(t) = -9.8 meters per second. First, we must find an equation for the velocity and height functions. Recall that the derivative of the velocity function is acceleration, or v'(t) = a(t). This also means that v(t) is the antiderivative of the constant function a(t). Find v(t). v(t) = [a(t) dt - S- -9.8 dt = -9.8 -9.8 t + C The initial velocity is the velocity at time t = 0. Find the initial velocity by substituting 0 for t in the equation above. v(0)= 9.8(0) + C Step 2 We have found that the velocity of the object thrown upward has the general solution v(t) = -9.8t + C, and the initial velocity is v(0) = C. Substituting v(0) for the constant C to find the particular solution for the velocity gives us the following. v(t) = -9.8t + v(0) Now recall that the derivative of the height function is the velocity, or s'(t) = v(t). This also means that s(t) is the antiderivative of v(t). Find s(t). s(t) = /v(t) dt - [o = (-9.8t + v(0)) dt x )t² + v(0)t + C₁ Submit Skip (you cannot come back)
Chapter3: Functions
Section3.2: Domain And Range
Problem 61SE: The cost in dollars of making x items is given by the function Cx)=10x+500. a. The fixed cost is...
Related questions
Question
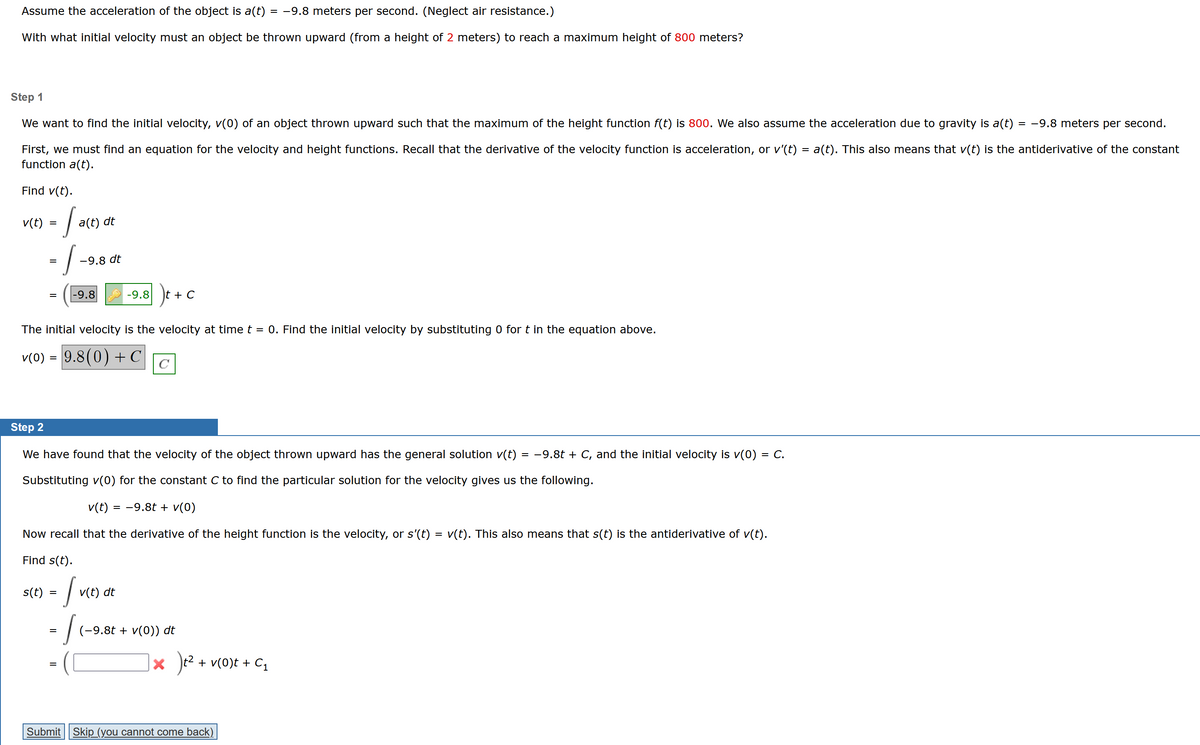
Transcribed Image Text:Assume the acceleration of the object is a(t) = -9.8 meters per second. (Neglect air resistance.)
With what initial velocity must an object be thrown upward (from a height of 2 meters) to reach a maximum height of 800 meters?
Step 1
We want to find the initial velocity, v(0) of an object thrown upward such that the maximum of the height function f(t) is 800. We also assume the acceleration due to gravity is a(t) = -9.8 meters per second.
First, we must find an equation for the velocity and height functions. Recall that the derivative of the velocity function is acceleration, or v'(t) = a(t). This also means that v(t) is the antiderivative of the constant
function a(t).
Find v(t).
v(t)
=
s(t)
falt
a(t) dt
= -9.8 dt
-1
-9.8
The initial velocity is the velocity at time t = 0. Find the initial velocity by substituting 0 for t in the equation above.
v(0) = 9.8(0) + C
=
Step 2
We have found that the velocity of the object thrown upward has the general solution v(t) = -9.8t + C, and the initial velocity is v(0) = C.
Substituting v(0) for the constant C to find the particular solution for the velocity gives us the following.
v(t) = −9.8t + v(0)
Now recall that the derivative of the height function is the velocity, or s'(t) = v(t). This also means that s(t) is the antiderivative of v(t).
Find s(t).
=
-/
= 1
-9.8 t + C
v(t) dt
(-9.8t + v(0)) dt
x t² + v(0)t + C₁
Submit Skip (you cannot come back).
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you


Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305115545
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305115545
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781337278461
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning