(x, Y), then y = The points (0, 0). P() and P (-) equilateral form an triangle.
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter11: Topics From Analytic Geometry
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 20T
Related questions
Question
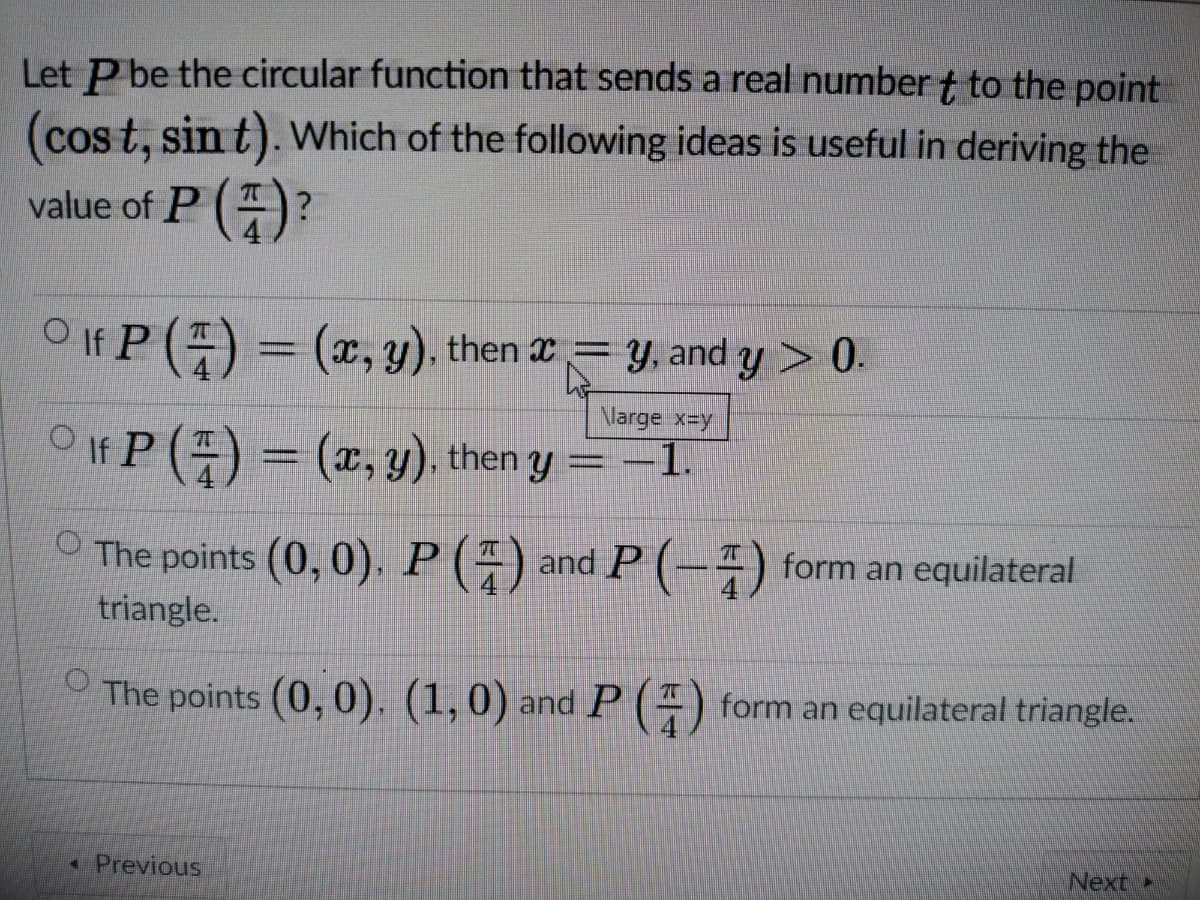
Transcribed Image Text:Let P be the circular function that sends a real number t to the point
(cos t, sin t). Which of the following ideas is useful in deriving the
value of P ()?
O If P () = (x, y). then 2= y, and y > 0.
Nlarge x-y
OIf P () = (x, y), then y =-1.
O The points (0, 0). P () and P (-) form an equilateral
triangle.
OThe points (0, 0), (1,0) and P (4) form an equilateral triangle.
«Previous
Next
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 5 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning