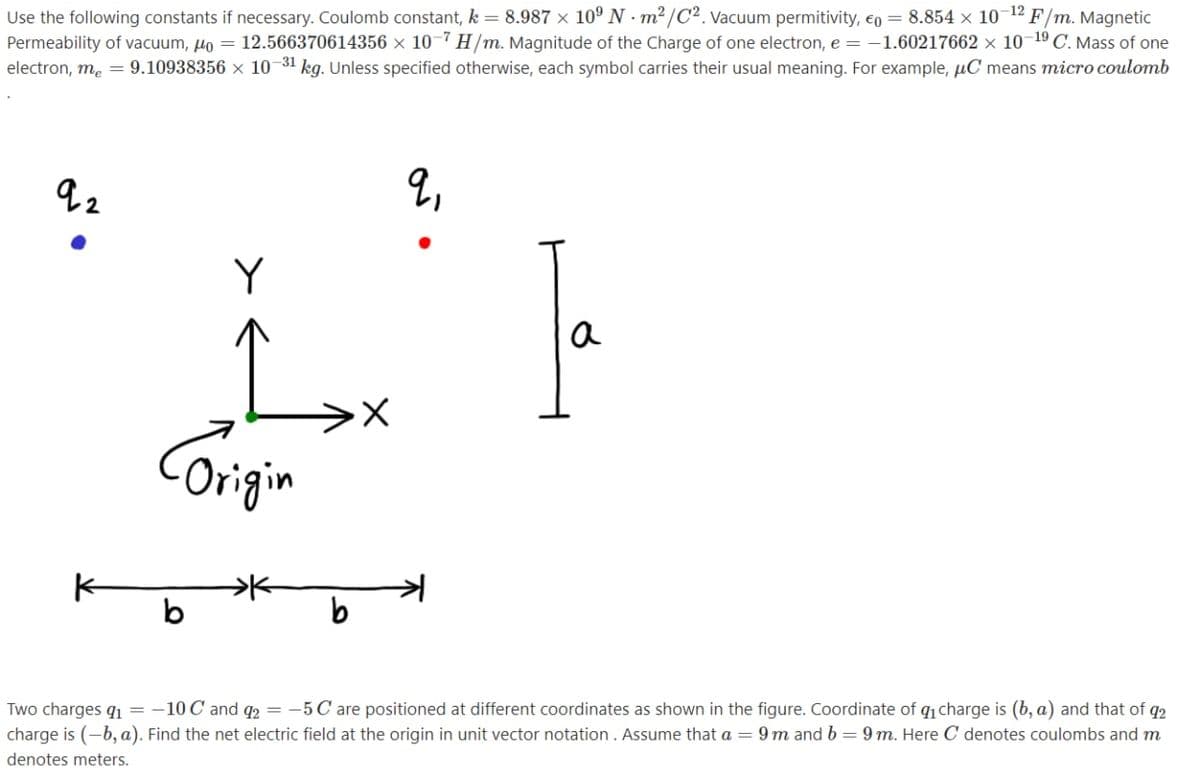
Y a Corgin b Two charges q = -10 C and q2 = -5C are positioned at different coordinates as shown in the figure. Coordinate of q charge is (b, a) and that of q2 charge is (-b, a). Find the net electric field at the origin in unit vector notation. Assume that a = 9 m and b=9m. Here C denotes coulombs and m denotes meters.
Y a Corgin b Two charges q = -10 C and q2 = -5C are positioned at different coordinates as shown in the figure. Coordinate of q charge is (b, a) and that of q2 charge is (-b, a). Find the net electric field at the origin in unit vector notation. Assume that a = 9 m and b=9m. Here C denotes coulombs and m denotes meters.
Related questions
Question
I need the answer as soon as possible
Transcribed Image Text:12
Use the following constants if necessary. Coulomb constant, k = 8.987 × 10º N - m² /C². Vacuum permitivity, €o = 8.854 x 10
Permeability of vacuum, µo = 12.566370614356 × 10–7 H/m. Magnitude of the Charge of one electron, e = -1.60217662 × 10 19 C. Mass of one
electron, m, = 9.10938356 × 10 31 kg. Unless specified otherwise, each symbol carries their usual meaning. For example, µC means micro coulomb
F/m. Magnetic
2,
Y
a
Corigin
Two charges qı = -10 C and q2 = -5C are positioned at different coordinates as shown in the figure. Coordinate of ị charge is (b, a) and that of q2
charge is (-b, a). Find the net electric field at the origin in unit vector notation. Assume that a = 9 m and b = 9 m. Here C denotes coulombs and m
denotes meters.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps
