You must represent it by respecting the following textual notation. Table name: is represented by the first word in capital letters in front of the parentheses. i.e. TABLE (); Columns name: are inside the parentheses separated by commas. i.e. (column1, column2); PK: Stay with the column which is the primary key. i.e. TABLE (column1 (PK), column2); FK: Stay with the column which is the foreign key. i.e. TABLE (column1 (PK), column2, column3 (FK)); CPK: Stay with the column that makes up the composite primary key, j.e. TARI F ((column1 column?
You must represent it by respecting the following textual notation. Table name: is represented by the first word in capital letters in front of the parentheses. i.e. TABLE (); Columns name: are inside the parentheses separated by commas. i.e. (column1, column2); PK: Stay with the column which is the primary key. i.e. TABLE (column1 (PK), column2); FK: Stay with the column which is the foreign key. i.e. TABLE (column1 (PK), column2, column3 (FK)); CPK: Stay with the column that makes up the composite primary key, j.e. TARI F ((column1 column?
COMPREHENSIVE MICROSOFT OFFICE 365 EXCE
1st Edition
ISBN:9780357392676
Author:FREUND, Steven
Publisher:FREUND, Steven
Chapter8: Working With Trendlines, Pivottables, Pivotcharts, And Slicers
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 4EYK
Related questions
Question
(
Question - Analyze the diagram and transform from conceptual model into logical model by using textual notation?

Transcribed Image Text:You must represent it by respecting the following textual notation.
Table name: is represented by the first word in capital letters in front of the parentheses. i.e. TABLE ();
Columns name: are inside the parentheses separated by commas. i.e. (column1, column2);
PK: Stay with the column which is the primary key. i.e. TABLE (column1 (PK), column2);
FK: Stay with the column which is the foreign key. i.e. TABLE (column1 (PK), column2, column3 (FK));
CPK: Stay with the column that makes up the composite primary key. i.e. TABLE ((column1, column2
(CPK)), column3);
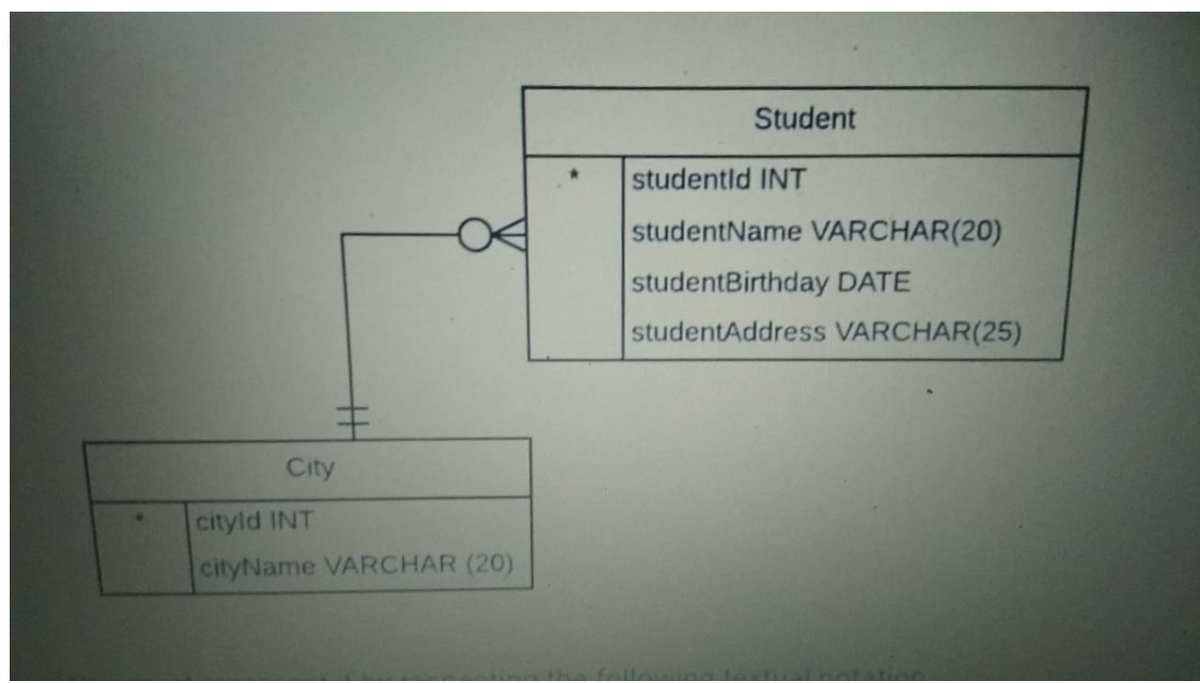
Transcribed Image Text:Student
studentld INT
studentName VARCHAR(20)
studentBirthday DATE
studentAddress VARCHAR(25)
City
cityld INT
cityName VARCHAR (20)
土
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, computer-science and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

COMPREHENSIVE MICROSOFT OFFICE 365 EXCE
Computer Science
ISBN:
9780357392676
Author:
FREUND, Steven
Publisher:
CENGAGE L

Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag…
Computer Science
ISBN:
9781305627482
Author:
Carlos Coronel, Steven Morris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag…
Computer Science
ISBN:
9781285196145
Author:
Steven, Steven Morris, Carlos Coronel, Carlos, Coronel, Carlos; Morris, Carlos Coronel and Steven Morris, Carlos Coronel; Steven Morris, Steven Morris; Carlos Coronel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

COMPREHENSIVE MICROSOFT OFFICE 365 EXCE
Computer Science
ISBN:
9780357392676
Author:
FREUND, Steven
Publisher:
CENGAGE L

Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag…
Computer Science
ISBN:
9781305627482
Author:
Carlos Coronel, Steven Morris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag…
Computer Science
ISBN:
9781285196145
Author:
Steven, Steven Morris, Carlos Coronel, Carlos, Coronel, Carlos; Morris, Carlos Coronel and Steven Morris, Carlos Coronel; Steven Morris, Steven Morris; Carlos Coronel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Np Ms Office 365/Excel 2016 I Ntermed
Computer Science
ISBN:
9781337508841
Author:
Carey
Publisher:
Cengage