ytes. The datagram(s) carrying the message will have to cross two rout 2) and 3 networks (NET1, NET2, and NET3) as described in the above f these networks has a specific MTU (for example the MTU of network ytes. MTU here stands for Maximum Transmission Unit, the largest dat rame can carry). Fill the table with the IP datagram(s) needed right afte hrough NET3 (no need to show your fragmentation for N1 or N2). Assu ptions in the header. Show all your details (for partial points in case yo re incorrect).
ytes. The datagram(s) carrying the message will have to cross two rout 2) and 3 networks (NET1, NET2, and NET3) as described in the above f these networks has a specific MTU (for example the MTU of network ytes. MTU here stands for Maximum Transmission Unit, the largest dat rame can carry). Fill the table with the IP datagram(s) needed right afte hrough NET3 (no need to show your fragmentation for N1 or N2). Assu ptions in the header. Show all your details (for partial points in case yo re incorrect).
Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edition)
7th Edition
ISBN:9780133594140
Author:James Kurose, Keith Ross
Publisher:James Kurose, Keith Ross
Chapter1: Computer Networks And The Internet
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem R1RQ: What is the difference between a host and an end system? List several different types of end...
Related questions
Question
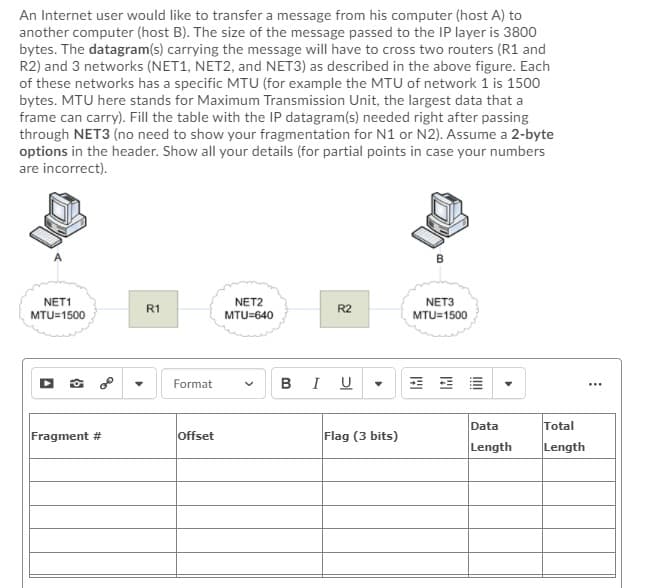
Transcribed Image Text:An Internet user would like to transfer a message from his computer (host A) to
another computer (host B). The size of the message passed to the IP layer is 3800
bytes. The datagram(s) carrying the message will have to cross two routers (R1 and
R2) and 3 networks (NET1, NET2, and NET3) as described in the above figure. Each
of these networks has a specific MTU (for example the MTU of network 1 is 1500
bytes. MTU here stands for Maximum Transmission Unit, the largest data that a
frame can carry). Fill the table with the IP datagram(s) needed right after passing
through NET3 (no need to show your fragmentation for N1 or N2). Assume a 2-byte
options in the header. Show all your details (for partial points in case your numbers
are incorrect).
NET1
MTU=1500
R1
NET2
MTU=640
R2
NET3
MTU 1500
V
BIU
Fragment #
Format
Offset
Flag (3 bits)
Data
Length
Total
Length
...
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi…
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9780133594140
Author:
James Kurose, Keith Ross
Publisher:
PEARSON

Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi…
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9780124077263
Author:
David A. Patterson, John L. Hennessy
Publisher:
Elsevier Science

Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9781337569330
Author:
Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean Andrews
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi…
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9780133594140
Author:
James Kurose, Keith Ross
Publisher:
PEARSON

Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi…
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9780124077263
Author:
David A. Patterson, John L. Hennessy
Publisher:
Elsevier Science

Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9781337569330
Author:
Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean Andrews
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Concepts of Database Management
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093422
Author:
Joy L. Starks, Philip J. Pratt, Mary Z. Last
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Prelude to Programming
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9780133750423
Author:
VENIT, Stewart
Publisher:
Pearson Education

Sc Business Data Communications and Networking, T…
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9781119368830
Author:
FITZGERALD
Publisher:
WILEY