Use Green's Theorem in the form of this equation to prove Green's first identity, where D and C satisfy the hypothesis of Green's Theorem and the appropriate partial derivatives of f and g exist and are continuous. (The quantity ∇g · n = Dng occurs in the line integral. This is the directional derivative in the direction of the normal vector n and is called the normal derivative of g.)
Use Green's Theorem in the form of this equation to prove Green's first identity, where D and C satisfy the hypothesis of Green's Theorem and the appropriate partial derivatives of f and g exist and are continuous. (The quantity ∇g · n = Dng occurs in the line integral. This is the directional derivative in the direction of the normal vector n and is called the normal derivative of g.)
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter1: Fundamental Concepts Of Algebra
Section1.2: Exponents And Radicals
Problem 31E
Related questions
Question
Use Green's Theorem in the form of this equation to prove Green's first identity, where D and C satisfy the hypothesis of Green's Theorem and the appropriate partial derivatives of f and g exist and are continuous. (The quantity ∇g · n = Dng occurs in the line integral. This is the directional derivative in the direction of the normal
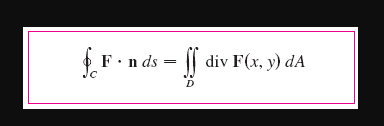
Transcribed Image Text:• F.n ds
div F(x, y) dA
D
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, advanced-math and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage


Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781337111348
Author:
Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage


Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781337111348
Author:
Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning