Answer – The term “residual volume” refers to the volume of air that remains in a person’s lungs even after maximum exhalation.
Explanation:
Residual volume (RV) ensures that there is always a continuous gas exchange (oxygen [O2] and carbon dioxide [CO2]) between the blood and the air in the lungs, even during exhalation. It also helps to maintain the structural integrity and elastic recoil of the lungs.
The RV remains unchanged, regardless of the lung volume at which expiration was started. It is usually 1–1.2 liters (20–25 ml/kg) in humans but can vary based on age, gender, height, weight, and physical activity levels. It can be calculated by using the two formulas:
- RV = FRC − ERV, where
- FRC is the functional residual capacity, and it represents the amount of air left in the lungs after a normal exhalation.
- ERV is the expiratory reserve volume and refers to the maximum amount of air that can be exhaled after a normal exhalation.
- RV = TLC − IC, where
- TLC is the total lung capacity, referring to the maximum amount of air the lungs can hold.
- IC is the inspiratory capacity and indicates the maximum amount of air that can be inhaled after a normal exhalation.
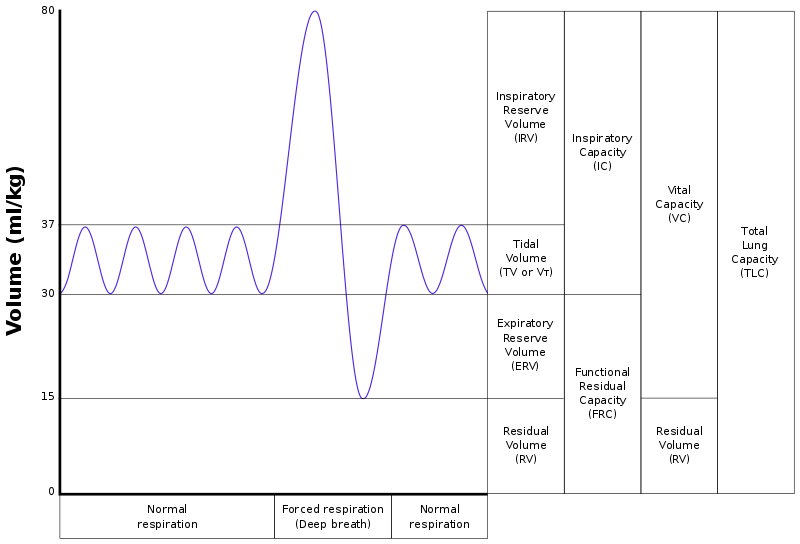
Image credit: Vihsadas / Wikimedia Commons (licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0)
All these values are usually obtained by a combination of a gas dilution test, a spirometer, or a body plethysmography.