. Draw the Transition Diagram and then determine the Transition Matrix. What happens long term? A Markov chain has three states, A, B, and C. The probability of going from state A to state B in one trial is .1, and the probability of going from state A to state C in one trial is .3. The probability of going from state B to state A in one trial is .2, and the probability of going from state B to state C in one trial is .5. The probability of going from state C to state C in one trial is 1. (C is an absorbing state)
. Draw the Transition Diagram and then determine the Transition Matrix. What happens long term? A Markov chain has three states, A, B, and C. The probability of going from state A to state B in one trial is .1, and the probability of going from state A to state C in one trial is .3. The probability of going from state B to state A in one trial is .2, and the probability of going from state B to state C in one trial is .5. The probability of going from state C to state C in one trial is 1. (C is an absorbing state)
Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
4th Edition
ISBN:9781285463247
Author:David Poole
Publisher:David Poole
Chapter3: Matrices
Section3.7: Applications
Problem 3EQ: In Exercises 1-4, let P=[0.50.30.50.7] be the transition matrix for a Markov chain with two states....
Related questions
Question
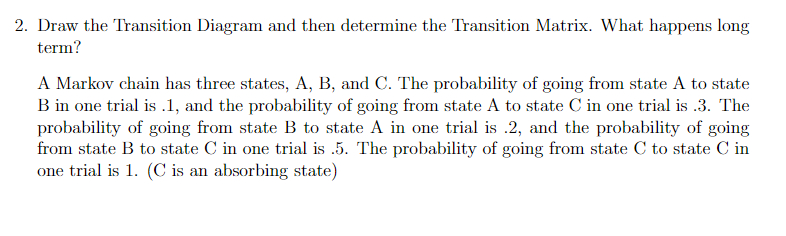
Transcribed Image Text:2. Draw the Transition Diagram and then determine the Transition Matrix. What happens long
term?
A Markov chain has three states, A, B, and C. The probability of going from state A to state
B in one trial is .1, and the probability of going from state A to state C in one trial is .3. The
probability of going from state B to state A in one trial is .2, and the probability of going
from state B to state C in one trial is .5. The probability of going from state C to state C in
one trial is 1. (C is an absorbing state)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning