.1 Calculate the following probabilities: The probability that a patient is a female or hasn't got a family history of CVD is: The probability that a male has a family history of CVD is: 1.2 Events CC and FF are: dependent, since P(C∩F)≠P(C)⋅P(F). independent, since P(C∩F)≠P(C)⋅P(F). dependent, since P(C∪F)≠P(C)+P(F). dependent, since P(C∩F)=P(C)⋅P(F). independent, since P(C∪F)=P(C)+P(F). independent, since P(C∪F)≠P(C)+P(F). independent, since P(C∩F)=P(C)⋅P(F). dependent, since P(C∪F)=P(C)+P(F). 1.3 Let: p= population proportion of patients with a family history of CVD p¯= sample proportion of patients with a family history of CVD The estimated standard error of p¯ is: The lower limit of a 90% confidence interval is:
.1 Calculate the following probabilities: The probability that a patient is a female or hasn't got a family history of CVD is: The probability that a male has a family history of CVD is: 1.2 Events CC and FF are: dependent, since P(C∩F)≠P(C)⋅P(F). independent, since P(C∩F)≠P(C)⋅P(F). dependent, since P(C∪F)≠P(C)+P(F). dependent, since P(C∩F)=P(C)⋅P(F). independent, since P(C∪F)=P(C)+P(F). independent, since P(C∪F)≠P(C)+P(F). independent, since P(C∩F)=P(C)⋅P(F). dependent, since P(C∪F)=P(C)+P(F). 1.3 Let: p= population proportion of patients with a family history of CVD p¯= sample proportion of patients with a family history of CVD The estimated standard error of p¯ is: The lower limit of a 90% confidence interval is:
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition 2012
1st Edition
ISBN:9780547587776
Author:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Chapter11: Data Analysis And Probability
Section11.8: Probabilities Of Disjoint And Overlapping Events
Problem 2C
Related questions
Question
1.1 Calculate the following probabilities:
- The probability that a patient is a female or hasn't got a family history of CVD is:
- The probability that a male has a family history of CVD is:
1.2
Events CC and FF are:
- dependent, since P(C∩F)≠P(C)⋅P(F).
- independent, since P(C∩F)≠P(C)⋅P(F).
- dependent, since P(C∪F)≠P(C)+P(F).
- dependent, since P(C∩F)=P(C)⋅P(F).
- independent, since P(C∪F)=P(C)+P(F).
- independent, since P(C∪F)≠P(C)+P(F).
- independent, since P(C∩F)=P(C)⋅P(F).
- dependent, since P(C∪F)=P(C)+P(F).
1.3 Let:
-
- p= population proportion of patients with a family history of CVD
- p¯= sample proportion of patients with a family history of CVD
The estimated standard error of p¯ is:
The lower limit of a 90% confidence interval is:
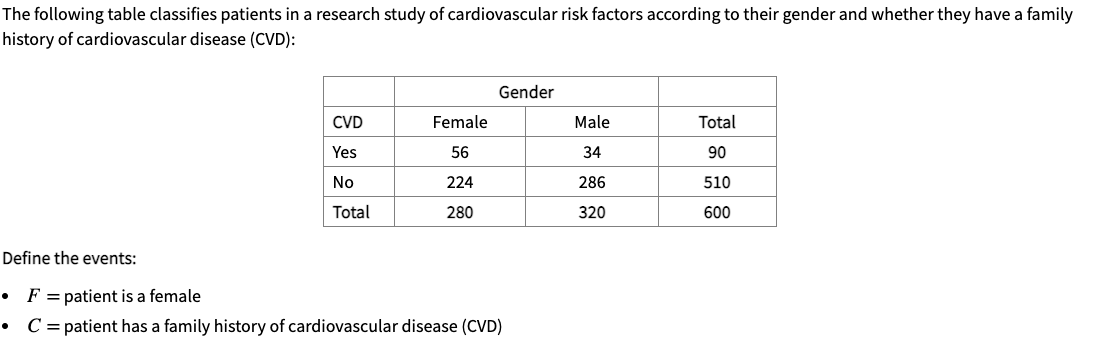
Transcribed Image Text:The following table classifies patients in a research study of cardiovascular risk factors according to their gender and whether they have a family
history of cardiovascular disease (CVD):
Gender
CVD
Female
Male
Total
Yes
56
34
90
No
224
286
510
Total
280
320
600
Define the events:
• F = patient is a female
C = patient has a family history of cardiovascular disease (CVD)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 5 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL


Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL


Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage