# 1 b) An allele for coat color in mice, Y, produces a yellow coat color when present. The phenotypes of the F1 generation are shown. A cross between a Non-yellow mouse and yellow mouse produces half yellow and half non-yellow progeny (offsprings). Non-yellow happens to be white in this example, but it does not need to be; it can be black, grey, or some other mouse color. How does the F1 generation ratio differ from the expected mendelian ratios for a heterozygous, hybrid cross? * generation Yellow Non-yellow Yellow Yellow Gametes Meiosis Fertilization 1/2 1/2 Yellow Non-yellow F generation Yellow Yellow Non-yellow Dead
# 1 b) An allele for coat color in mice, Y, produces a yellow coat color when present. The phenotypes of the F1 generation are shown. A cross between a Non-yellow mouse and yellow mouse produces half yellow and half non-yellow progeny (offsprings). Non-yellow happens to be white in this example, but it does not need to be; it can be black, grey, or some other mouse color. How does the F1 generation ratio differ from the expected mendelian ratios for a heterozygous, hybrid cross? * generation Yellow Non-yellow Yellow Yellow Gametes Meiosis Fertilization 1/2 1/2 Yellow Non-yellow F generation Yellow Yellow Non-yellow Dead
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Course List)
11th Edition
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Michael Cummings
Chapter5: The Inheritance Of Complex Traits
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 5QP: As it turned out, one of the tallest Potsdam Guards had an unquenchable attraction to short women....
Related questions
Question
100%
Answer pls
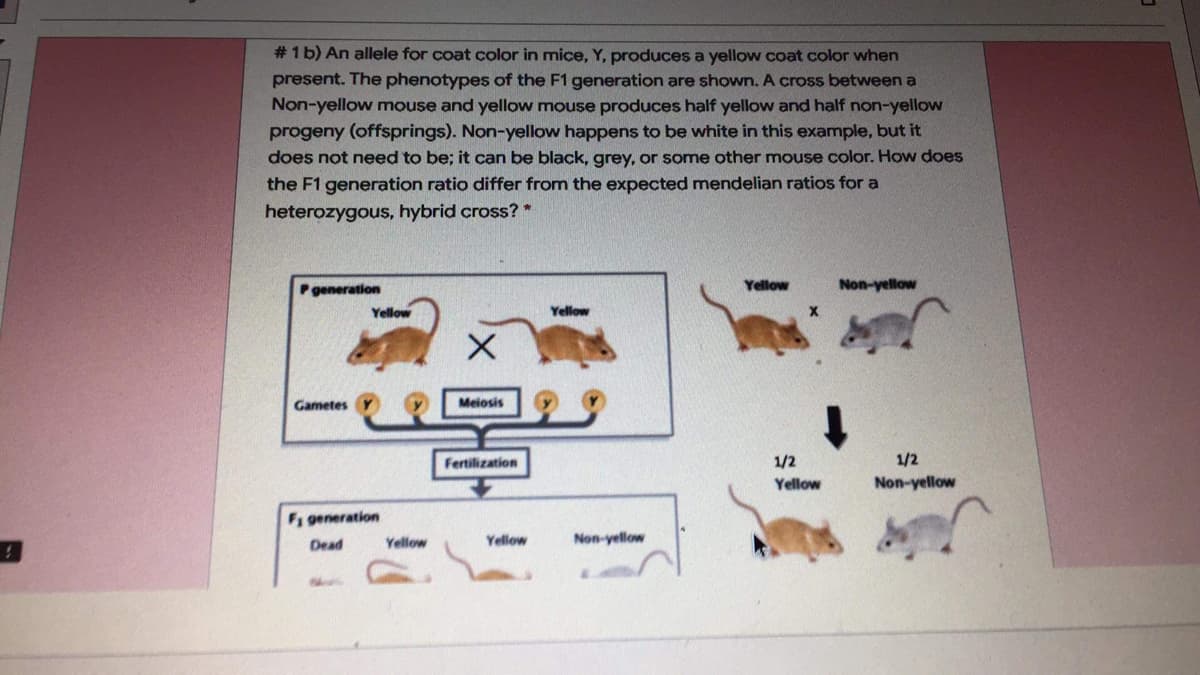
Transcribed Image Text:# 1 b) An allele for coat color in mice, Y, produces a yellow coat color when
present. The phenotypes of the F1 generation are shown. A cross between a
Non-yellow mouse and yellow mouse produces half yellow and half non-yellow
progeny (offsprings). Non-yellow happens to be white in this example, but it
does not need to be; it can be black, grey, or some other mouse color. How does
the F1 generation ratio differ from the expected mendelian ratios for a
heterozygous, hybrid cross? *
Pgeneration
Yellow
Non-yellow
Yellow
Yellow
Gametes
Meiosis
Fertilization
1/2
1/2
Yellow
Non-yellow
F1 generation
Dead
Yellow
Yellow
Non-yellow
Expert Solution
Step 1
This is due to the effect of dominant lethal genes.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305251052
Author:
Michael Cummings
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305251052
Author:
Michael Cummings
Publisher:
Cengage Learning