1. A). Determine the output voltage vo for the following circuit and B). specify the linear range for vs. Assume Vcc = 12 V and Vo = 1 V. Remember your op-amp rules! The voltage source Vo changes the gain equation slightly so don't just use an inverting or non-inverting equation. Hint: The 100 ks resistor doesn't contribute to the gain equation. The linear (or dynamic) range is the range (max/min) that vs can be to get as close to Vcc without saturation/clipping. Using your gain equation that describes the relationship for vo as a function of v₁, calculate what vs is when vo= 15 and vo= (-)15. Express linear range in terms of min ≤ vs s max. 200 ΚΩ
1. A). Determine the output voltage vo for the following circuit and B). specify the linear range for vs. Assume Vcc = 12 V and Vo = 1 V. Remember your op-amp rules! The voltage source Vo changes the gain equation slightly so don't just use an inverting or non-inverting equation. Hint: The 100 ks resistor doesn't contribute to the gain equation. The linear (or dynamic) range is the range (max/min) that vs can be to get as close to Vcc without saturation/clipping. Using your gain equation that describes the relationship for vo as a function of v₁, calculate what vs is when vo= 15 and vo= (-)15. Express linear range in terms of min ≤ vs s max. 200 ΚΩ
Power System Analysis and Design (MindTap Course List)
6th Edition
ISBN:9781305632134
Author:J. Duncan Glover, Thomas Overbye, Mulukutla S. Sarma
Publisher:J. Duncan Glover, Thomas Overbye, Mulukutla S. Sarma
Chapter12: Power System Controls
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 12.3P
Related questions
Question
Please answer in typing format solution please only typing format solution please
Please I will sure like it
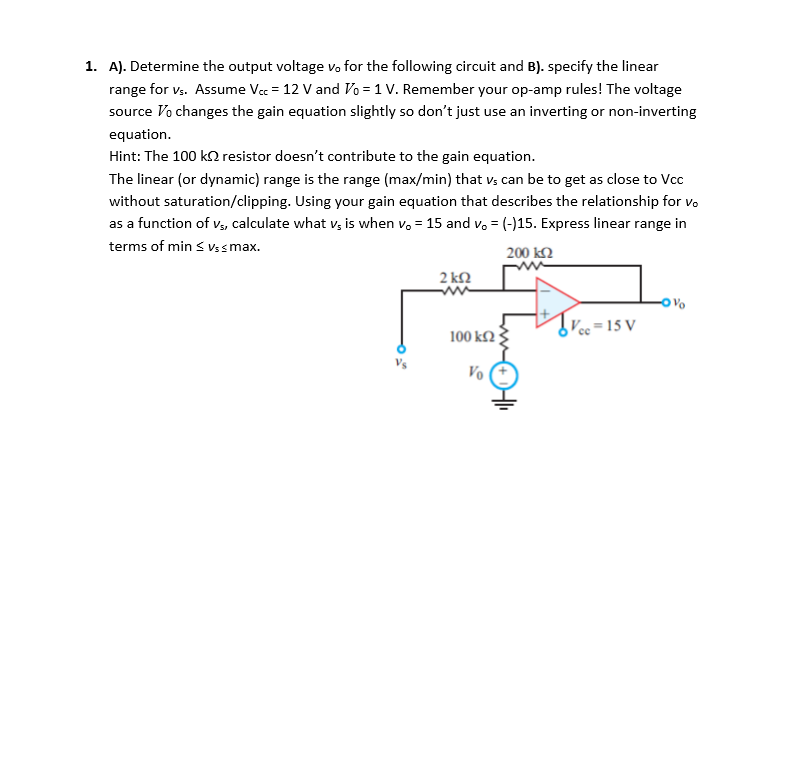
Transcribed Image Text:1. A). Determine the output voltage vo for the following circuit and B). specify the linear
range for vs. Assume Vcc = 12 V and Vo = 1 V. Remember your op-amp rules! The voltage
source Vo changes the gain equation slightly so don't just use an inverting or non-inverting
equation.
Hint: The 100 kn resistor doesn't contribute to the gain equation.
The linear (or dynamic) range is the range (max/min) that vs can be to get as close to Vcc
without saturation/clipping. Using your gain equation that describes the relationship for vo
as a function of v5, calculate what vs is when vo = 15 and vo= (-)15. Express linear range in
terms of min ≤ vs s max.
200 ΚΩ
2kQ2
100 ΚΩ
Vo
Vcc=15 V
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Power System Analysis and Design (MindTap Course …
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305632134
Author:
J. Duncan Glover, Thomas Overbye, Mulukutla S. Sarma
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Power System Analysis and Design (MindTap Course …
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305632134
Author:
J. Duncan Glover, Thomas Overbye, Mulukutla S. Sarma
Publisher:
Cengage Learning