1. a. What is the abbreviated name for the molecule below? (3 letters) What is the abbreviated name of this molecule if it has two phosphates? What is the abbreviated name of this molecule if it has one phosphate? From your answers above, circle the form of the molecule that has the most energy. What type of energy is this? circle all that apply: (KINETIC / POTENTIAL / CHEMICAL) Where is the energy? b. Identify the three main parts of this molecule. (write on the red brackets i-iii) c. Parts ii and ii together make (blue vertical bracket) ii. NH2 N. Но- ОН ОН ОН i. ОН ОН iii d. What is the specific name for this molecule? (be specific) e. This molecule is also a monomer building block of which biomolecule The general name for this type of monomer is O=d-
1. a. What is the abbreviated name for the molecule below? (3 letters) What is the abbreviated name of this molecule if it has two phosphates? What is the abbreviated name of this molecule if it has one phosphate? From your answers above, circle the form of the molecule that has the most energy. What type of energy is this? circle all that apply: (KINETIC / POTENTIAL / CHEMICAL) Where is the energy? b. Identify the three main parts of this molecule. (write on the red brackets i-iii) c. Parts ii and ii together make (blue vertical bracket) ii. NH2 N. Но- ОН ОН ОН i. ОН ОН iii d. What is the specific name for this molecule? (be specific) e. This molecule is also a monomer building block of which biomolecule The general name for this type of monomer is O=d-
Anatomy & Physiology
1st Edition
ISBN:9781938168130
Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark Womble
Publisher:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark Womble
Chapter2: The Chemical Level Of Organization
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1ILQ: Visit this website (http://openstaxcollege.org/l/ptable) to view the periodic table. In the periodic...
Related questions
Question
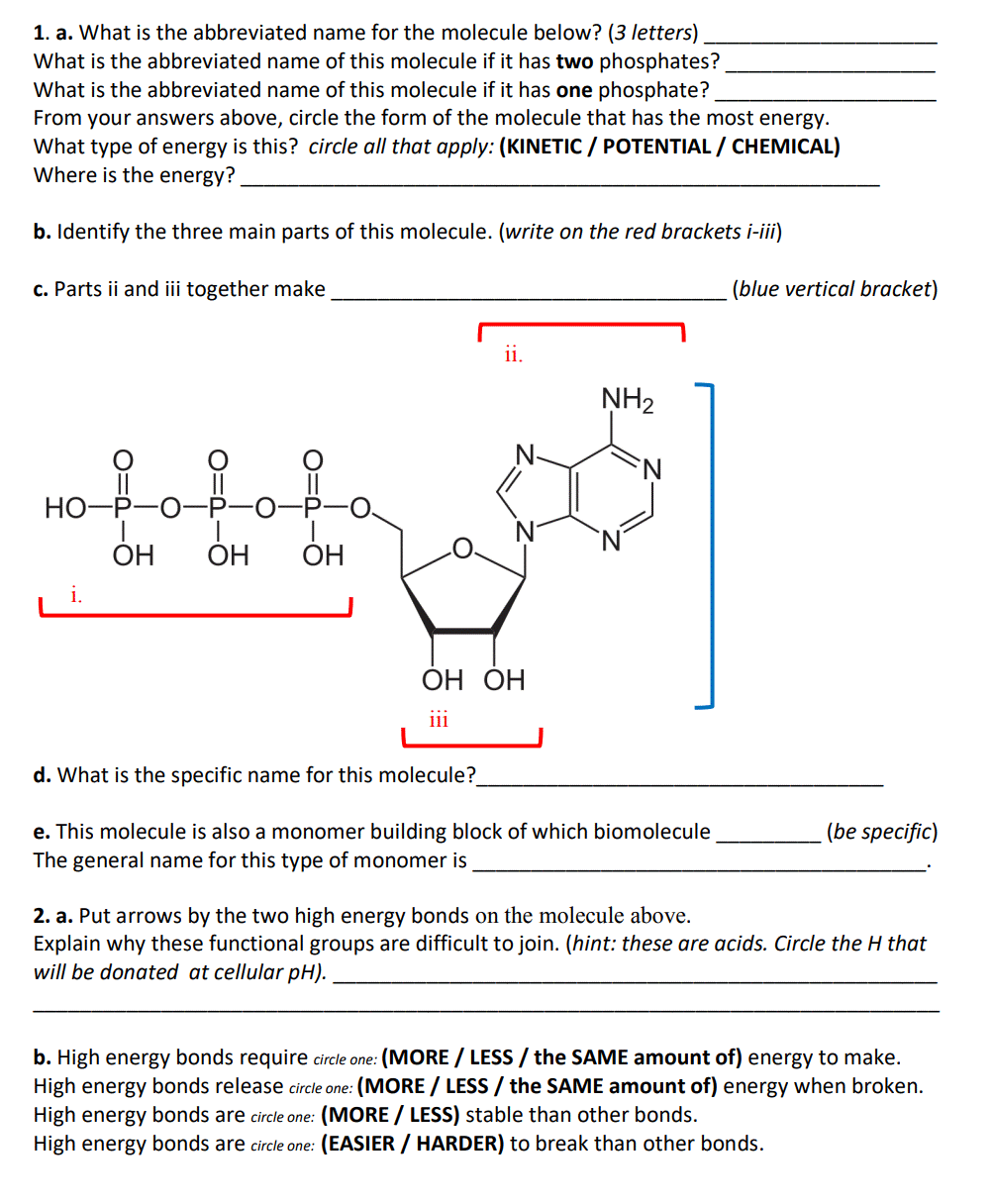
Transcribed Image Text:1. a. What is the abbreviated name for the molecule below? (3 letters)
What is the abbreviated name of this molecule if it has two phosphates?
What is the abbreviated name of this molecule if it has one phosphate?
From your answers above, circle the form of the molecule that has the most energy.
What type of energy is this? circle all that apply: (KINETIC / POTENTIAL / CHEMICAL)
Where is the energy?
b. Identify the three main parts of this molecule. (write on the red brackets i-iii)
c. Parts ii and ii together make
(blue vertical bracket)
ii.
NH2
НО-Р
ОН
ОН
ОН
ОН ОН
iii
d. What is the specific name for this molecule?
e. This molecule is also a monomer building block of which biomolecule
(be specific)
The general name for this type of monomer is
2. a. Put arrows by the two high energy bonds on the molecule above.
Explain why these functional groups are difficult to join. (hint: these are acids. Circle the H that
will be donated at cellular pH).
(MORE / LESS/ the SAME amount of) energy to make.
b. High energy bonds require circle one:
High energy bonds release circle one: (MORE / LESS / the SAME amount of) energy when broken.
High energy bonds are circle one: (MORE / LESS) stable than other bonds.
High energy bonds are circle one: (EASIER / HARDER) to break than other bonds.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:
9781938168130
Author:
Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark Womble
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:
9781938168130
Author:
Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark Womble
Publisher:
OpenStax College