1. Based on the financial information in Appendix A, how much would revenues have to have been in 2021 in order for Uber to break even? 2. What level of Revenue would Uber need to have reached in 2021 to make a profit of $2 billion. 3. What percentage increase would Contribution Margin need to increase in order for Uber to break-even on Revenues of $19 billion (assuming that fixed costs do not change)?
1. Based on the financial information in Appendix A, how much would revenues have to have been in 2021 in order for Uber to break even? 2. What level of Revenue would Uber need to have reached in 2021 to make a profit of $2 billion. 3. What percentage increase would Contribution Margin need to increase in order for Uber to break-even on Revenues of $19 billion (assuming that fixed costs do not change)?
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
3rd Edition
ISBN:9781337788281
Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Publisher:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Chapter4: The Balance Sheet And The Statement Of Shareholders' Equity
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 2C: It is the end of 2019 and you are an accountant for Stone Company. During 2019, sales of the...
Related questions
Question
Question 1,2,3 plz
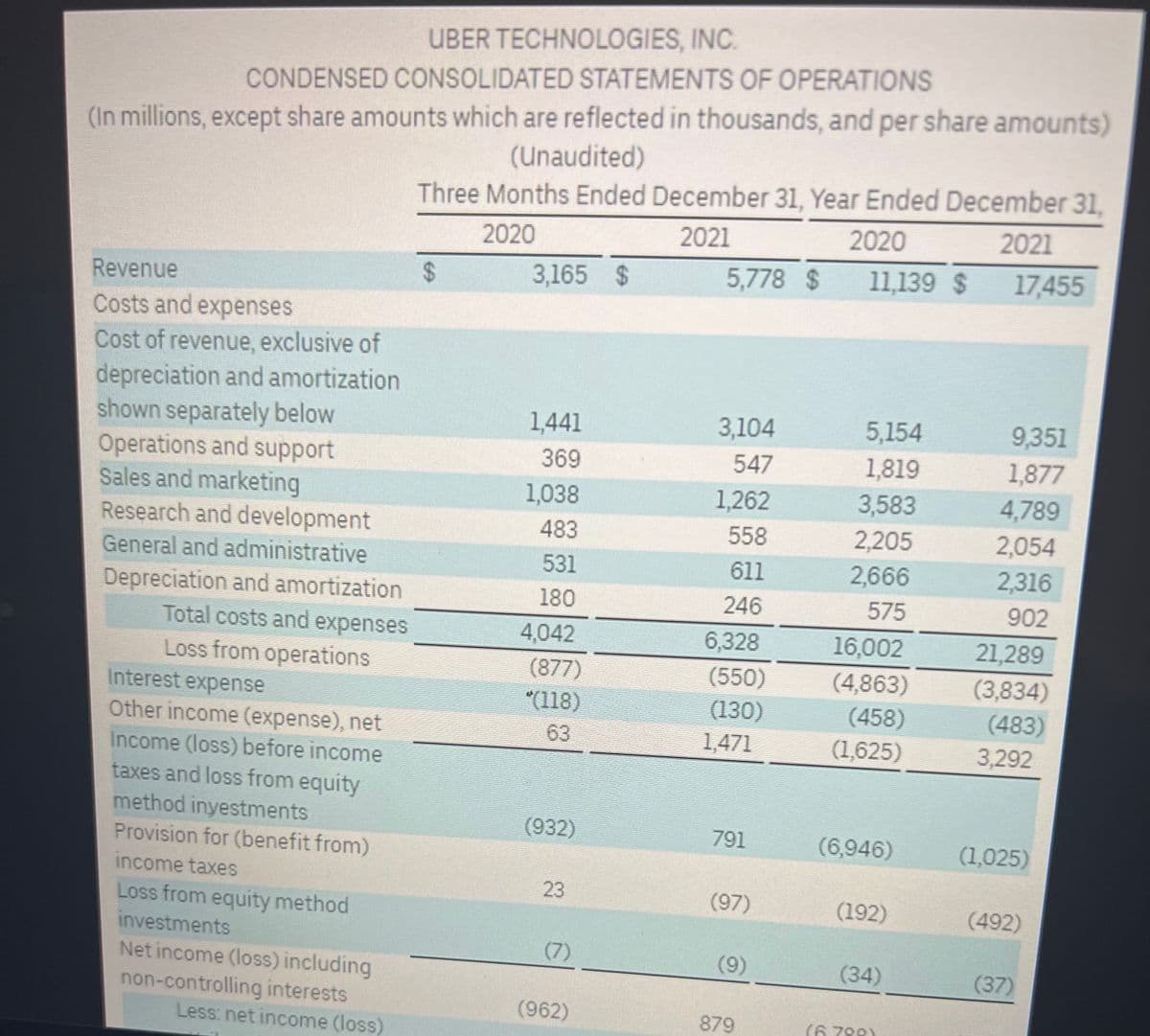
Transcribed Image Text:UBER TECHNOLOGIES, INC.
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
(In millions, except share amounts which are reflected in thousands, and per share amounts)
(Unaudited)
Three Months Ended December 31, Year Ended December 31,
2021
2020
2021
2020
3,165 $
5,778 $
11,139 $
17,455
Revenue
Costs and expenses
Cost of revenue, exclusive of
depreciation and amortization
shown separately below
Operations and support
Sales and marketing
Research and development
General and administrative
Depreciation and amortization
Total costs and expenses
Loss from operations
Interest expense
Other income (expense), net
Income (loss) before income
taxes and loss from equity
method inyestments
Provision for (benefit from)
1,441
3,104
5,154
9,351
369
547
1,819
1,877
1,038
1,262
3,583
4,789
483
558
2,205
2,054
531
611
2,666
2,316
180
246
575
902
4,042
6,328
16,002
21,289
(877)
"(118)
63
(550)
(4,863)
(3,834)
(130)
(458)
(483)
1,471
(1,625)
3,292
(932)
791
(6,946)
(1,025)
income taxes
23
(97)
(192)
Loss from equity method
investments
(492)
Net income (loss) including
(7)
(9)
(34)
(37)
non-controlling interests
(962)
879
(6 788)
Less: net income (loss)
%24

Transcribed Image Text:Recently, Uber released its financial statements for the year ended Dec 31 2021 (Appendix
A). Uber showed a loss of $570 million on sales of 17.455 billion. Some analysts are quick
to blame Covid-19 for this loss, but others pointed to bigger long-term issues and reminded
investors that Uber has consistently lost money over the past few years, and generated a
loss of $8.5 billion on sales of 13.0 billion in 2019 (a year before Covid, also known as the-
before-times).
For simplicity purposed, assume the following cost structure:
Cost of Revenues and Operations & Support expenses are all variable
Sales and Marketing , R+D, General + Administrative, and Depreciation +
Amortization expenses are all fixed.
Interest Expense, Other income (expense), and tax and loss from equity method can
be ignored for this analysis
1. Based on the financial information in Appendix A, how much would revenues have
to have been in 2021 in order for Uber to break even?
2. What level of Revenue would Uber need to have reached in 2021 to make a profit of
$2 billion.
3. What percentage increase would Contribution Margin need to increase in order for
Uber to break-even on Revenues of $19 billion (assuming that fixed costs do not
change)?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337788281
Author:
James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337788281
Author:
James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Publisher:
Cengage Learning