1. Let f be defined on an open interval (a, b) and assume that f has a local maximum or a local minimum at an interior point c of (a, b). If ƒ has a derivative (finite or infinite) at c, then f'(c) must be 0.
1. Let f be defined on an open interval (a, b) and assume that f has a local maximum or a local minimum at an interior point c of (a, b). If ƒ has a derivative (finite or infinite) at c, then f'(c) must be 0.
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
12th Edition
ISBN:9781305652231
Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Chapter3: Functions
Section3.3: More On Functions; Piecewise-defined Functions
Problem 99E: Determine if the statemment is true or false. If the statement is false, then correct it and make it...
Related questions
Question
130 2
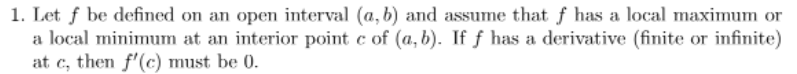
Transcribed Image Text:1. Let f be defined on an open interval (a, b) and assume that f has a local maximum or
a local minimum at an interior point c of (a, b). If f has a derivative (finite or infinite)
at c, then f'(c) must be 0.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
