1. Let G(x, y) denote that x gets y; W (x, y) denote that x wants y, and P(x) denote that is a person. Match the following sentences with their equivalent sentence of predicate logic: a. If everyone wants something, then no one gets it. b. Some people want only things they don't get. c. There is something that nobody wants. 1. Ex: Vy: P(y) ⇒¬W(y,x). 2. Ex: Vy: P(y) ^ W (y, x) ⇒ ¬³z: P(z) ^ G(z, x). 3. Vx: (Vy: P(y) ^ W (y,x) ⇒ ¬³z : P(z) ^ G(z, x)). 4. Ex: P(x) ^ Vy: (W(x, y) ⇒¬G(x, y)). 5. Ex: P(x) ^ (Vy: W(x, y) ⇒ \z¬G(x, z)). 6. Ex: Vy: P(y) ^ W (y, x) ⇒ ¬³z : P(z) ^ G(z, x). 7. Ex: Vy: P(y) ^¬W (y,x).
1. Let G(x, y) denote that x gets y; W (x, y) denote that x wants y, and P(x) denote that is a person. Match the following sentences with their equivalent sentence of predicate logic: a. If everyone wants something, then no one gets it. b. Some people want only things they don't get. c. There is something that nobody wants. 1. Ex: Vy: P(y) ⇒¬W(y,x). 2. Ex: Vy: P(y) ^ W (y, x) ⇒ ¬³z: P(z) ^ G(z, x). 3. Vx: (Vy: P(y) ^ W (y,x) ⇒ ¬³z : P(z) ^ G(z, x)). 4. Ex: P(x) ^ Vy: (W(x, y) ⇒¬G(x, y)). 5. Ex: P(x) ^ (Vy: W(x, y) ⇒ \z¬G(x, z)). 6. Ex: Vy: P(y) ^ W (y, x) ⇒ ¬³z : P(z) ^ G(z, x). 7. Ex: Vy: P(y) ^¬W (y,x).
Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1
(REV)00th Edition
ISBN:9780395977224
Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. Cole
Publisher:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. Cole
Chapter10: Inequalities
Section10.3: Solving Problems Involving Inequalities
Problem 28E
Related questions
Question
discrete structure
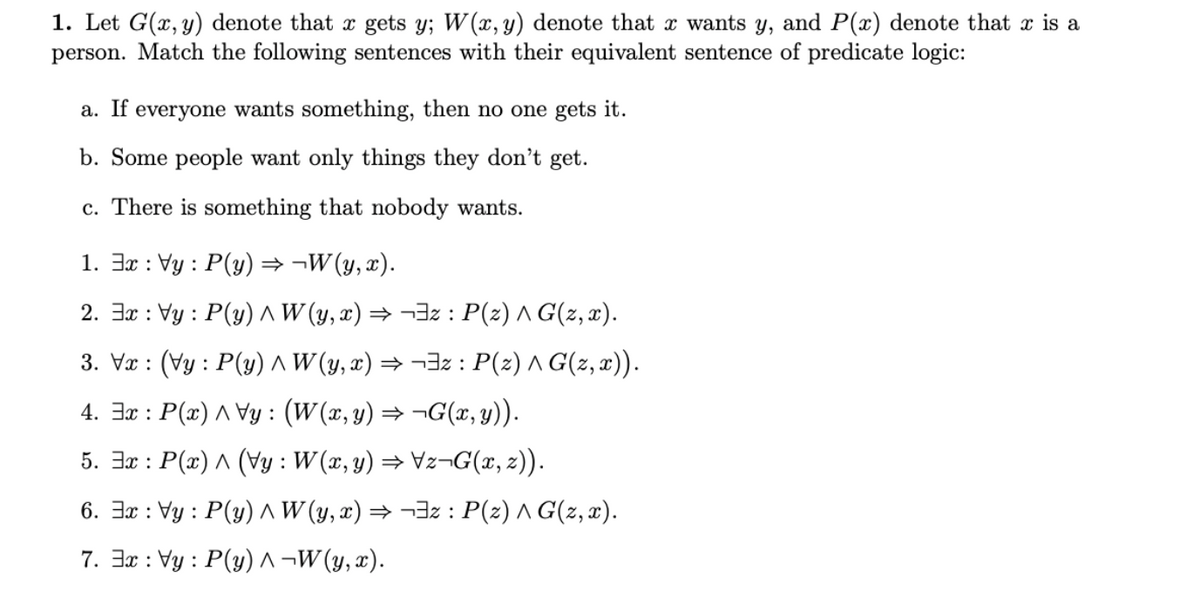
Transcribed Image Text:1. Let G(x, y) denote that x gets y; W(x, y) denote that x wants y, and P(x) denote that x is a
person. Match the following sentences with their equivalent sentence of predicate logic:
a. If everyone wants something, then no one gets it.
b. Some people want only things they don't get.
c. There is something that nobody wants.
1. 3x : Vy : P(y) → ¬W(y, x).
2. 3x : Vy : P(y) ^ W (y, x) → ¬3z : P(z) A G(z, x).
3. Vr : (Vy : P(y) ^W (y, x) → ¬3z : P(z) ^ G(z, x)).
4. 3x : P(x) ^ Vy : (W(x, y) → ¬G(x, y)).
5. 3x : P(x) ^ (Vy : W(x, y) → Vz¬G(x, z)).
6. 3x : Vy : P(y) ^ W (y, x) → ¬3z : P(z) ^ G(z, x).
7. 3x : Vy : P(y) ^ ¬W (y, x).
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, advanced-math and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1
Algebra
ISBN:
9780395977224
Author:
Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. Cole
Publisher:
McDougal Littell

Elements Of Modern Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463230
Author:
Gilbert, Linda, Jimmie
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1
Algebra
ISBN:
9780395977224
Author:
Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. Cole
Publisher:
McDougal Littell

Elements Of Modern Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463230
Author:
Gilbert, Linda, Jimmie
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,