1. Sources of monopoly power A monopolist, unlike a competitive firm, has some market power. It can raise its price, within limits, without the quantity demanded falling to zero. The main way it retains its market power is through barriers to entry-that is, other companies cannot enter the market to create competition in that particular industry. Complete the following table by indicating which barrier to entry appropriately explains why a monopoly exists in each scenario. Barriers to Entry Exclusive Ownership of a Key Government- Created Economies Scenario Monopolies of Scale Resource In the natural gas industry, low average total costs are obtained only through large-scale production. In other words, the initial cost of setting up all the necessary pipes and hoses makes it risky and, most likely, unprofitable for competitors to enter the market. In an imaginary country, there is only one federally licensed lottery agency in any state; that is, it is impossible for any private firm to start up a competitive lottery without a government license to do so. Throughout much of the 20th century, many people viewed South Africa's De Beers Group as a monopoly because it controlled a large percentage of diamond production and sales.
1. Sources of monopoly power A monopolist, unlike a competitive firm, has some market power. It can raise its price, within limits, without the quantity demanded falling to zero. The main way it retains its market power is through barriers to entry-that is, other companies cannot enter the market to create competition in that particular industry. Complete the following table by indicating which barrier to entry appropriately explains why a monopoly exists in each scenario. Barriers to Entry Exclusive Ownership of a Key Government- Created Economies Scenario Monopolies of Scale Resource In the natural gas industry, low average total costs are obtained only through large-scale production. In other words, the initial cost of setting up all the necessary pipes and hoses makes it risky and, most likely, unprofitable for competitors to enter the market. In an imaginary country, there is only one federally licensed lottery agency in any state; that is, it is impossible for any private firm to start up a competitive lottery without a government license to do so. Throughout much of the 20th century, many people viewed South Africa's De Beers Group as a monopoly because it controlled a large percentage of diamond production and sales.
Principles of Microeconomics
7th Edition
ISBN:9781305156050
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:N. Gregory Mankiw
Chapter15: Monopoly
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 11PA
Related questions
Question
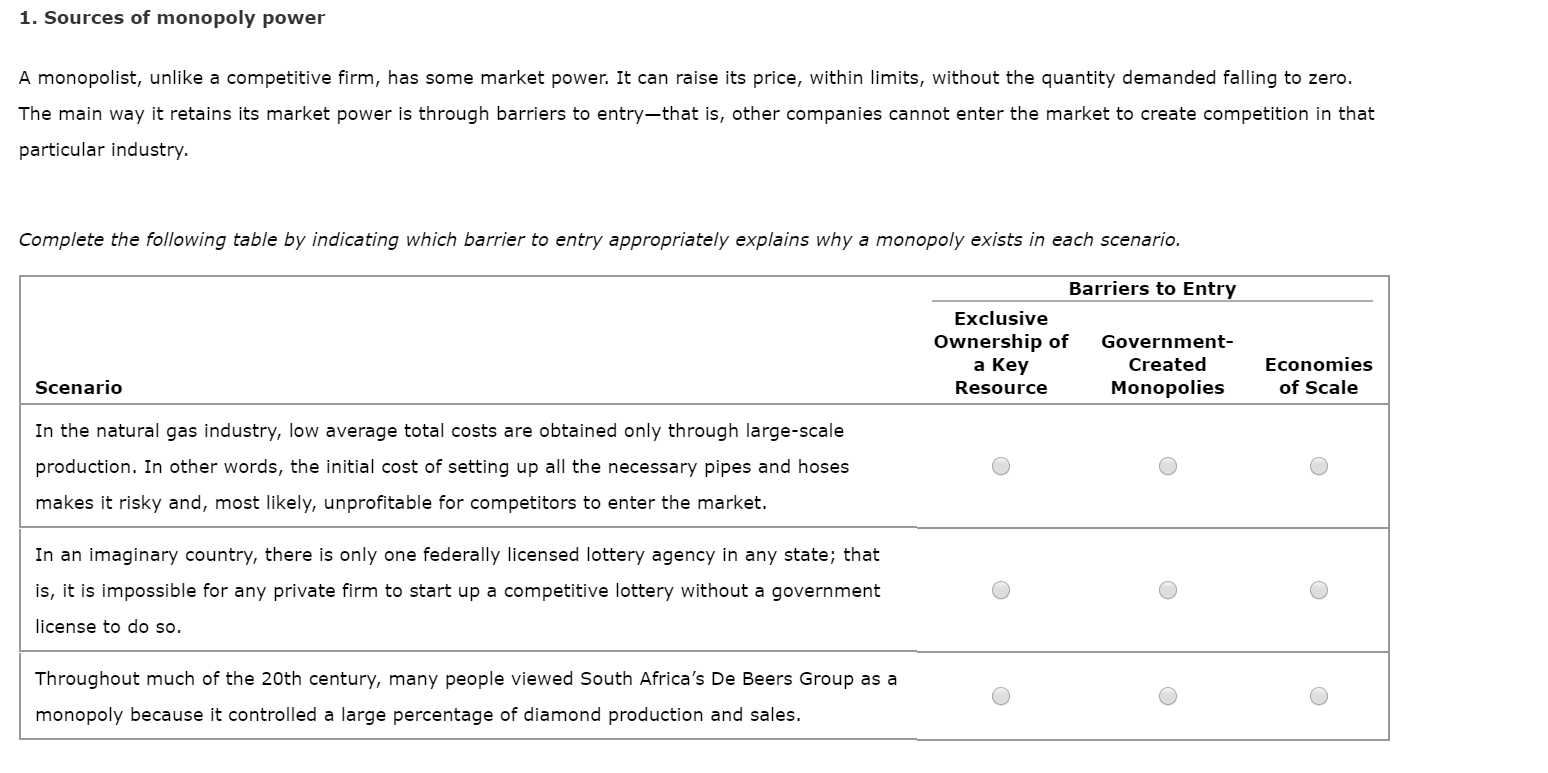
Transcribed Image Text:1. Sources of monopoly power
A monopolist, unlike a competitive firm, has some market power. It can raise its price, within limits, without the quantity demanded falling to zero.
The main way it retains its market power is through barriers to entry-that is, other companies cannot enter the market to create competition in that
particular industry.
Complete the following table by indicating which barrier to entry appropriately explains why a monopoly exists in each scenario.
Barriers to Entry
Exclusive
Ownership of
a Key
Government-
Created
Economies
Scenario
Monopolies
of Scale
Resource
In the natural gas industry, low average total costs are obtained only through large-scale
production. In other words, the initial cost of setting up all the necessary pipes and hoses
makes it risky and, most likely, unprofitable for competitors to enter the market.
In an imaginary country, there is only one federally licensed lottery agency in any state; that
is, it is impossible for any private firm to start up a competitive lottery without a government
license to do so.
Throughout much of the 20th century, many people viewed South Africa's De Beers Group as a
monopoly because it controlled a large percentage of diamond production and sales.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Microeconomics
Economics
ISBN:
9781305156050
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781285165875
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305585126
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Microeconomics
Economics
ISBN:
9781305156050
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781285165875
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305585126
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Microeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305971493
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091992
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
