1. Using (2n +1)Pn= Pn+1-P-1: prove that P(x) = (2n-1) Pn-1(x) + (2n-5) Pn-2+(2n-9) Pn-3+.... - and hence further prove that [*|P²(x)}²dx == n(n + 1).
1. Using (2n +1)Pn= Pn+1-P-1: prove that P(x) = (2n-1) Pn-1(x) + (2n-5) Pn-2+(2n-9) Pn-3+.... - and hence further prove that [*|P²(x)}²dx == n(n + 1).
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter10: Sequences, Series, And Probability
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 51RE
Related questions
Question
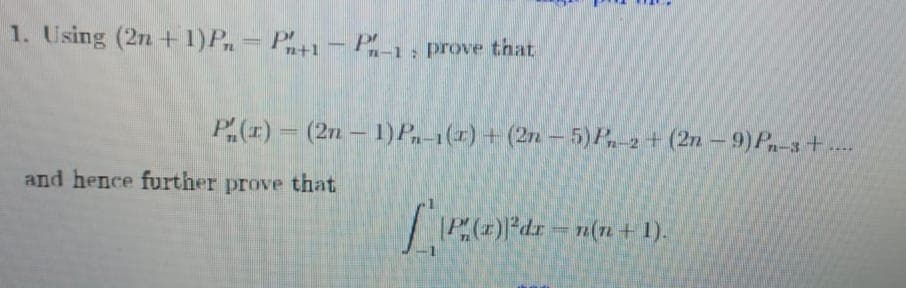
Transcribed Image Text:1. Using (2n +1)Pn
= P+1 – P1; prove that
P(1)= (2n – 1)P,-1(1) + (27n – 5)P, 2 + (2n – 9)P-3+ ...
and hence further prove that
POdr = n(7n + 1).
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage


Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage


Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elements Of Modern Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463230
Author:
Gilbert, Linda, Jimmie
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,