1. What is the name of John Dalton's theory? 2. What are elements made of? 3. An atom of hydrogen and an atom of carbon are 4. What are compounds made of? 5. The ratio of atoms in HCI is: J. J. Thomson was an English scientist He discovered the electron when Atomic Structure he was experimenting with gas discharge tubes. He noticed a movement in a tube. He called the movement cathode rays. The rays moved from the negative end of the tube to the positive end. He realized that the rays were made of negatively charged particles - electrons.
1. What is the name of John Dalton's theory? 2. What are elements made of? 3. An atom of hydrogen and an atom of carbon are 4. What are compounds made of? 5. The ratio of atoms in HCI is: J. J. Thomson was an English scientist He discovered the electron when Atomic Structure he was experimenting with gas discharge tubes. He noticed a movement in a tube. He called the movement cathode rays. The rays moved from the negative end of the tube to the positive end. He realized that the rays were made of negatively charged particles - electrons.
Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Chapter5: Gases
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 74QAP: Glycine is an amino acid made up of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen atoms. Combustion of a...
Related questions
Concept explainers
Atomic Structure
The basic structure of an atom is defined as the component-level of atomic structure of an atom. Precisely speaking an atom consists of three major subatomic particles which are protons, neutrons, and electrons. Many theories have been stated for explaining the structure of an atom.
Shape of the D Orbital
Shapes of orbitals are an approximate representation of boundaries in space for finding electrons occupied in that respective orbital. D orbitals are known to have a clover leaf shape or dumbbell inside where electrons can be found.
Question
Transcribed Image Text:11:15 .l .l
5.00
KB/S
A O (12 4
app.teachermade.com/fill/13c37t
(4)
C Q Q
T TI 4 v
Save for Later
I'm Done
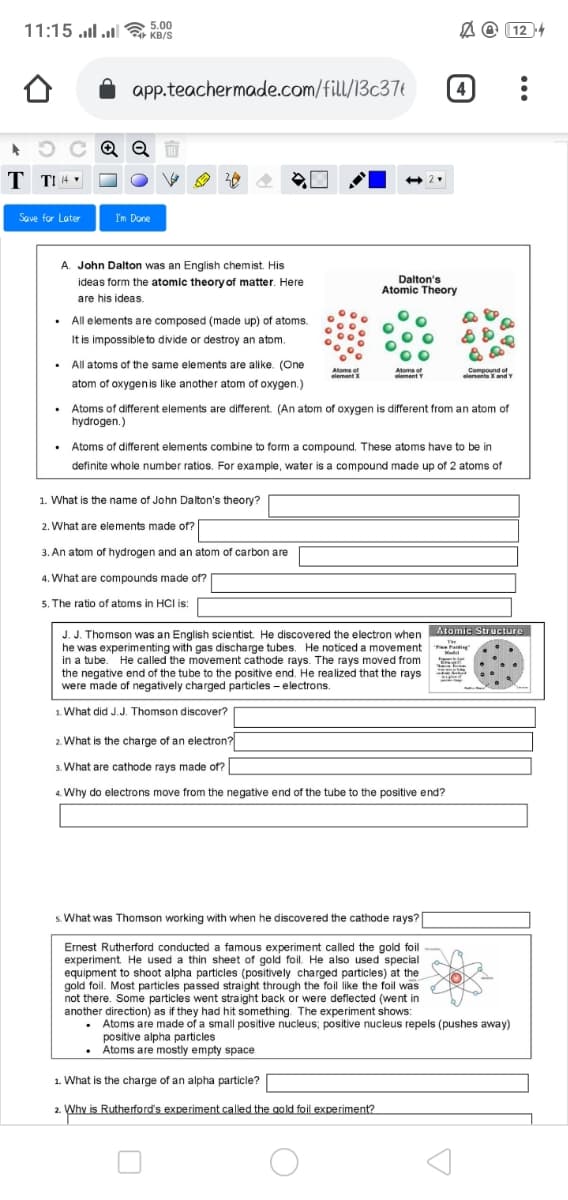
A. John Dalton was an English chemist. His
Dalton's
Atomic Theory
ideas form the atomic theory of matter. Here
are his ideas.
• All elements are composed (made up) of atoms.
It is impossible to divide or destroy an atom.
• All atoms of the same elements are alike. (One
Atoms of
element X
Atoms of
ement Y
Compound of
elemeite XandY
atom of oxygenis like another atom of oxygen.)
• Atoms of different elements are different. (An atom of oxygen is different from an atom of
hydrogen.)
• Atoms of different elements combine to form a compound. These atoms have to be in
definite whole number ratios. For example, water is a compound made up of 2 atoms of
1. What is the name of John Dalton's theory?
2. What are elements made of?
3. An atom of hydrogen and an atom of carbon are
4. What are compounds made of?
5. The ratio of atoms in HCI is:
Atomic Structure
J. J. Thomson was an English scientist. He discovered the electron when
he was experimenting with gas discharge tubes. He noticed a movement
in a tube. He called the movement cathode rays. The rays moved from
the negative end of the tube to the positive end. He realized that the rays
were made of negatively charged particles - electrons.
Mudel
1. What did J.J. Thomson discover?
2. What is the charge of an electron?
3. What are cathode rays made of?
4. Why do electrons move from the negative end of the tube to the positive end?
s. What was Thomson working with when he discovered the cathode rays?|
Ernest Rutherford conducted a famous experiment called the gold foil
experiment. He used a thin sheet of gold foil. He also used special
equipment to shoot alpha particles (positively charged particles) at the
gold foil. Most particles passed straight through the foil like the foil was
not there. Some particles went straight back or were deflected (went in
another direction) as if they had hit something. The experiment shows:
Atoms are made of a small positive nucleus; positive nucleus repels (pushes away)
positive alpha particles
Atoms are mostly empty space
1. What is the charge of an alpha particle?
Why is Rutherford's experiment called the gold foil experiment?
2.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199023
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199023
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning