Chapter3: Electronic Structure And The Periodic Law
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 3.59E
Related questions
Question
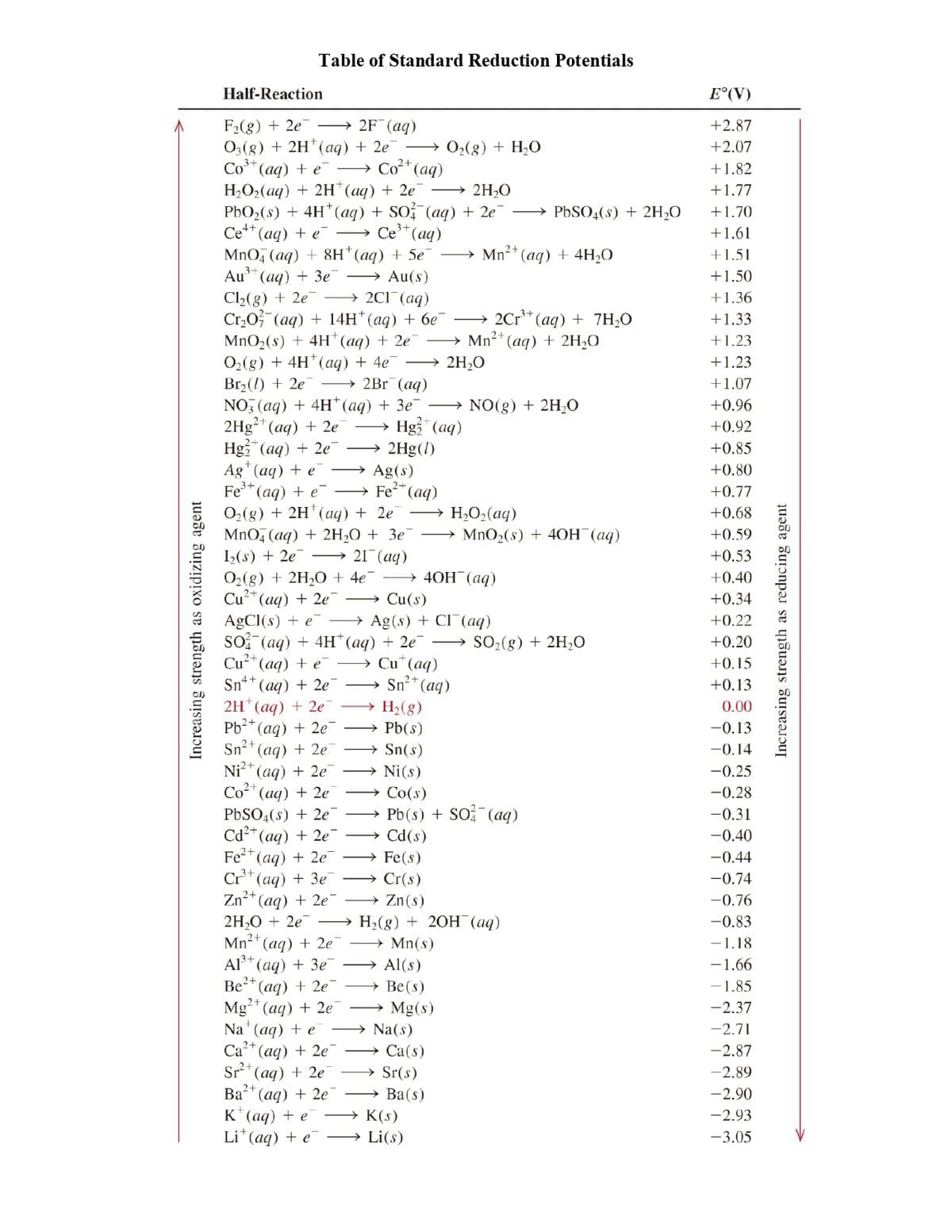
1. Which two species will be able to oxidize Pb(s)?
Co³⁺ and Ce³⁺
Ca and Cr
Cd²⁺ and Cl₂
Cr and Cu
None of the given.
None of the given.
2. Which species will NOT be able to reduce PbO₂(s) to PbSO₄(s)?
Cl₂
Cr
Cu
Ce³⁺
None of the given.
None of the given.
Transcribed Image Text:Increasing strength as oxidizing agent
Table of Standard Reduction Potentials
Half-Reaction
F₂(g) + 2e →→→ 2F¯ (aq)
O3(g) + 2H¹ (aq) + 2e¯ → O₂(g) + H₂O
Co³+ (aq) + e → Co (aq)
H₂O₂(aq) + 2H(aq) + 2e
→ 2H₂O
PbO₂ (s) + 4H+ (aq) + SO²(aq)
Ce+ (aq) + e
Ce³+ (aq)
+ 2e¯ →→→ PbSO4(s) + 2H₂O
2+
→Mn²+ (aq) + 4H₂O
MnO4 (aq) + 8H+ (aq) + 5e7
Au³+
(aq) + 3e - Au(s)
Cl₂(g) + 2e →→→ 2Cl¯¯(aq)
3+
Cr₂O² (aq) + 14H*(aq) + 6e¯
2Cr³+ (aq) + 7H₂O
2+
MnO₂ (s) + 4H+ (aq) + 2e7
→→Mn²+
(aq) + 2H₂O
O₂(g) + 4H+ (aq) + 4e¯ →→→ 2H₂O
Br₂() +2e7 →→→→2Br (aq)
NO3(aq) + 4H+ (aq) + 3e¯→→→→→ NO(g) + 2H₂O
2Hg²+ (aq) + 2e
Hg2+ (aq)
Hg2+ (aq) + 2e
→ 2Hg(1)
Ag+ (aq) + e →
Ag(s)
Fe³+ (aq) + e→→→→→ Fe²+ (aq)
O₂(g) + 2H+ (aq) + 2e7 →→→→H₂O₂(aq)
MnO4 (aq) + 2H₂O + 3e7
1₂(s) + 2e
21 (aq)
O₂(g) + 2H₂O + 4e¯
→→→40H(aq)
Cu(s)
Cu²+ (aq) + 2e
AgCl(s) + e
Ag(s) + Cl(aq)
SO (aq) + 4H+ (aq) + 2e¯
Cu²+ (aq) + e
Cu (aq)
Sn4+
(aq) + 2e
2H(aq) + 2e
Pb²+ (aq) + 2e-
Sn²+ (aq) + 2e
Ni²+ (aq) + 2e
Co²+
(aq) + 2e
PbSO4(s) + 2e
Cd²+ (aq) + 2e
Fe²+ (aq) + 2e
Cr³+ (aq) + 3e
Zn²+ (aq) + 2e
2H₂O + 2e
Mn²+ (aq) + 2e
A1³+ (aq) + 3e¯
Be²+ (aq) + 2e
Mg2+ (aq) + 2e
Na (aq) + e
2+
Ca²+ (aq) + 2e
Sr²+ (aq) + 2e
Ba²+ (aq) + 2e
K+ (aq) + e → K(s)
Li (aq) + e →
Li(s)
Sn²+ (aq)
H₂(g)
Pb(s)
Sn(s)
Ni(s)
Co(s)
→ Pb(s) + SO² (aq)
Cd(s)
Fe(s)
Cr(s)
Zn(s)
H₂(g) + 2OH(aq)
→→ Mn(s)
Al(s)
Be(s)
Mg(s)
Na(s)
MnO₂ (s) + 40H(aq)
SO₂(g) + 2H₂O
Ca(s)
Sr(s)
→Ba(s)
E°(V)
+2.87
+2.07
+1.82
+1.77
+1.70
+1.61
+1.51
+1.50
+1.36
+1.33
+1.23
+1.23
+1.07
+0.96
+0.92
+0.85
+0.80
+0.77
+0.68
+0.59
+0.53
+0.40
+0.34
+0.22
+0.20
+0.15
+0.13
0.00
-0.13
-0.14
-0.25
-0.28
-0.31
-0.40
-0.44
-0.74
-0.76
-0.83
-1.18
-1.66
-1.85
-2.37
-2.71
-2.87
-2.89
-2.90
-2.93
-3.05
Increasing strength as reducing agent
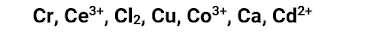
Transcribed Image Text:Cr, Ce³+, Cl₂, Cu, Co³+, Ca, Cd²+
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning