1. Write all the possible KCL and KVL equations that can be derived from the circuit belo Simplify all derived equations and arrange its variables in ascending order with the const at the right side of the equation. 2. Solve I1, I2, I3, I4, and Is using Maxwell's Mesh Equations (use the indicated Me currents – IA, IB, and Ic) 3. Solve Vab, Vbe, and Vea using Nodal Equations (use node 'c' as reference) 4. Solve In using Thevenin's Theorem. 5. Solve Iz using Norton's Theorem. 6. Solve I3 using purely Source Transformation Theorem ONLY. 7. Solve Is using Superposition Theorem. a b 20 20V 14 Is lc 60 30 IB 6A 40
1. Write all the possible KCL and KVL equations that can be derived from the circuit belo Simplify all derived equations and arrange its variables in ascending order with the const at the right side of the equation. 2. Solve I1, I2, I3, I4, and Is using Maxwell's Mesh Equations (use the indicated Me currents – IA, IB, and Ic) 3. Solve Vab, Vbe, and Vea using Nodal Equations (use node 'c' as reference) 4. Solve In using Thevenin's Theorem. 5. Solve Iz using Norton's Theorem. 6. Solve I3 using purely Source Transformation Theorem ONLY. 7. Solve Is using Superposition Theorem. a b 20 20V 14 Is lc 60 30 IB 6A 40
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
13th Edition
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:Robert L. Boylestad
Chapter1: Introduction
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P: Visit your local library (at school or home) and describe the extent to which it provides literature...
Related questions
Question
4 decimal places please
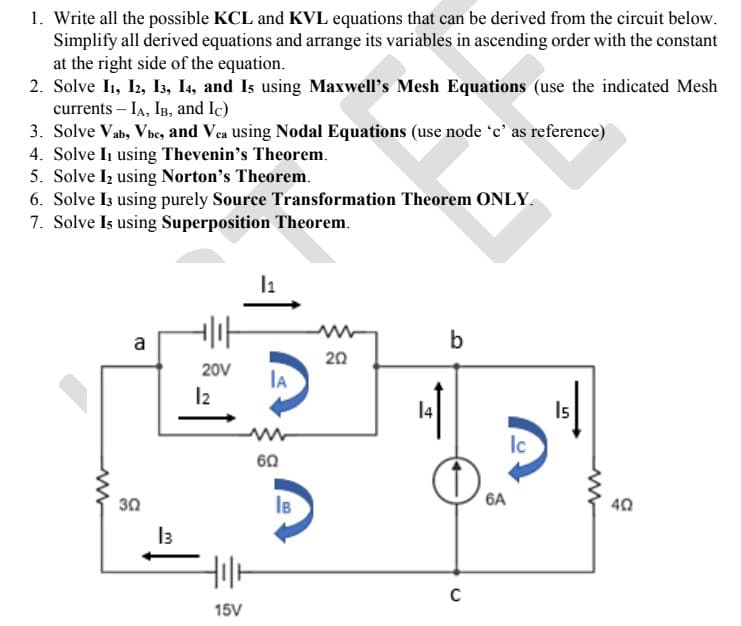
Transcribed Image Text:1. Write all the possible KCL and KVL equations that can be derived from the circuit below.
Simplify all derived equations and arrange its variables in ascending order with the constant
at the right side of the equation.
2. Solve I1, I2, I3, I4, and Is using Maxwell's Mesh Equations (use the indicated Mesh
currents – IA, IB, and Ic)
3. Solve Vab, Vbe, and Vea using Nodal Equations (use node 'c' as reference)
4. Solve I using Thevenin's Theorem.
5. Solve Iz using Norton's Theorem.
6. Solve Iz using purely Source Transformation Theorem ONLY.
7. Solve Is using Superposition Theorem.
a
b
20
20V
lA
I2
Is
Ic
60
30
IB
6A
40
I3
15V
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133923605
Author:
Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:
PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337900348
Author:
Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780073373843
Author:
Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133923605
Author:
Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:
PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337900348
Author:
Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780073373843
Author:
Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780078028229
Author:
Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134746968
Author:
James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:
PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780078028151
Author:
Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:
Mcgraw-hill Education,