1.50 mol of an ideal gas with a constant ratio of heat capacities at constant pressure and volume y =2 = 1.40 is taken through the (reversible) cycle shown in the figure below. The process A - B is an expansion at constant temperature, whereas B →C and C → A are constant-pressure compression and constant-volume processes, respectively. 040 a) What is the temperature TA of the gas at A? P (atm) For the cycle as a whole, b) calculate the (net) work done W (by the gas), 04021 c) calculate the (total) heat transfer Q, Isothermal process d) find the change in the (internal) energy U of the gas, B e) verify that the 1" law of thermodynamics is satisfied. 1 liter=1.00x10 m , 1 atm=1.01x105 N/m² , ks = 1.38x1023 J/K, NA=6.02x1023 mol. V (liters) 50 10
1.50 mol of an ideal gas with a constant ratio of heat capacities at constant pressure and volume y =2 = 1.40 is taken through the (reversible) cycle shown in the figure below. The process A - B is an expansion at constant temperature, whereas B →C and C → A are constant-pressure compression and constant-volume processes, respectively. 040 a) What is the temperature TA of the gas at A? P (atm) For the cycle as a whole, b) calculate the (net) work done W (by the gas), 04021 c) calculate the (total) heat transfer Q, Isothermal process d) find the change in the (internal) energy U of the gas, B e) verify that the 1" law of thermodynamics is satisfied. 1 liter=1.00x10 m , 1 atm=1.01x105 N/m² , ks = 1.38x1023 J/K, NA=6.02x1023 mol. V (liters) 50 10
Chapter3: The First Law Of Thermodynamics
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 11CQ: It is unlikely that a process can be isothermal unless it is a very slow process. Explain why. Is...
Related questions
Question
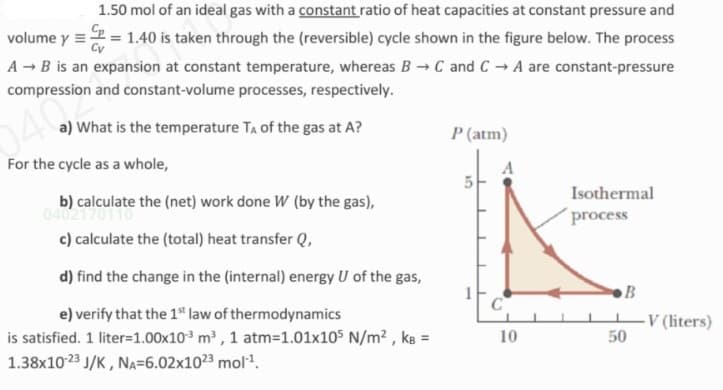
Transcribed Image Text:1.50 mol of an ideal gas with a constant ratio of heat capacities at constant pressure and
volume y =2 = 1.40 is taken through the (reversible) cycle shown in the figure below. The process
A - B is an expansion at constant temperature, whereas B →C and C → A are constant-pressure
compression and constant-volume processes, respectively.
040
a) What is the temperature TA of the gas at A?
P (atm)
For the cycle as a whole,
Isothermal
b) calculate the (net) work done W (by the gas),
04021
c) calculate the (total) heat transfer Q,
process
d) find the change in the (internal) energy U of the gas,
B
e) verify that the 1" law of thermodynamics
C
is satisfied. 1 liter=1.00x10 m , 1 atm=1.01x105 N/m² , kɛ =
1.38x1023 J/K , NA=6.02x1023 mol.
-V (liters)
50
10
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

