12. Which type of interaction is formed when lonic solutes undergo dissolution in water? A. Hydrogen bonding B. Dipole-dipole interaction C. lonic bonding D. lon-dipole interaction
12. Which type of interaction is formed when lonic solutes undergo dissolution in water? A. Hydrogen bonding B. Dipole-dipole interaction C. lonic bonding D. lon-dipole interaction
Chemistry: The Molecular Science
5th Edition
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Chapter13: The Chemistry Of Solutes And Solutions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 27QRT: Refer to Figure 13.10 ( Sec. 13-4b) to answer these questions. (a) Does a saturated solution occur...
Related questions
Question
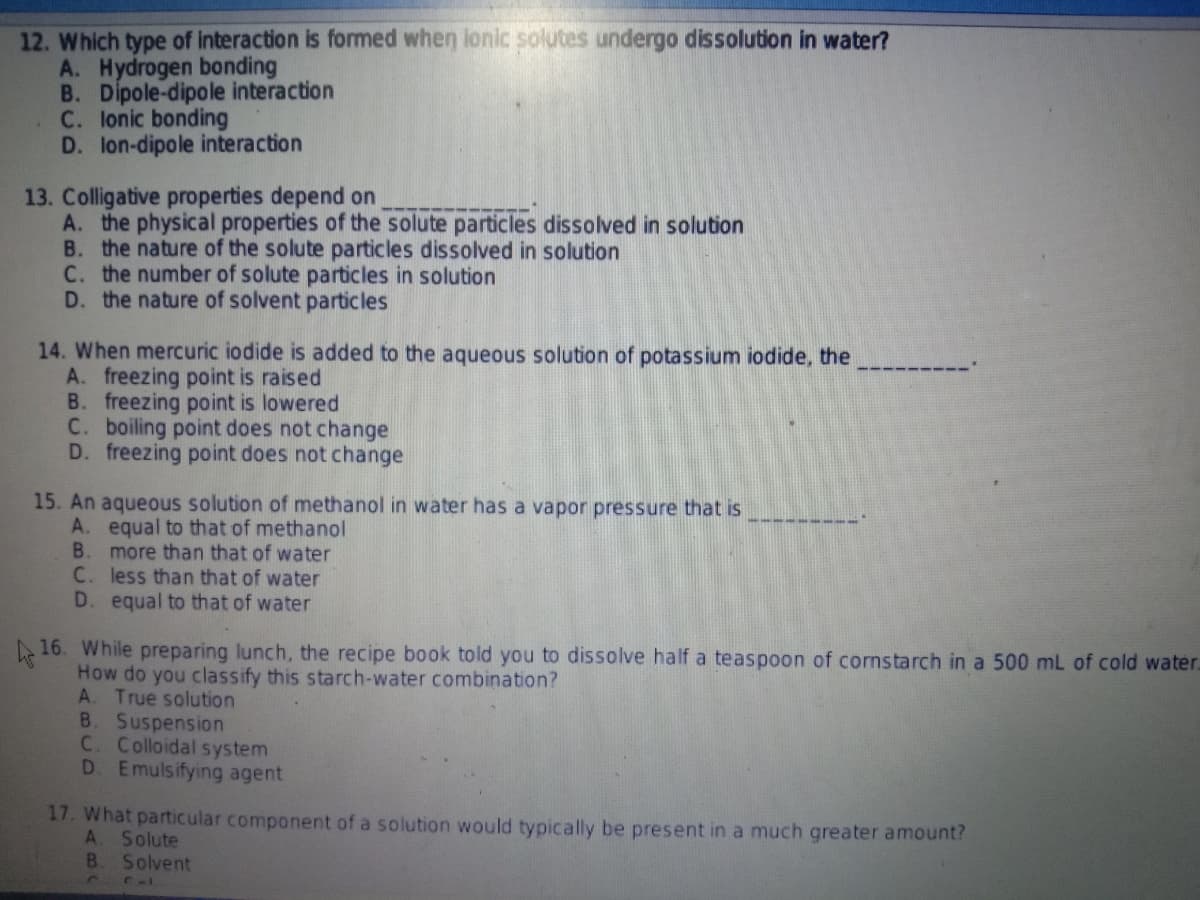
Transcribed Image Text:12. Which type of interaction is formed when lonic solutes undergo dissolution in water?
A. Hydrogen bonding
B. Dipole-dipole interaction
C. lonic bonding
D. lon-dipole interaction
13. Colligative properties depend on
A. the physical properties of the solute particles dissolved in solution
B. the nature of the solute particles dissolved in solution
C. the number of solute particles in solution
D. the nature of solvent particles
14. When mercuric iodide is added to the aqueous solution of potassium iodide, the
A. freezing point is raised
B. freezing point is lowered
C. boiling point does not change
D. freezing point does not change
15. An aqueous solution of methanol in water has a vapor pressure that is
A. equal to that of methanol
B. more than that of water
C. less than that of water
D. equal to that of water
16. While preparing lunch, the recipe book told you to dissolve half a teaspoon of cornstarch in a 500 mL of cold water.
How do you classify this starch-water combination?
A. True solution
B. Suspension
C. Colloidal system
D. Emulsifying agent
17. What particular component of a solution would typically be present in a much greater amount?
A. Solute
B.
Solvent
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
