16. Two hoops, starting from rest, roll down identical inclined planes. The work done by nonconservative forces, such as air resistance, is zero (Wnc = 0 J). Both have the same mass M, but, as the drawing shows, one hoop has twice the radius of the other. The moment of inertia for each hoop is I = Mr, where r is its radius. Which hoop, if either, has the greater total kinetic energy (translational plus rotational) at the bottom of the incline? (a) The larger hoop (b) The smaller hoop (c) Both have the same total kinetic energy. Radius = R Mass = M Radius = R Mass - M
16. Two hoops, starting from rest, roll down identical inclined planes. The work done by nonconservative forces, such as air resistance, is zero (Wnc = 0 J). Both have the same mass M, but, as the drawing shows, one hoop has twice the radius of the other. The moment of inertia for each hoop is I = Mr, where r is its radius. Which hoop, if either, has the greater total kinetic energy (translational plus rotational) at the bottom of the incline? (a) The larger hoop (b) The smaller hoop (c) Both have the same total kinetic energy. Radius = R Mass = M Radius = R Mass - M
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
5th Edition
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Chapter10: Rotational Motion
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 18P: Rigid rods of negligible mass lying along the y axis connect three particles (Fig. P10.18). The...
Related questions
Question
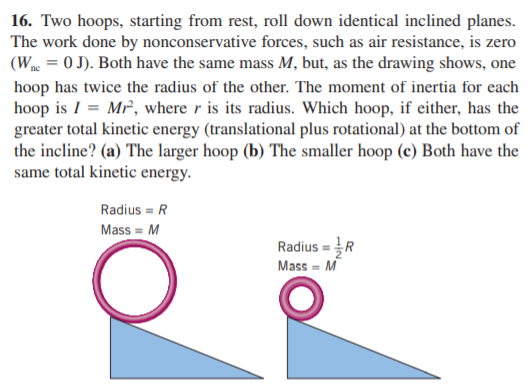
Transcribed Image Text:16. Two hoops, starting from rest, roll down identical inclined planes.
The work done by nonconservative forces, such as air resistance, is zero
(Wnc = 0 J). Both have the same mass M, but, as the drawing shows, one
hoop has twice the radius of the other. The moment of inertia for each
hoop is I = Mr, where r is its radius. Which hoop, if either, has the
greater total kinetic energy (translational plus rotational) at the bottom of
the incline? (a) The larger hoop (b) The smaller hoop (c) Both have the
same total kinetic energy.
Radius = R
Mass = M
Radius = R
Mass - M
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning