17-14 EXCESS CAPACITY Krogh Lumber's 2018 financial statements are shown here. Krogh Lumber: Balance Sheet as of December 31, 2018 (Thousands of Dollars) Cash $ 1,800 Accounts payable $ 7,200 Receivables 10,800 Accrued liabilities 2,520 Inventories 12,600 Notes payable 3,472 Total current assets $25,200 Total current liabilities $13,192 Mortgage bonds 5,000 Net fixed assets 21,600 Common stock 2,000 Retained earnings 26,608 $46,800 Total liabilities and equity Total assets $46,800 Krogh Lumber: Income Statement for December 31, 2018 (Thousands of Dollars) Sales $36,000 Operating costs including depreciation 30,783 Earnings before interest and taxes $ 5,217 Interest 1,017 $ 4,200 Earnings before taxes Taxes (40%) 1,680 Net income $ 2,520 Dividends (60%) $ 1,512 Addition to retained earnings $ 1,008 a. Assume that the company was operating at full capacity in 2018 with regard to all items except fixed assets; fixed assets in 2018 were being utilized to only 75% of capac- ity. By what percentage could 2019 sales increase over 2018 sales without the need for an increase in fixed assets? b. Now suppose 2019 sales increase by 25% over 2018 sales. Assume that Krogh can- not sell any fixed assets. All assets other than fixed assets will grow at the same rate as sales; however, after reviewing industry averages, the firm would like to reduce its operating costs/sales ratio to 82% and increase its total liabilities-to- assets ratio to 42%. The firm will maintain its 60% dividend payout ratio, and it currently has 1 million shares outstanding. The firm plans to raise 35% of its 2019 forecasted interest-bearing debt as notes payable, and it will issue bonds for the remainder. The firm forecasts that its before-tax cost of debt (which includes both short- and long-term debt) is 11%. Any stock issuances or repurchases will be made at the firm's current stock price of $40. Develop Krogh's projected financial statements like those shown in Table 17.2. What are the balances of notes payable, bonds, common stock, and retained earnings?
17-14 EXCESS CAPACITY Krogh Lumber's 2018 financial statements are shown here. Krogh Lumber: Balance Sheet as of December 31, 2018 (Thousands of Dollars) Cash $ 1,800 Accounts payable $ 7,200 Receivables 10,800 Accrued liabilities 2,520 Inventories 12,600 Notes payable 3,472 Total current assets $25,200 Total current liabilities $13,192 Mortgage bonds 5,000 Net fixed assets 21,600 Common stock 2,000 Retained earnings 26,608 $46,800 Total liabilities and equity Total assets $46,800 Krogh Lumber: Income Statement for December 31, 2018 (Thousands of Dollars) Sales $36,000 Operating costs including depreciation 30,783 Earnings before interest and taxes $ 5,217 Interest 1,017 $ 4,200 Earnings before taxes Taxes (40%) 1,680 Net income $ 2,520 Dividends (60%) $ 1,512 Addition to retained earnings $ 1,008 a. Assume that the company was operating at full capacity in 2018 with regard to all items except fixed assets; fixed assets in 2018 were being utilized to only 75% of capac- ity. By what percentage could 2019 sales increase over 2018 sales without the need for an increase in fixed assets? b. Now suppose 2019 sales increase by 25% over 2018 sales. Assume that Krogh can- not sell any fixed assets. All assets other than fixed assets will grow at the same rate as sales; however, after reviewing industry averages, the firm would like to reduce its operating costs/sales ratio to 82% and increase its total liabilities-to- assets ratio to 42%. The firm will maintain its 60% dividend payout ratio, and it currently has 1 million shares outstanding. The firm plans to raise 35% of its 2019 forecasted interest-bearing debt as notes payable, and it will issue bonds for the remainder. The firm forecasts that its before-tax cost of debt (which includes both short- and long-term debt) is 11%. Any stock issuances or repurchases will be made at the firm's current stock price of $40. Develop Krogh's projected financial statements like those shown in Table 17.2. What are the balances of notes payable, bonds, common stock, and retained earnings?
Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305961883
Author:Carl Warren
Publisher:Carl Warren
Chapter9: Metric-analysis Of Financial Statements
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 9.2.1P
Related questions
Question
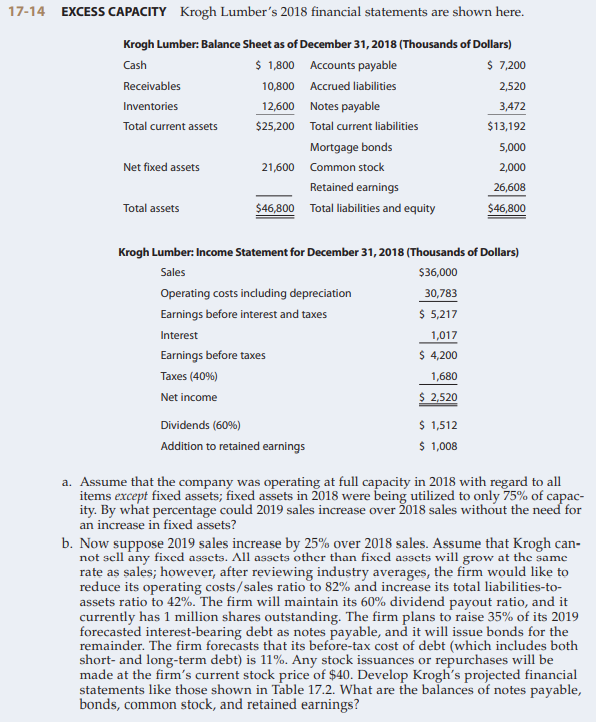
Transcribed Image Text:17-14 EXCESS CAPACITY Krogh Lumber's 2018 financial statements are shown here.
Krogh Lumber: Balance Sheet as of December 31, 2018 (Thousands of Dollars)
$ 1,800 Accounts payable
$ 7,200
Cash
Receivables
10,800 Accrued liabilities
2,520
Inventories
12,600 Notes payable
3,472
Total current assets
$25,200 Total current liabilities
$13,192
Mortgage bonds
5,000
Net fixed assets
21,600 Common stock
2,000
Retained earnings
26,608
$46,800 Total liabilities and equity
$46,800
Total assets
Krogh Lumber: Income Statement for December 31, 2018 (Thousands of Dollars)
Sales
$36,000
Operating costs including depreciation
30,783
Earnings before interest and taxes
$ 5,217
Interest
1,017
Earnings before taxes
$ 4,200
Taxes (40%)
1,680
$ 2,520
Net income
$ 1,512
$ 1,008
Dividends (60%)
Addition to retained earnings
a. Assume that the company was operating at full capacity in 2018 with regard to all
items except fixed assets; fixed assets in 2018 were being utilized to only 75% of capac-
ity. By what percentage could 2019 sales increase over 2018 sales without the need for
an increase in fixed assets?
b. Now suppose 2019 sales increase by 25% over 2018 sales. Assume that Krogh can-
not scll any fixcd assets. All assets other than fixed assets will grow at the same
rate as sales; however, after reviewing industry averages, the firm would like to
reduce its operating costs/sales ratio to 82% and increase its total liabilities-to-
assets ratio to 42%. The firm will maintain its 60% dividend payout ratio, and it
currently has 1 million shares outstanding. The firm plans to raise 35% of its 2019
forecasted interest-bearing debt as notes payable, and it will issue bonds for the
remainder. The firm forecasts that its before-tax cost of debt (which includes both
short- and long-term debt) is 11%. Any stock issuances or repurchases will be
made at the firm's current stock price of $40. Develop Krogh's projected financial
statements like those shown in Table 17.2. What are the balances of notes payable,
bonds, common stock, and retained earnings?

Transcribed Image Text:PRO FORMA INCOME STATEMENT At the end of last year, Roberts Inc. reported the follow-
ing income statement (in millions of dollars):
17-7
Sales
$3,000
Operating costs excluding depreciation
2,450
ЕВITDA
$ 550
Depreciation
250
EBIT
$ 300
Interest
125
EBT
$ 175
Taxes (40%)
70
Net income
$ 105
Looking ahead to the following year, the company's CFO has assembled this information:
• Year-end sales are expected to be 10% higher than the $3 billion in sales generated
last year.
Year-end operating costs, excluding depreciation, are expected to equal 80% of year-
end sales.
Depreciation is expected to increase at the same rate as sales.
Interest costs are expected to remain unchanged.
The tax rate is expected to remain at 40%.
On the basis of that information, what will be the forecast for Roberts' year-end net income?
17-8
LONG-TERM FINANCING NEEDED At year-end 2018, total assets for Arrington Inc. were
$1.8 million and accounts payable were $450,000. Sales, which in 2018 were $3.0 million,
are expected to increase by 25% in 2019. Total assets and accounts payable are proportional
to sales, and that relationship will be maintained; that is, they will grow at the same rate as
sales. Arrington typically uses no current liabilities other than accounts payable. Common
stock amounted to $500,000 in 2018, and retained earnings were $475,000. Árrington plans
to sell new common stock in the amount of $130,000. The firm's profit margin on sales is
5%; 35% of earnings will be retained.
a. What were Arrington's total liabilities in 2018?
b. How much new long-term debt financing will be needed in 2019?
(Hint: AFN – New stock = New long-term debt.)
17-9
SALES INCREASE Paladin Furnishings generated $4 million in sales during 2018, and
its year-end total assets were $3.2 million. Also, at year-end 2018, current liabilities were
$500,000, consisting of $200,000 of notes payable, $200,000 of accounts payable, and
$100,000 of accrued liabilities. Looking ahead to 2019, the company estimates that its assets
must increase by $0.80 for every $1.00 increase in sales. Paladin's profit margin is 3%, and
its retention ratio is 50%. How large of a sales increase can the company achieve without
having to raise funds externally?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305961883
Author:
Carl Warren
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337115773
Author:
Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. Heitger
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
Finance
ISBN:
9781337514835
Author:
MOYER
Publisher:
CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT

Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305961883
Author:
Carl Warren
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337115773
Author:
Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. Heitger
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
Finance
ISBN:
9781337514835
Author:
MOYER
Publisher:
CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT

Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337788281
Author:
James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
