19.3 Electrical Potential Due to a Point Charge Point charges, such as electrons, are among the fundamental building blocks of matter. Furthermore, spherical charge distributions (like on a metal sphere) create external electric fields exactly like a point charge. The electric potential due to a point charge is, thus, a case we need to consider. Using calculus to find the work needed to move a test charge q from a large distance away to a distance of r from a point charge Q, and noting the connection between work and potential (W = - qAV), it can be shown that the electric potential V of a point charge is (19.37) V = (Point Charge), kQ where k is a constant equal to 9.0x10° N · m²/C² .
19.3 Electrical Potential Due to a Point Charge Point charges, such as electrons, are among the fundamental building blocks of matter. Furthermore, spherical charge distributions (like on a metal sphere) create external electric fields exactly like a point charge. The electric potential due to a point charge is, thus, a case we need to consider. Using calculus to find the work needed to move a test charge q from a large distance away to a distance of r from a point charge Q, and noting the connection between work and potential (W = - qAV), it can be shown that the electric potential V of a point charge is (19.37) V = (Point Charge), kQ where k is a constant equal to 9.0x10° N · m²/C² .
Chapter5: Electric Charges And Fields
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 98P: From a distance of 10 cm, a proton is projected with a speed of v=4.0106 m/s directly at a large,...
Related questions
Question
Electrical Potential Due to a Point Charge
• Explain point charges and express the equation for electric potential of a point charge.
• Distinguish between electric potential and electric field.
• Determine the electric potential of a point charge given charge and distance.
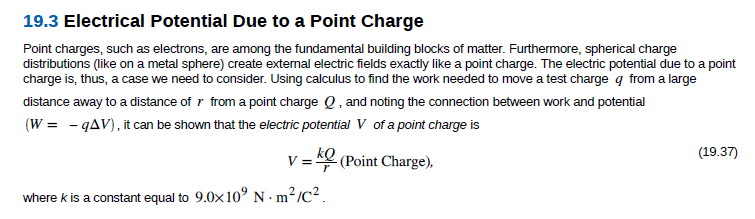
Transcribed Image Text:19.3 Electrical Potential Due to a Point Charge
Point charges, such as electrons, are among the fundamental building blocks of matter. Furthermore, spherical charge
distributions (like on a metal sphere) create external electric fields exactly like a point charge. The electric potential due to a point
charge is, thus, a case we need to consider. Using calculus to find the work needed to move a test charge q from a large
distance away to a distance of r from a point charge Q, and noting the connection between work and potential
(W = - qAV), it can be shown that the electric potential V of a point charge is
(19.37)
V = (Point Charge),
kQ
where k is a constant equal to 9.0x10° N · m²/C² .
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

