Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
1st Edition
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Katz, Debora M.
Chapter39: Relativity
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 11PQ
Related questions
Question
Please explain
Transcribed Image Text:8:47
A webassign.net
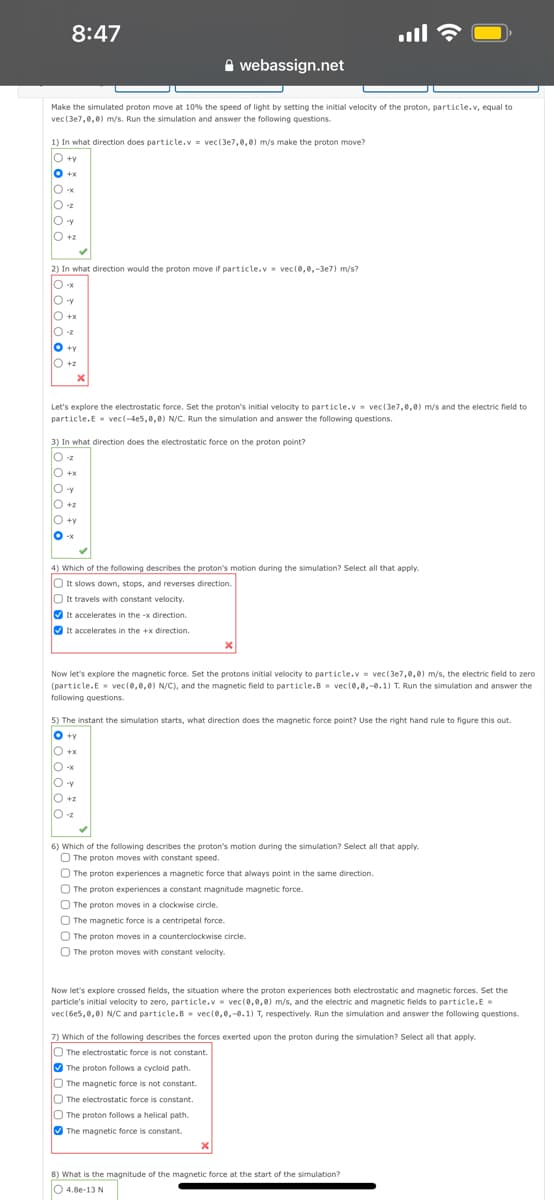
Make the simulated proton move at 10% the speed of light by setting the initial velocity of the proton, particle.v, equal to
vec(3e7,0,0) mys. Run the simulation and answer the following questions.
1) In what direction does particle.v = vec(3e7,0,0) m/s make the proton move?
O +y
O +x
X- O
O :x
O-z
O -y
O +z
2) In what direction would the proton move if particle.v - vec(0.0.-3e7) m/s?
X- O
O -x
O -y
O +x
z- O
O +y
O +z
Let's explore the electrostatic force. Set the proton's initial velocity to particle.v vec(3e7,0,0) m/s and the electric field to
particle.E vec(-4e5,0,e) N/C. Run the simulation and answer the following questions.
3) In what direction does the electrostatic force on the proton point?
z- O
O +x
O -y
O +z
O +y
O -x
4) Which of the following describes the proton's motion during the simulation? Select all that apply.
O It slows down, stops, and reverses direction.
O It travels with constant velocity.
O It accelerates in the -x direction.
O it accelerates in the +x direction.
Now let's explore the magnetic force. Set the protons initial velocity to particle.v = vec(3e7,0,0) m/s, the electric field to zero
(particle.E - vec(0,0.0) N/C), and the magnetic field to particle.B - vec(0,0.-0.1) T. Run the simulation and answer the
following questions.
5) The instant the simulation starts, what direction does the magnetic force point? Use the right hand rule to figure this out.
O +y
X+ O
O -x
O -y
O +z
O z
6) Which of the following describes the proton's motion during the simulation? Select all that apply.
O The proton moves with constant speed.
O The proton experiences a magnetic force that always point in the same direction.
O The proton experiences a constant magnitude magnetic force.
The proton moves in a clockwise circle.
O The magnetic force is a centripetal force.
O The proton moves in a counterclockwise circle.
O The proton moves with constant velocity.
Now let's explore crossed fields, the situation where the proton experiences both electrostatic and magnetic forces. Set the
particle's initial velocity to zero, particle.v vec(e,0.0) m/s, and the electric and magnetic fields to particle.E
vec(6es,0,e) N/C and particle.B- vec(0,0,-0.1) T, respectively. Run the simulation and answer the following questions.
7) Which of the following describes the forces exerted upon the proton during the simulation? Select all that apply.
O The electrostatic force is not constant.
O The proton follows a cycloid path.
O The magnetic force is not constant.
O The electrostatic force is constant.
O The proton follows a helical path.
O The magnetic force is constant.
8) What is the magnitude of the magnetic force at the start of the simulation?
O 4.8e-13 N
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning