2) Long run market equilibrium Consider a market with small, identical, price-taking firms, each of which has long run total cost: TC = 3q² + a) Calculate marginal and average costs. What is each firm's exit price, and what is the minimum quantity each would be willing to supply? b) Find the long-run equilibrium price if this market is perfectly competitive. c) If market demand is given by QD = 10 – P, how many firms will this market have in the long run perfectly competitive equilibrium? d) If demand for this product increases to Qº = 23 – P, how many more firms will enter the market? e) Find the firm-level supply function g$(P). Did you need to find it before now?
2) Long run market equilibrium Consider a market with small, identical, price-taking firms, each of which has long run total cost: TC = 3q² + a) Calculate marginal and average costs. What is each firm's exit price, and what is the minimum quantity each would be willing to supply? b) Find the long-run equilibrium price if this market is perfectly competitive. c) If market demand is given by QD = 10 – P, how many firms will this market have in the long run perfectly competitive equilibrium? d) If demand for this product increases to Qº = 23 – P, how many more firms will enter the market? e) Find the firm-level supply function g$(P). Did you need to find it before now?
Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
8th Edition
ISBN:9781337091992
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:N. Gregory Mankiw
Chapter13: Firms In Competitive Markets
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 10PA
Related questions
Question
Give an explanation to the answer and ensure all the steps are shown.
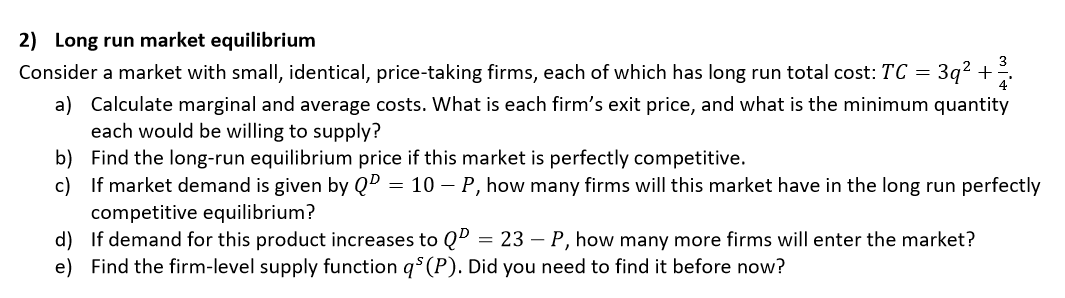
Transcribed Image Text:2) Long run market equilibrium
3
Consider a market with small, identical, price-taking firms, each of which has long run total cost: TC = 3q² + .
a) Calculate marginal and average costs. What is each firm's exit price, and what is the minimum quantity
each would be willing to supply?
b) Find the long-run equilibrium price if this market is perfectly competitive.
c) If market demand is given by QD = 10 – P, how many firms will this market have in the long run perfectly
competitive equilibrium?
d) If demand for this product increases to Q"
e) Find the firm-level supply function q$ (P). Did you need to find it before now?
= 23 – P, how many more firms will enter the market?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091992
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091992
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
