2. An object oscillates with simple harmonic motion along the x axis. Its displacement from the origin varies with time according to the equationx = 4cos (nt +) where tis in seconds and the angles in the parentheses are in radians. (a) Detemine the position x, velocity v, and acceleration a of the object at t = 1 sec. (b) Determine the maximum speed vm and maximum acceleration a,m of the object. HARMONIC OCSILLATIONS A Theory The period T (sec) of a simple harmonic oscillator is given by 1. T = 2n here k is force constant or stiffness coefficient (N/m), m is mass of oscillating particle (kg). Frequencyf (Hz) of a simple harmonic oscillator 2. f = = Circular frequency of oscillations w, (rad/sec) 3. here k is force constant or stiffness coefficient (N/m), m is mass of oscillating particle (kg) 4. Relationship between circular frequency and period here T is the oscillation period (sec), wo is circular frequency (rad/sec) 5. Law of harmonic motion In general, a particle moving along the x axis exhibits simple hamonic motion when x, the particle's displacement from equilibrium, varies intime according to the relationship x(t) = Acos(@ot + Po), here x is the particles displacement (m) at moment of time t (sec); A is maximum displacement from equilibrium or amplitude (m); 4 = wot + wo is phase of oscillatory motion (rad); 4, is initial phase (rad); wo is circular frequancy (rad/sec). Position Amplitude X 6. Speed v (m/sec) of a simple harmonic oscillator = -Awosin(@ot + Po) = -Vmsin(wot + Po), v(t) = dt here vm = Aw, is maximum speed, or speed amplitude. 7. Accelerationa (m/sec) of a simple harmonic oscillator = -Awžcos(wot + Po) = -amcos(wot + Po), a(t) = dt? here am = Aw is maximum acceleration or amplidude of acceleration Kinetic energy Ex J) of a simple harmonic oscillator E, = m = KA sin? (wnt + @o). 8. kA2 mv2 Potential energy E, () of a simple harmonic oscillator 9. kx? cos? (wot + Po). Ep = = J) of a simple harmonic oscillator Full energy E 10. kA? тодА? %3D E = Ex + E, = 2 A rad =180° or 1 rad = 180° 30° () 45° G 90° E 60° 0° VZ/2 V3/2 sin(0) 1/2 V3/2 VZ/2 1/2 cos(0) V3/3 V3 1 tg(0) cos (0 + n) = -cose sin(0 + n) = -sine
2. An object oscillates with simple harmonic motion along the x axis. Its displacement from the origin varies with time according to the equationx = 4cos (nt +) where tis in seconds and the angles in the parentheses are in radians. (a) Detemine the position x, velocity v, and acceleration a of the object at t = 1 sec. (b) Determine the maximum speed vm and maximum acceleration a,m of the object. HARMONIC OCSILLATIONS A Theory The period T (sec) of a simple harmonic oscillator is given by 1. T = 2n here k is force constant or stiffness coefficient (N/m), m is mass of oscillating particle (kg). Frequencyf (Hz) of a simple harmonic oscillator 2. f = = Circular frequency of oscillations w, (rad/sec) 3. here k is force constant or stiffness coefficient (N/m), m is mass of oscillating particle (kg) 4. Relationship between circular frequency and period here T is the oscillation period (sec), wo is circular frequency (rad/sec) 5. Law of harmonic motion In general, a particle moving along the x axis exhibits simple hamonic motion when x, the particle's displacement from equilibrium, varies intime according to the relationship x(t) = Acos(@ot + Po), here x is the particles displacement (m) at moment of time t (sec); A is maximum displacement from equilibrium or amplitude (m); 4 = wot + wo is phase of oscillatory motion (rad); 4, is initial phase (rad); wo is circular frequancy (rad/sec). Position Amplitude X 6. Speed v (m/sec) of a simple harmonic oscillator = -Awosin(@ot + Po) = -Vmsin(wot + Po), v(t) = dt here vm = Aw, is maximum speed, or speed amplitude. 7. Accelerationa (m/sec) of a simple harmonic oscillator = -Awžcos(wot + Po) = -amcos(wot + Po), a(t) = dt? here am = Aw is maximum acceleration or amplidude of acceleration Kinetic energy Ex J) of a simple harmonic oscillator E, = m = KA sin? (wnt + @o). 8. kA2 mv2 Potential energy E, () of a simple harmonic oscillator 9. kx? cos? (wot + Po). Ep = = J) of a simple harmonic oscillator Full energy E 10. kA? тодА? %3D E = Ex + E, = 2 A rad =180° or 1 rad = 180° 30° () 45° G 90° E 60° 0° VZ/2 V3/2 sin(0) 1/2 V3/2 VZ/2 1/2 cos(0) V3/3 V3 1 tg(0) cos (0 + n) = -cose sin(0 + n) = -sine
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
5th Edition
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Chapter12: Oscillatory Motion
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 14P: In an engine, a piston oscillates with simple harmonic motion so that its position varies according...
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:2. An object oscillates with simple harmonic motion along the x axis. Its displacement from
the origin varies with time according to the equationx = 4cos (nt +) where tis in seconds and
the angles in the parentheses are in radians. (a) Detemine the position x, velocity v, and
acceleration a of the object at t = 1 sec. (b) Determine the maximum speed vm and maximum
acceleration a,m of the object.
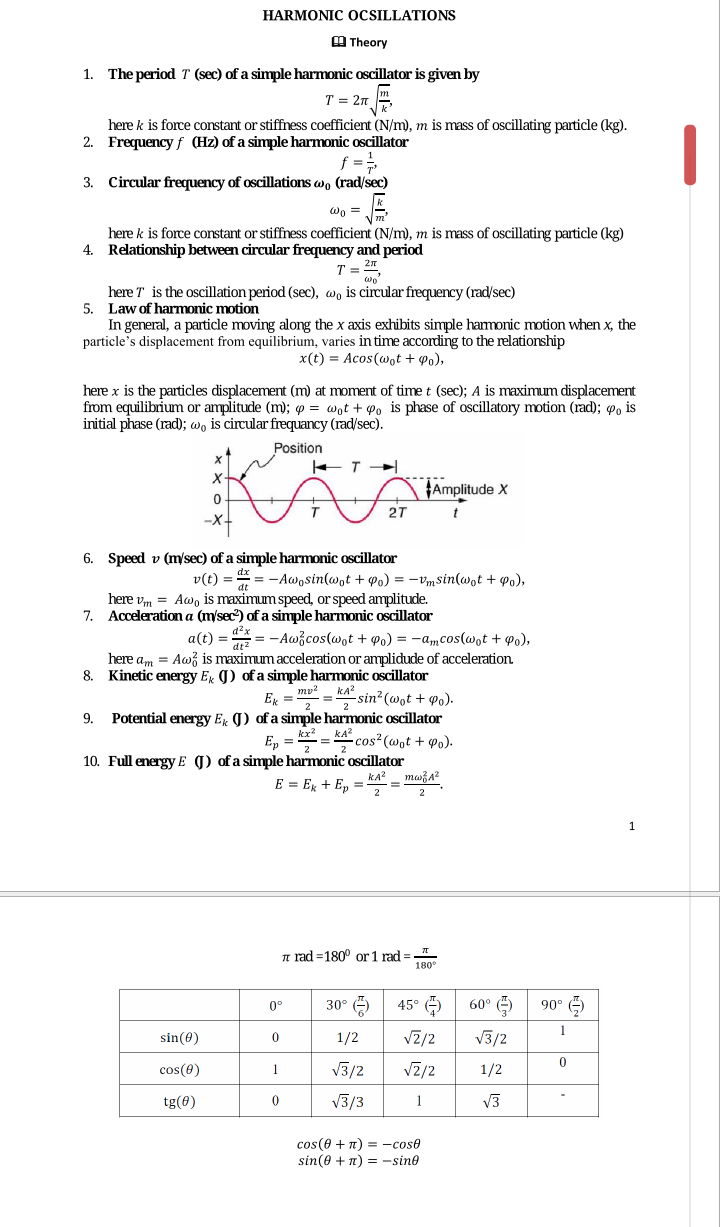
Transcribed Image Text:HARMONIC OCSILLATIONS
A Theory
The period T (sec) of a simple harmonic oscillator is given by
1.
T = 2n
here k is force constant or stiffness coefficient (N/m), m is mass of oscillating particle (kg).
Frequencyf (Hz) of a simple harmonic oscillator
2.
f = =
Circular frequency of oscillations w, (rad/sec)
3.
here k is force constant or stiffness coefficient (N/m), m is mass of oscillating particle (kg)
4.
Relationship between circular frequency and period
here T is the oscillation period (sec), wo is circular frequency (rad/sec)
5. Law of harmonic motion
In general, a particle moving along the x axis exhibits simple hamonic motion when x, the
particle's displacement from equilibrium, varies intime according to the relationship
x(t) = Acos(@ot + Po),
here x is the particles displacement (m) at moment of time t (sec); A is maximum displacement
from equilibrium or amplitude (m); 4 = wot + wo is phase of oscillatory motion (rad); 4, is
initial phase (rad); wo is circular frequancy (rad/sec).
Position
Amplitude X
6.
Speed v (m/sec) of a simple harmonic oscillator
= -Awosin(@ot + Po) = -Vmsin(wot + Po),
v(t) =
dt
here vm = Aw, is maximum speed, or speed amplitude.
7. Accelerationa (m/sec) of a simple harmonic oscillator
= -Awžcos(wot + Po) = -amcos(wot + Po),
a(t) =
dt?
here am = Aw is maximum acceleration or amplidude of acceleration
Kinetic energy Ex J) of a simple harmonic oscillator
E, = m = KA sin? (wnt + @o).
8.
kA2
mv2
Potential energy E, () of a simple harmonic oscillator
9.
kx?
cos? (wot + Po).
Ep = =
J) of a simple harmonic oscillator
Full energy E
10.
kA?
тодА?
%3D
E = Ex + E, =
2
A rad =180° or 1 rad =
180°
30° ()
45° G
90° E
60°
0°
VZ/2
V3/2
sin(0)
1/2
V3/2
VZ/2
1/2
cos(0)
V3/3
V3
1
tg(0)
cos (0 + n) = -cose
sin(0 + n) = -sine
Expert Solution
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 9 steps with 9 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning