2. Suppose that f is defined on (0, b) and that f is differentiable at c € (0, b). (Do not assume that f is differentiable at any other points.) Evaluate each of the following limits; the answers will be in terms of c, f'(c), etc. f(x)-f(c) xf (c) - cf(x) a) lim b) lim x1c - C² c) lim f(x²)-f(c) x-√c
2. Suppose that f is defined on (0, b) and that f is differentiable at c € (0, b). (Do not assume that f is differentiable at any other points.) Evaluate each of the following limits; the answers will be in terms of c, f'(c), etc. f(x)-f(c) xf (c) - cf(x) a) lim b) lim x1c - C² c) lim f(x²)-f(c) x-√c
Chapter3: Functions
Section3.3: Rates Of Change And Behavior Of Graphs
Problem 2SE: If a functionfis increasing on (a,b) and decreasing on (b,c) , then what can be said about the local...
Related questions
Question
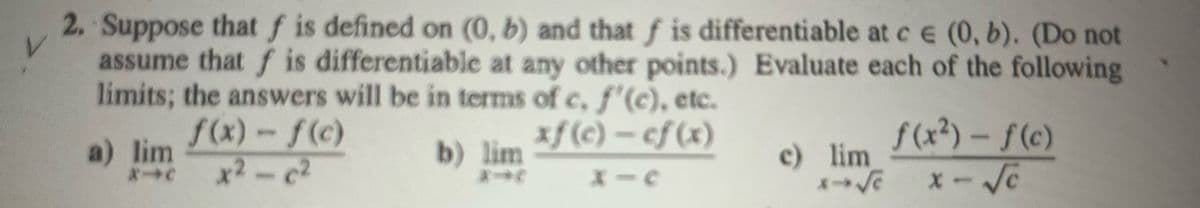
Transcribed Image Text:2. Suppose that f is defined on (0, b) and that f is differentiable at ce (0, b). (Do not
assume that f is differentiable at any other points.) Evaluate each of the following
limits; the answers will be in terms of c, f'(c), etc.
f(x) - f(c)
xf(c) - cf(x)
x²-c²
X=
a) lim
X-C
b) lim
-
c) lim
x→ √e
f(x²) - f(c)
x-√c
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images

Recommended textbooks for you

