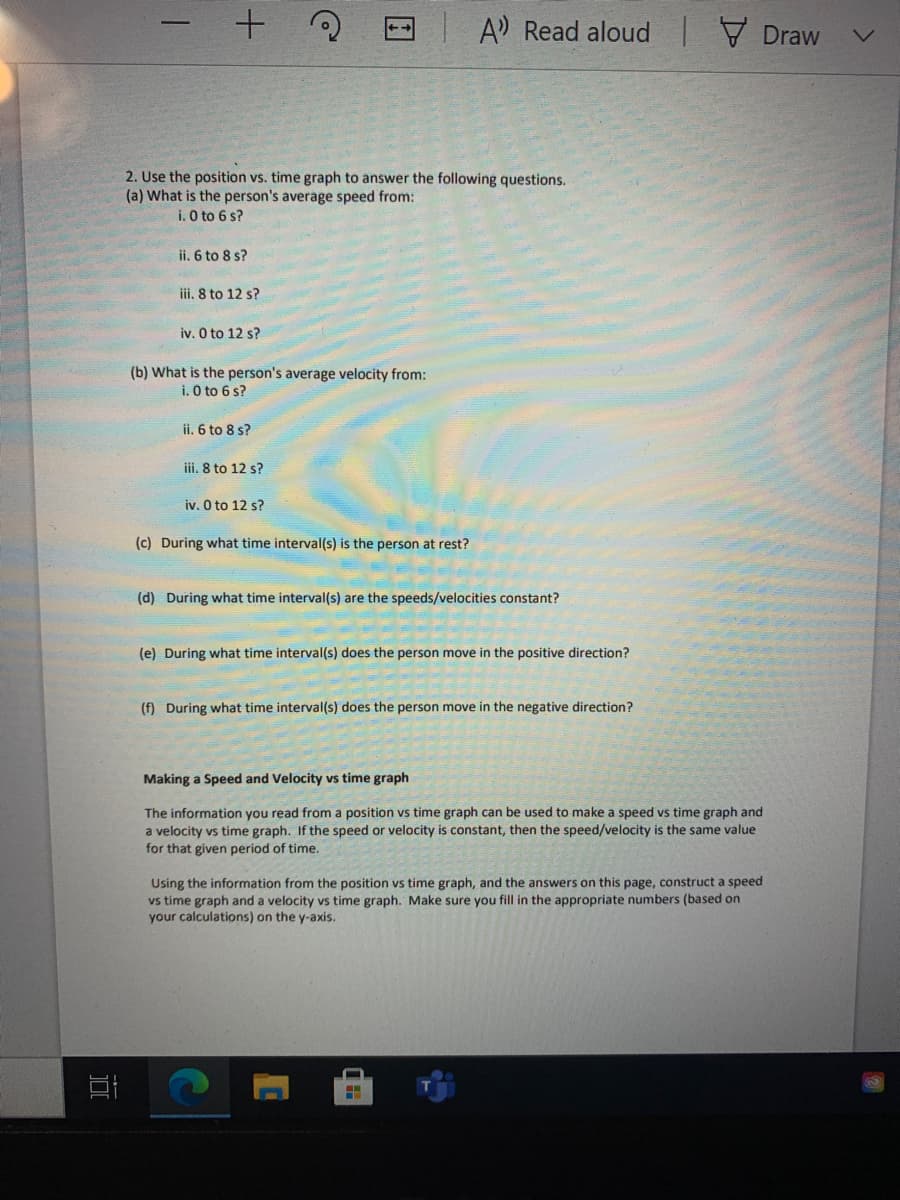
2. Use the position vs. time graph to answer the following questions. (a) What is the person's average speed from: i. O to 6 s? ii. 6 to 8 s? iii. 8 to 12 s? iv. O to 12 s? (b) What is the person's average velocity from: i. O to 6 s? ii. 6 to 8 s? ii. 8 to 12 s? iv. O to 12 s? (c) During what time interval(s) is the person at rest?
2. Use the position vs. time graph to answer the following questions. (a) What is the person's average speed from: i. O to 6 s? ii. 6 to 8 s? iii. 8 to 12 s? iv. O to 12 s? (b) What is the person's average velocity from: i. O to 6 s? ii. 6 to 8 s? ii. 8 to 12 s? iv. O to 12 s? (c) During what time interval(s) is the person at rest?
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Chapter2: Motion In One Dimension
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 26P: PROBLEM A race car starting from rest accelerates at a constant rate of 5.00 m/s2, (a) What is the...
Related questions
Question
Please answer these ASAP
Transcribed Image Text:A" Read aloud
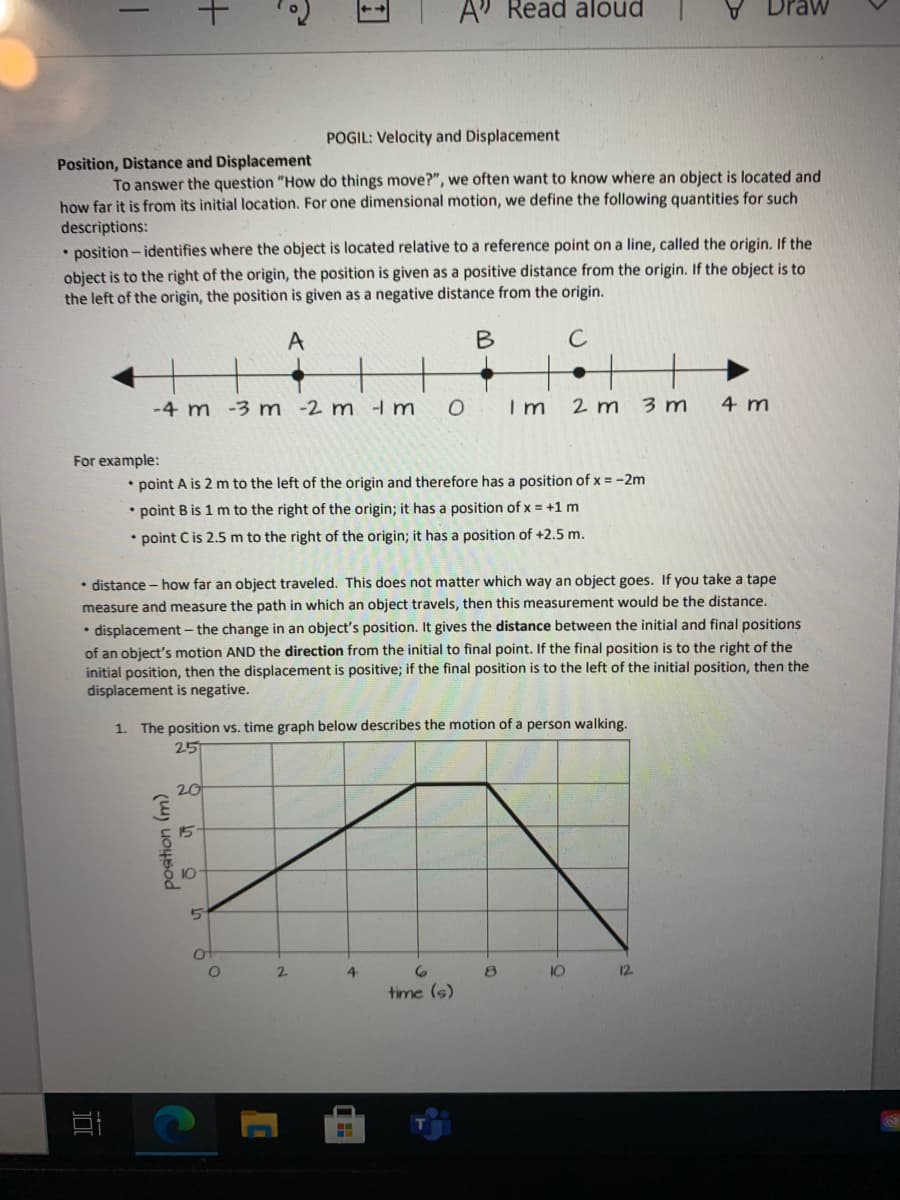
POGIL: Velocity and Displacement
Position, Distance and Displacement
To answer the question "How do things move?", we often want to know where an object is located and
how far it is from its initial location. For one dimensional motion, we define the following quantities for such
descriptions:
• position - identifies where the object is located relative to a reference point on a line, called the origin. If the
object is to the right of the origin, the position is given as a positive distance from the origin. If the object is to
the left of the origin, the position is given as a negative distance from the origin.
A
C
-4 m -3 m -2 m -I m
O Im
2 m
3 m
4 m
For example:
• point A is 2 m to the left of the origin and therefore has a position of x = -2m
• point B is 1 m to the right of the origin; it has a position of x = +1 m
• point C is 2.5 m to the right of the origin; it has a position of +2.5 m.
• distance - how far an object traveled. This does not matter which way an object goes. If you take a tape
measure and measure the path in which an object travels, then this measurement would be the distance.
• displacement- the change in an object's position. It gives the distance between the initial and final positions
of an object's motion AND the direction from the initial to final point. If the final position is to the right of the
initial position, then the displacement is positive; if the final position is to the left of the initial position, then the
displacement is negative.
1. The position vs. time graph below describes the motion of a person walking.
25
20
15
10
2.
4
10
12
time (s)
position (m)
Transcribed Image Text:A Read aloud Draw
2. Use the position vs. time graph to answer the following questions.
(a) What is the person's average speed from:
i. O to 6 s?
ii. 6 to 8 s?
iii. 8 to 12 s?
iv. O to 12 s?
(b) What is the person's average velocity from:
i. O to 6 s?
ii. 6 to 8 s?
iii. 8 to 12 s?
iv. O to 12 s?
(c) During what time interval(s) is the person at rest?
(d) During what time interval(s) are the speeds/velocities constant?
(e) During what time interval(s) does the person move in the positive direction?
(f) During what time interval(s) does the person move in the negative direction?
Making a Speed and Velocity vs time graph
The information you read from a position vs time graph can be used to make a speed vs time graph and
a velocity vs time graph. If the speed or velocity is constant, then the speed/velocity is the same value
for that given period of time.
Using the information from the position vs time graph, and the answers on this page, construct a speed
vs time graph and a velocity vs time graph. Make sure you fill in the appropriate numbers (based on
your calculations) on the y-axis.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University