200 mg/s Q33C3 500 mg/s Q33 = 120 Q13 = 40 Q12 = 90 Q23 = 60 30 Q21
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter5: Inverse, Exponential, And Logarithmic Functions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 44RE
Related questions
Question
Figure below shows three reactors linked by pipes. As indicated, the rate of transfer of chemicals through each pipe is equal to a flow rate (Q, with units of cubic meters per second) multiplied by the concentration of the reactor from which the flow originates (c, with units of milligrams per cubic meter). If the system is at a steady-state, the transfer into each reactor will balance the transfer out. Develop mass-balance equations for the reactors and solve the three simultaneous
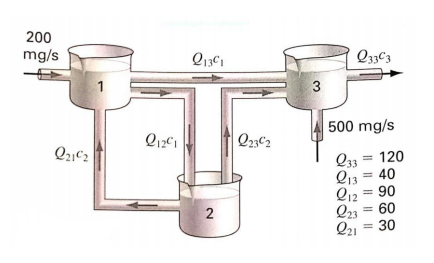
Transcribed Image Text:200
mg/s
Q33C3
3
500 mg/s
Q23C2
Q33 = 120
Q13 = 40
Q12 = 90
Q23 = 60
Q21 = 30
%3D
2
%3D
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, advanced-math and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage