26. ao The drawing shows three situations in which a block is attached to a spring. The position labeled “O m" represents the unstrained position of the spring. The block is moved from an initial position x, to a final position x, the magnitude of the displacement being denoted by the sym- bol s. Suppose the spring has a spring constant of k = 46.0 N/m. Using the data provided in the drawing, determine the total work done by the restoring force of the spring for each situation. Position of box when (a) spring is unstrained Om +1.00 m +3.00 m (b) -3.00 m Om +1.00 m -3.00 m Om +3.00 m
26. ao The drawing shows three situations in which a block is attached to a spring. The position labeled “O m" represents the unstrained position of the spring. The block is moved from an initial position x, to a final position x, the magnitude of the displacement being denoted by the sym- bol s. Suppose the spring has a spring constant of k = 46.0 N/m. Using the data provided in the drawing, determine the total work done by the restoring force of the spring for each situation. Position of box when (a) spring is unstrained Om +1.00 m +3.00 m (b) -3.00 m Om +1.00 m -3.00 m Om +3.00 m
University Physics Volume 1
18th Edition
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Chapter8: Potential Energy And Conservation Of Energy
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 57P: In a Coyote/Road Runner cartoon clip (https://openstaxcollege.org/l/21coyroadcarcl), a spring...
Related questions
Question
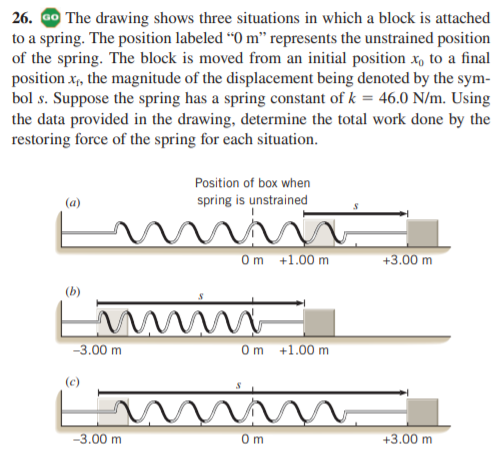
Transcribed Image Text:26. ao The drawing shows three situations in which a block is attached
to a spring. The position labeled “O m" represents the unstrained position
of the spring. The block is moved from an initial position x, to a final
position x, the magnitude of the displacement being denoted by the sym-
bol s. Suppose the spring has a spring constant of k = 46.0 N/m. Using
the data provided in the drawing, determine the total work done by the
restoring force of the spring for each situation.
Position of box when
(a)
spring is unstrained
Om +1.00 m
+3.00 m
(b)
-3.00 m
Om +1.00 m
-3.00 m
Om
+3.00 m
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168000
Author:
Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:
OpenStax College

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168000
Author:
Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill