26. Why do polar substances such as NaCI dissolve so readily in water? Water dissociates salts by separating the cations and anions B. New interactions are formed between the water polar ends (8- and &+) and the Nat and CF ions. C. Spheres of hydration form between the water molecules and the Na+ and Cl- ions. D. All of the above E. None of the above A.
26. Why do polar substances such as NaCI dissolve so readily in water? Water dissociates salts by separating the cations and anions B. New interactions are formed between the water polar ends (8- and &+) and the Nat and CF ions. C. Spheres of hydration form between the water molecules and the Na+ and Cl- ions. D. All of the above E. None of the above A.
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
1st Edition
ISBN:9781938168390
Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Chapter11: Solutions And Colloids
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 8E: Solutions of hydrogen in palladium may be formed by exposing Pd metal to H2 gas. The concentration...
Related questions
Question
Please do both
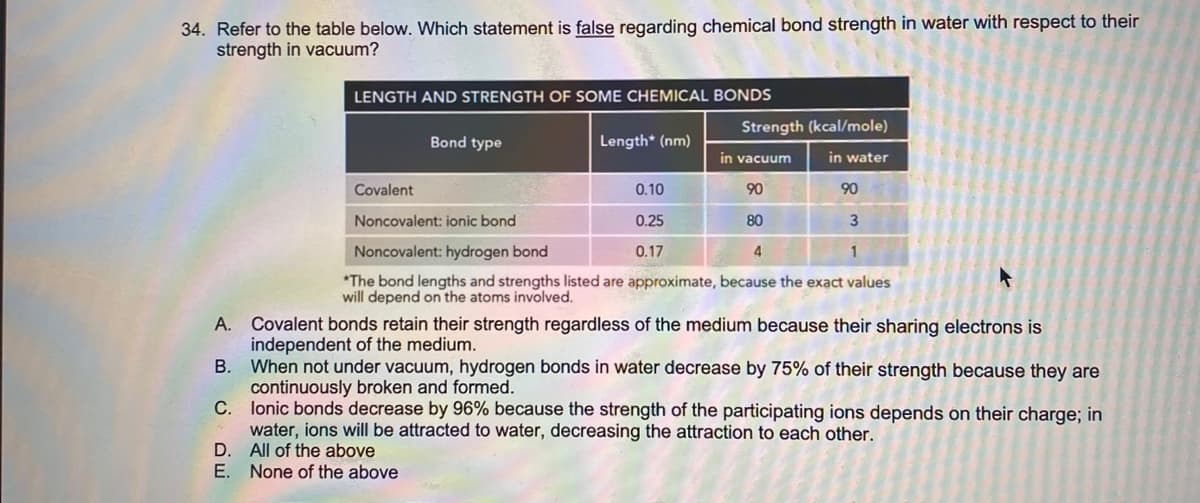
Transcribed Image Text:34. Refer to the table below. Which statement is false regarding chemical bond strength in water with respect to their
strength in vacuum?
LENGTH AND STRENGTH OF SOME CHEMICAL BONDS
Strength (kcal/mole)
Bond type
Length* (nm)
in vacuum
in water
Covalent
0.10
90
90
Noncovalent: ionic bond
0.25
80
Noncovalent: hydrogen bond
0.17
4
*The bond lengths and strengths listed are approximate, because the exact values
will depend on the atoms involved.
Covalent bonds retain their strength regardless of the medium because their sharing electrons is
independent of the medium.
В.
А.
When not under vacuum, hydrogen bonds in water decrease by 75% of their strength because they are
continuously broken and formed.
C. lonic bonds decrease by 96% because the strength of the participating ions depends on their charge; in
water, ions will be attracted to water, decreasing the attraction to each other.
D.
All of the above
E. None of the above

Transcribed Image Text:26. Why do polar substances such as NaCI dissolve so readily in water?
Water dissociates salts by separating the cations and anions
B. New interactions are formed between the water polar ends (8- and &+) and the Na+ and CF ions.
C. Spheres of hydration form between the water molecules and the Na+ and CH ions.
D.
A.
All of the above
E. None of the above
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079250
Author:
Mark S. Cracolice, Ed Peters
Publisher:
Cengage Learning