2The known data sequence is (130, 116, 48492, 8, 236, 350, 66, 25, 371), please give the schematic diagram of radix sorting process
Q: In CRC, show the relationship between the following entities (size means the number of bits): a. The…
A: CRC stands for Cyclic Redundancy Check, it is an Error detection method. It contains Code word, Data…
Q: Automatic scaling must be defined.
A: AUTOMATIC SCALING: Automatic scaling is also termed auto-scaling. The process of automatic scaling…
Q: .Normalization the table below to 3NF to overcome the problems in it DID Pname Alpha Beta Dname EID…
A: We need to convert the given table into the 3NF normal form.
Q: ive a brief tabular comparison of 8051 family m
A: Required: Give a brief tabular comparison of 8051 family members.
Q: QUESTION 3 Time Time Gene point point Cluster 1 2 g1 o o g2 8 g3 g4 2 g5 7 Shown above is expression…
A:
Q: 2. (a) (b) What do you understand by Time and Space complexity? How is Big-0 notation used for…
A:
Q: The record searching technique in which the searching of records is done by block by block is…
A: Heap search : In the file, every record has a unique id, and every page in a file is of the same…
Q: Could you please provide me with an example explains the concept of Data parallelism
A: Data parallelism is a concept of handling the same task at the same time with different processors…
Q: Give some Advantages of horizontal and vertical partitioning.
A: Advantages of Horizontal Partitioning: Horizontal Partitioning separates table rows into discrete…
Q: The Triple code of Model of number processing explains how we process whole numbers or integers.…
A: import java.util.Scanner; public class Rational { //begin class private int Numerator; private int…
Q: Define merge sort
A: Lets see the solution in the next steps
Q: B. D H. 1. Problem 4 Use Excel, to create a histogram for the data set. Calculate the cumulate…
A: Histograms for translation of random sample data are often used as an indicator of basic human…
Q: Explain what is the differences between Breadth First Search (BFS) and Depth First Search (DFS).
A: To explain difference between DFS and BFS.
Q: Construct a forward and a backward table from the following table:
A: The format of forward differnce table is given below: x y Δy Δ2y Δ3y Δ4y x0 = 2 y0 = 4.310…
Q: b) Describe how a Savings and Loans Company can use singly-linked lists to keep track of customers…
A: b) A linked list is a type of data structure that stores data components. The linked list is the…
Q: You are a teaching Assistant at University of Ghana, Legon. 523 students from 4 faculties; namely:…
A: Given: Your professor has asked you to sort the CS304 exam scripts of the 523 students in ascending…
Q: • Based on the graph given, perform the following: 3. DFS @ 11: (Highest Data Value) 4. BFS @ 11:…
A: Dfs-depth first search Bfs-bredth first search Dfs consists stack data structure Bfs consists queue…
Q: Consider a dynamic partitioning scheme. Show that, on average, the memory contains half as many…
A:
Q: My student claimed that the three fundamental page replacement algorithms (FIFO, LRU, and optimal)…
A: Page Replacement: Computers are designed with many levels of memory. As the memory's transmission…
Q: ] What is the time complexity and Big-O notation of the code below? Count and name all assignments…
A: here have to determine about time complexity of given function.
Q: Ilowing data elements: 13, 15, 59, 9,
A: Explanation: first, 13 will be added it will work as a root for others then all the node which are…
Q: DRW 30 15 CNS) 48 24 22 ASP 31 BNE 15 15 CBR SYD PER ADL 32 12 MEL
A: in the graph , the name of vertex are in character , which make the program very complex , so…
Q: 20. Consider the following tables GAMES and PLAYER and answer the following parts of this question :…
A: i. 2 ii. 19-Mar-2004 , 12-Dec-2003 iii. Ravi shai Lawn Tennis iv. 101 108 103
Q: What is the best data structure and algorithm used to solve Dijkstra's Shortest-Distance Algorithm?
A: Dijkstra’s Algorithm is used for solving single source shortest path problems. In this algorithm, a…
Q: 3. What issues are significant when assessing the relative merits of different sorting algorithms?…
A: INTRODUCTION: We need to answer the 3rd question.
Q: Discuss briefly about similarities between data objects and similarity measures for binary data.
A: The Answer is in below steps
Q: An example illustrates the following. • Parallel data
A: Parallel data Multiple data bits are sent over several networks at the same time as data is sent…
Q: Compute the similarity between R and T by using Jaccard Coeficient and SMC (Mathematically
A: Task : Given the dataset having two rows. Find the Jaccard Coeficient and SMC.
Q: 9.22 - Sketch both the output polygons and the resultant attribute table from the over- lay shown…
A:
Q: Question 6-Create a chart depicting order count datewise. Empl Rcd# ID 311587 645109 645109 835119…
A: The given excel data is :
Q: Normalization the table below to 3NF to overcome the problems in it. EID Ename Huey Dewey Louie DID…
A: Here key for the given relation is (DID, EID) The FDs possible are DID->Dname EID -> Ename…
Q: In terms of search algorithms, what is the difference between a BFS (Breadth First Search) and a DFS…
A: BFS ( Breadth First Search ) : This alogithms is used to traverse the node present in tree/ graph…
Q: Data Structure and Algorithm 4. Define the following terms: Node Head Next Data
A: A simple linked list is a type of indirectly linked list that can only be cut in one direction, from…
Q: Write down the working principle of Region Merging Algorithm.
A: The ability to segment images is critical to our interpretation of them. As a result, a lot of time…
Q: Merge sort and merge algorithm and time complexity analysis 5 3 1 11 29 2
A: Below I have provided a clear analysis of the given question:
Q: Writing a 3-way partitioning algorithm in php
A: 1. Choose a pivot element, e.g. the first element.2. Scan the array A from left to right and for…
Q: Given the following 2 dimensional list, how many rows and how many columns are in the list? nums =…
A: Python program to count number of rows and column in 2d list of array
Q: d everything from a single bit to a database in a data h
A: Required: Find everything from a single bit to a database in a data hierarchy.
Q: For each of the algorithms below, draw the spanning tree and find the sequence of visited nodes…
A: Handwritten solution of the given question is:
Q: Parallel Programming question: What are the associated data structures and underlying communication…
A: Answer: I have given answer in the hand written format in details. Parallel programming -in which…
Q: What is Greedy Algorithm in data Structure , explain and also provide example of the same ?
A: An algorithm is a program that is designed to find the optimal solution to a given problem.…
Q: chromosome
A: This article is going to discuss the concept of Genetic Algorithm in a way that is easy to…
Q: do you provide answers for statistics Sas programming?
A: Sas programming
Q: The known data sequence is (130, 116, 48492, 8, 236, 350, 66, 25, 371), please give the schematic…
A: Radix sort is based on sorting significant value of a number first sort ones value, next hundreds…
Q: Q1. Use MATLAB to write the following matrix 1 5 7 C=0 2 4 6 9 3. Then 1. What is the output for…
A: According to the Bartelby guideline we are suppose to answer only one question at a time Kindly…
Q: ) What algorithm does OSPF employ?
A: Introduction OSPF is an IGP that routes packets within a single autonomous system (AS). OSPF makes…
Q: Explain the difference between data parallelism and task parallelism.
A: Lets see the solution.
Q: Suppose our Accumulo system stores entire documents in the value column using the following data…
A: Answer: I have given answer in hand written format.
Q: Please help answer the following: Define DFS (depth first search) and BFS (breadth first search)…
A: Exactly is the BFS tree: The storytelling ability search (BFS) methodology is used to analyze a leaf…
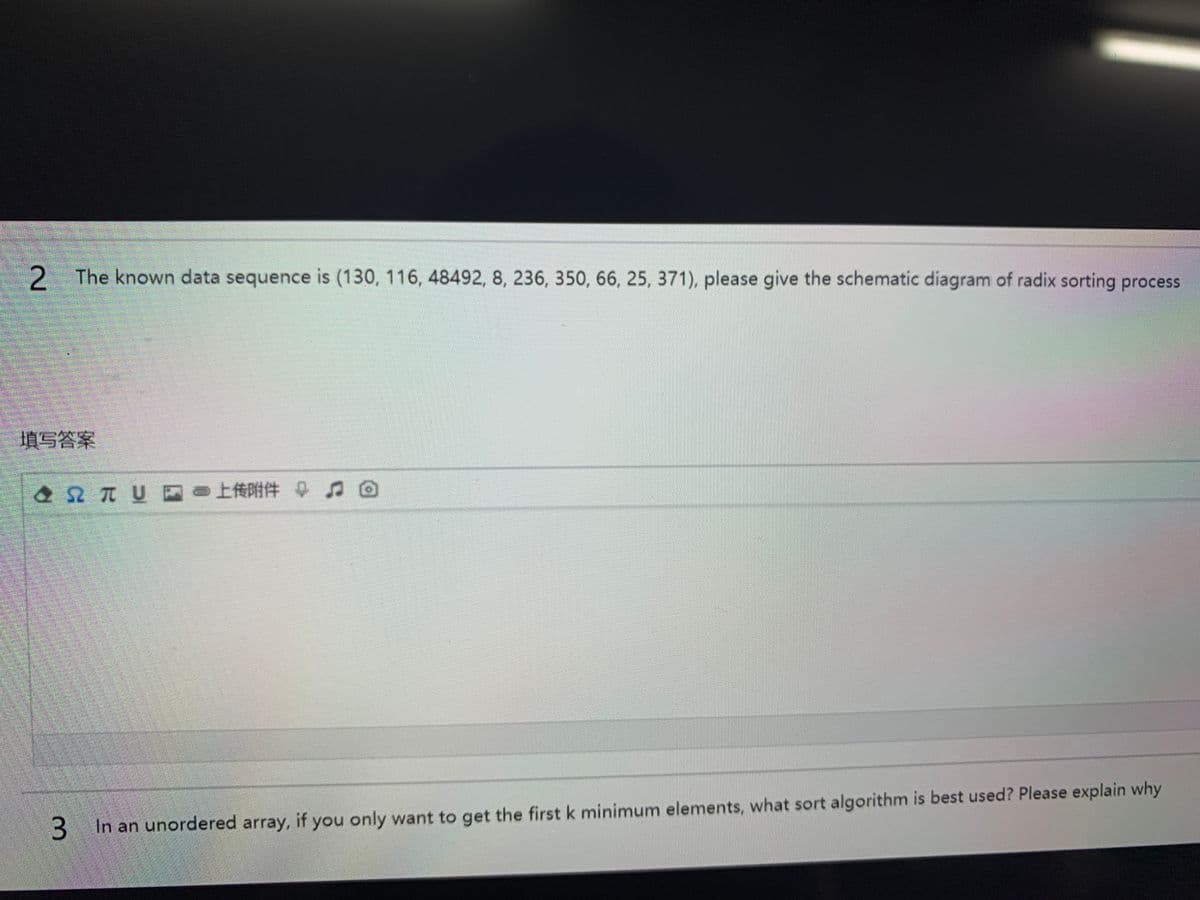
Given sequence:
130, 116, 48492, 8, 236, 350, 66, 25, 371
Max element = 48492 has 5 digits, so we make all numbers as 5 digits.
New sequence:
00130, 00116, 48492, 00008, 00236, 00350, 00066, 00025, 00371
First step: sorting in Ascending order, consider one’s place:
00130,00350,00371,48492,00025,00116,00236,00066,00008
Second Step: consider 10’s place
00008,00116,00025,00130,00236,00350,00066,00371,48492
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

- 1. (a)The objective is to shuffle a given array of n different elements. You would like to compare various shuffling algorithms and select the best of them. What does it mean: “the best shuffling algorithm”? What is a requirement for the perfect shuffling algorithm? (b) Is the Fisher-Yates Shuffle the perfect shuffling algorithm? Present a formal mathematical proof that this algorithm meets (or does not meet) the requirement given in (a). (c) Evaluate empirically performance of the Fisher-Yates Shuffle for selected numerical values of n. Propose your evaluation criteria and explain your evaluation methodology. Report your observations and conclusions.This question concerns the following sorting algorithm (attachment). (b) Consider the operation of SORT on a list of length N. How many comparisons in line 4 take place when i = 1 and when i = N-1? (c) How many comparisons take place in total? Show your working. You may use the result 1+2+...+n=n[(n+1)/2] (d) Based on the analysis above, or otherwise, what is the worst, best and average- case time complexity of SORT? Explain your answer.A) Consider the procedure SUM-ARRAY on the facing page. It computes the sum of the n numbers in array A[1:n]. State a loop invariant for this procedure, and use its initialization, maintenance, and termination properties to show that the SUMARRAY procedure returns the sum of the numbers in A[1:n]. SUM-ARRAY(A, n)1 sum = 02 for i = 1 to n3 sum = sum + A[i]4 return sum B) Rewrite the INSERTION-SORT procedure to sort into monotonically decreasing instead of monotonically increasing order.
- Consider the array L = 387, 690, 234 435 567 123 441 as an example. The number of components in this case is 7, the number of numbers is 3, and the radix is 10. This suggests that radix sort would require 10 bins and 3 cycles to complete the sorting. shows how the radix order is followed by the list. Each key is probably thrown into the garbage bin facing down. Each bin is turned into a key when the output to the is to be attached to the phrase: at the end of the bin.Show how quick sort sorts the following sequences of keys in ascending order. 12, 25, 35, 43, 48, 59, 77, 85, 86, 94? b) Discuss the time complexity of the quick sort algorithm for the above case?Given the following Array A = {3, 13, 89, 34, 21, 44, 99, 56, 9}Illustrate the execution of the sorting algorithms on the given array:• Merge-sort algorithm • Quicksort (using the median-of-three pivot) algorithm• Selection Sort algorithm For each fundamental iteration or recursion of the algorithm, write the content of the array.
- 4 I enrolled in the Algorithms, Part II course on Coursera, and considering that the question is given after the Radix Sort lecture, I'm assuming the intent is to use one of the Radix Sorts. Given an unsorted array A[] of N 64-bit integers and a target value T, determine whether there aretwo distinct integers i and j such that a[i] + a[j] = T. Briefly explain why your algorithm is correct. Your algorithm should run O(N) in the worst case.Please justify your answer: Some sorting algorithms require extra space, apart from the space needed for the original array that needs to be sorted. Which one of the following statements on the space usage of sorting algorithms is correct? a.) A Heapsort for sorting an array of size N requires an amount of extra space proportional to N. b.) Insertion Sort for sorting an array of size N requires an amount of extra space proportional to N. c.) Merge sort for sorting an array of size N requires an amount of extra space proportional to N. d.) Quicksort for sorting an array of size N requires an amount of extra space proportional to N. e.) None of the above(b) Explain in your own words why even the more efficient versions of bubble sort are considered to be slow algorithms. Illustrate your answer using the example data: {17, 15, 11, 13}
- Answer the given question with a proper explanation and step-by-step solution. Devise formulas (based on n, p and i) for my_first_i and my_last_i for processor i, in the global sum example (Like above). Assume that the processor numbers and array index start from 0. Remember that each core should be assigned roughly the same number of elements of computations in the loop. Hint: First consider the case when n is evenly divisible by p. n --> total number (1,2,3 .... n)p --> total number of processors We need to calculate sum of numbers.Consider a hybrid sorting algorithm that combines Mergesort with Insertion Sort.It uses Mergesort until the number of elements in the input becomes smaller than or equal to 8, after which it switches to Insertion Sort. What is the number of key comparisons performed by this hybrid sorting algorithm in the best case when running on an input array of size n? Briefly justify your answer. You could assume n = 2k, k is more than 3Consider the following list: L = 387, 690, 234, 435, 567, 123, 441. The number of components n = 7, the number of numbers l = 3, and the radix r = 10 are used here. This indicates that radix sort would require 10 bins and would arrange in three passes. demonstrates the radix sort passes over the array. It is believed that each key is tossed face down into the bin. When the keys are gathered in order from each bin at the conclusion of each run, the list of keys in each bin is flipped upside down and added to the output list.

