2x + 4 h(x) = 1 2x 1 f (x) = 1 –x g(x) = 3( x + 2x 6. | 3 -- 8. a.lim -4 · f (x) d.lim (8 · f(x) – g(x) – 2 · h(x)) X→2 x→2 b.lim (g(x) – h(x)) e.lim (-2· f(x) + 4 • g(x) + 2 · h(x)) X→2 X→2 c.lim (4 · f(x) + h(x)) f.lim f(x) + g(x) + 2 · h(x)) 3 X→2 X→2 +
2x + 4 h(x) = 1 2x 1 f (x) = 1 –x g(x) = 3( x + 2x 6. | 3 -- 8. a.lim -4 · f (x) d.lim (8 · f(x) – g(x) – 2 · h(x)) X→2 x→2 b.lim (g(x) – h(x)) e.lim (-2· f(x) + 4 • g(x) + 2 · h(x)) X→2 X→2 c.lim (4 · f(x) + h(x)) f.lim f(x) + g(x) + 2 · h(x)) 3 X→2 X→2 +
College Algebra
7th Edition
ISBN:9781305115545
Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Chapter3: Polynomial And Rational Functions
Section3.6: Rational Functions
Problem 2E
Related questions
Question
Type exact answer only. No other unnecessary symbols or words. Write DNE if you think the limit does not exist.
answer F only
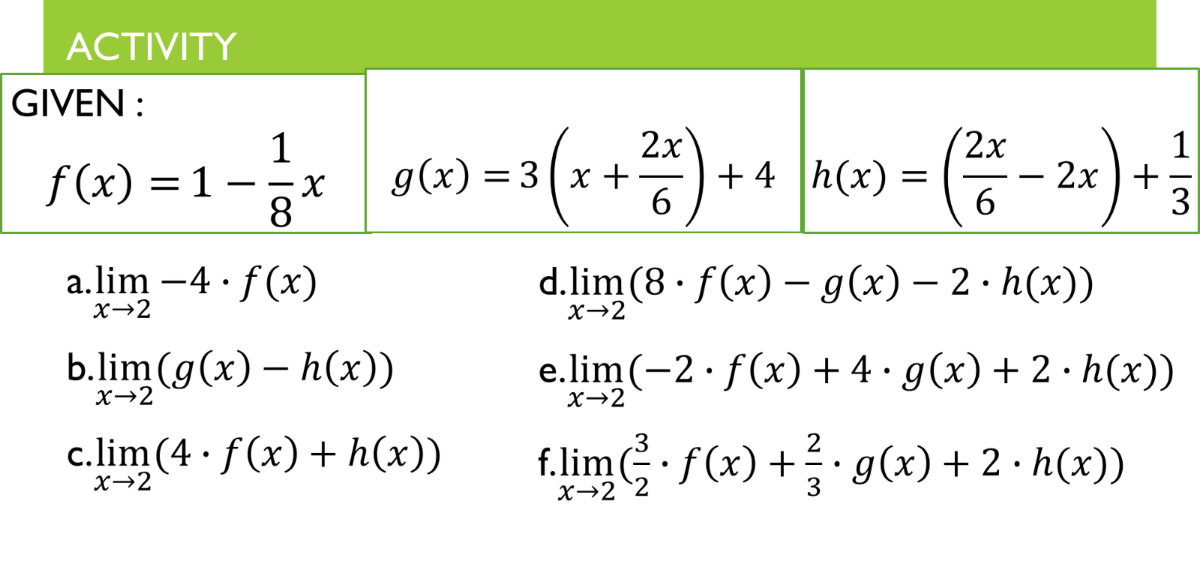
Transcribed Image Text:АCTIVITY
GIVEN :
2x
+ 4 h(x) =
2x
1
2х +
3
1
f (x) = 1 –x
8
g(x) = 3(x +
a.lim -4 · f (x)
X→2
d.lim (8 · f(x) – g(x) – 2 · h(x))
|
X→2
b.lim (g(x) – h(x))
e.lim (-2· f(x) + 4 • g(x) + 2 · h(x))
X→2
X→2
c.lim (4 · f (x) + h(x))
.3
f.lim G f(x) + g(x)+ 2· h(x))
X→2
X→2 `2
3
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305115545
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305115545
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage