3 13 15 Boiler Turbines 2 Condenser 1 P Pump In a reheat ideal Rankine cycle, steam enters the high-pressure turbine at 8.6 MPa and 600°C. The steam expands until it saturated vapor and then reheated to 500°C. It re-enters a low-pressure turbine and expands to a condenser pressure of Determine the following: (a) Temperature, Pressure, and Enthalpy of the stream leaving the high-pressure turbine to be reheated (Stream 4) (b) Work generated by the two (2) turbines; (b) Work done on the pump; and (c) cycle efficiency. Note that the stream leaving the low-pressure turbine can either be a wet steam or a superheated steam. As part of your solution, fill up the table below. Stream P (in bar) H (in kJ/kg) S (in kJ/kg-K) (you do not need to completely fill this table, only those needed in the calculations) 1 2 HP LP WT 6
3 13 15 Boiler Turbines 2 Condenser 1 P Pump In a reheat ideal Rankine cycle, steam enters the high-pressure turbine at 8.6 MPa and 600°C. The steam expands until it saturated vapor and then reheated to 500°C. It re-enters a low-pressure turbine and expands to a condenser pressure of Determine the following: (a) Temperature, Pressure, and Enthalpy of the stream leaving the high-pressure turbine to be reheated (Stream 4) (b) Work generated by the two (2) turbines; (b) Work done on the pump; and (c) cycle efficiency. Note that the stream leaving the low-pressure turbine can either be a wet steam or a superheated steam. As part of your solution, fill up the table below. Stream P (in bar) H (in kJ/kg) S (in kJ/kg-K) (you do not need to completely fill this table, only those needed in the calculations) 1 2 HP LP WT 6
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
ChapterMA: Math Assessment
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1MA
Related questions
Question
Need asap answer c and table only
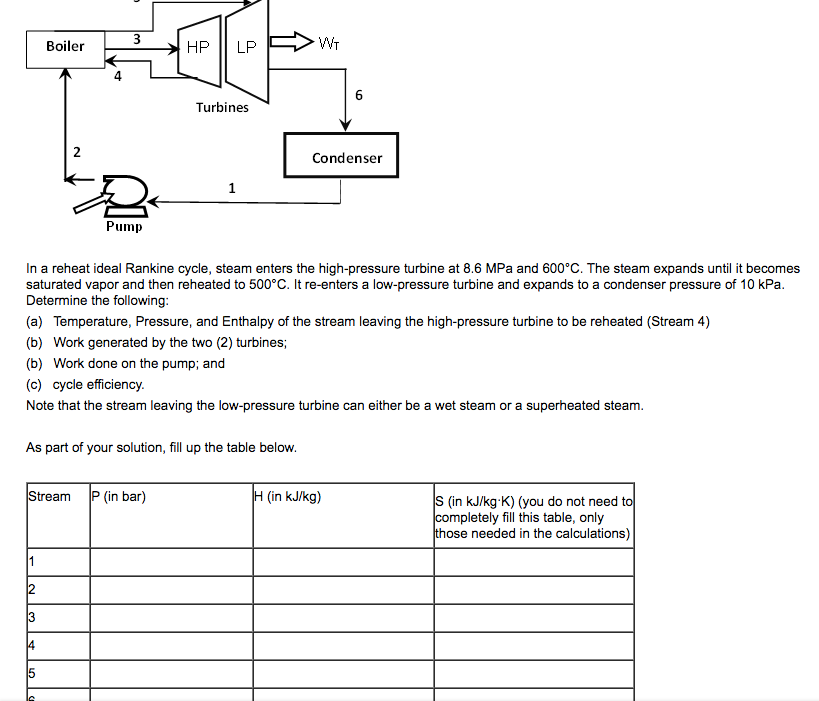
Transcribed Image Text:Boiler
3
LP
6
Turbines
Condenser
1
똔
Pump
In a reheat ideal Rankine cycle, steam enters the high-pressure turbine at 8.6 MPa and 600°C. The steam expands until it becomes
saturated vapor and then reheated to 500°C. It re-enters a low-pressure turbine and expands to a condenser pressure of 10 kPa.
Determine the following:
(a) Temperature, Pressure, and Enthalpy of the stream leaving the high-pressure turbine to be reheated (Stream 4)
(b) Work generated by the two (2) turbines;
(b) Work done on the pump; and
(c) cycle efficiency.
Note that the stream leaving the low-pressure turbine can either be a wet steam or a superheated steam.
As part of your solution, fill up the table below.
Stream P (in bar)
H (in kJ/kg)
S (in kJ/kg-K) (you do not need to
completely fill this table, only
those needed in the calculations)
3
4
A
HP
WT
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118170519
Author:
Norman S. Nise
Publisher:
WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118807330
Author:
James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:
WILEY