3) Consider a system on the left where the center point is origin of Cartesian coordinate system, and 2= 0 is the boundary plane for material-air interface. The medium 2 is air, and medium 1 is a material with o = 10-3 S/m, ur = 2 and er = 5 Material Air The frequency is 2 GHz, and incident angle for the incident uniform plane wave is 6 degrees. The incident wave at the origin is given in the phasor domain as Ē, (0,0,0) = A(Bâ, +0.5â, –0.5â,) V/m Medium 1 Medium 2 where A and B are nonnegative real numbers to be calculated.
3) Consider a system on the left where the center point is origin of Cartesian coordinate system, and 2= 0 is the boundary plane for material-air interface. The medium 2 is air, and medium 1 is a material with o = 10-3 S/m, ur = 2 and er = 5 Material Air The frequency is 2 GHz, and incident angle for the incident uniform plane wave is 6 degrees. The incident wave at the origin is given in the phasor domain as Ē, (0,0,0) = A(Bâ, +0.5â, –0.5â,) V/m Medium 1 Medium 2 where A and B are nonnegative real numbers to be calculated.
Related questions
Question
Magnetic field problem
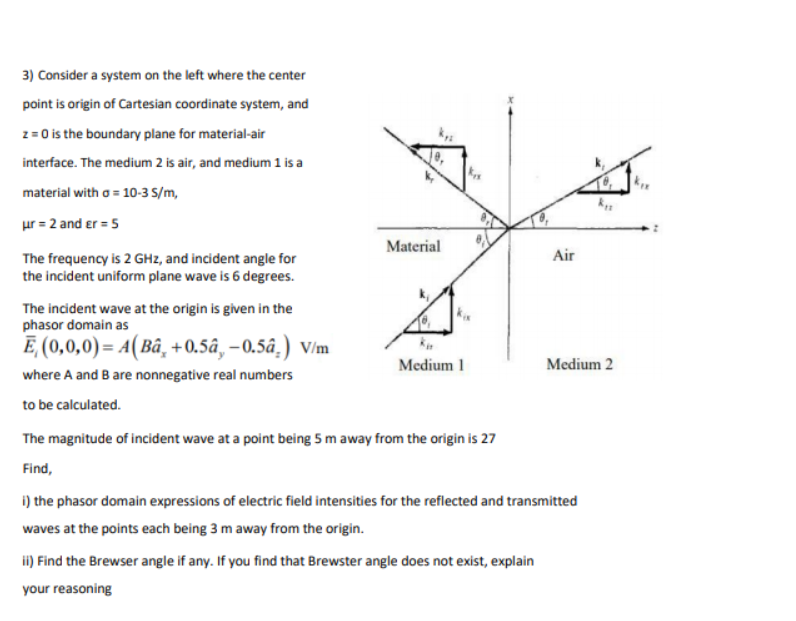
Transcribed Image Text:3) Consider a system on the left where the center
point is origin of Cartesian coordinate system, and
2= 0 is the boundary plane for material-air
interface. The medium 2 is air, and medium 1 is a
material with o = 10-3 S/m,
ur = 2 and er = 5
Material
Air
The frequency is 2 GHz, and incident angle for
the incident uniform plane wave is 6 degrees.
The incident wave at the origin is given in the
phasor domain as
Ē, (0,0,0) = A(Bâ, +0.5â, –0.5â,) V/m
Medium 1
Medium 2
where A and B are nonnegative real numbers
to be calculated.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 7 steps with 7 images
