3, tor as a fune (b) Estimate the frequency. v (m/s) +5 0. 0.1 0.2 0.3 -5 Figure P11.11 11.2 EXAMPLES OF SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION 12. The period of oscillation for a mass-on-a-spring system is 0.22 s. If m = 3.5 kg, what is the spring constant of the spring?
3, tor as a fune (b) Estimate the frequency. v (m/s) +5 0. 0.1 0.2 0.3 -5 Figure P11.11 11.2 EXAMPLES OF SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION 12. The period of oscillation for a mass-on-a-spring system is 0.22 s. If m = 3.5 kg, what is the spring constant of the spring?
University Physics Volume 1
18th Edition
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Chapter15: Oscillations
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 67AP: A 2.00-kg block lies at rest on a frictionless table. A spring, with a spring constant of 100 N/m is...
Related questions
Concept explainers
Question
Problem 14. Must use formula from formula sheet. I’m not sure where to start
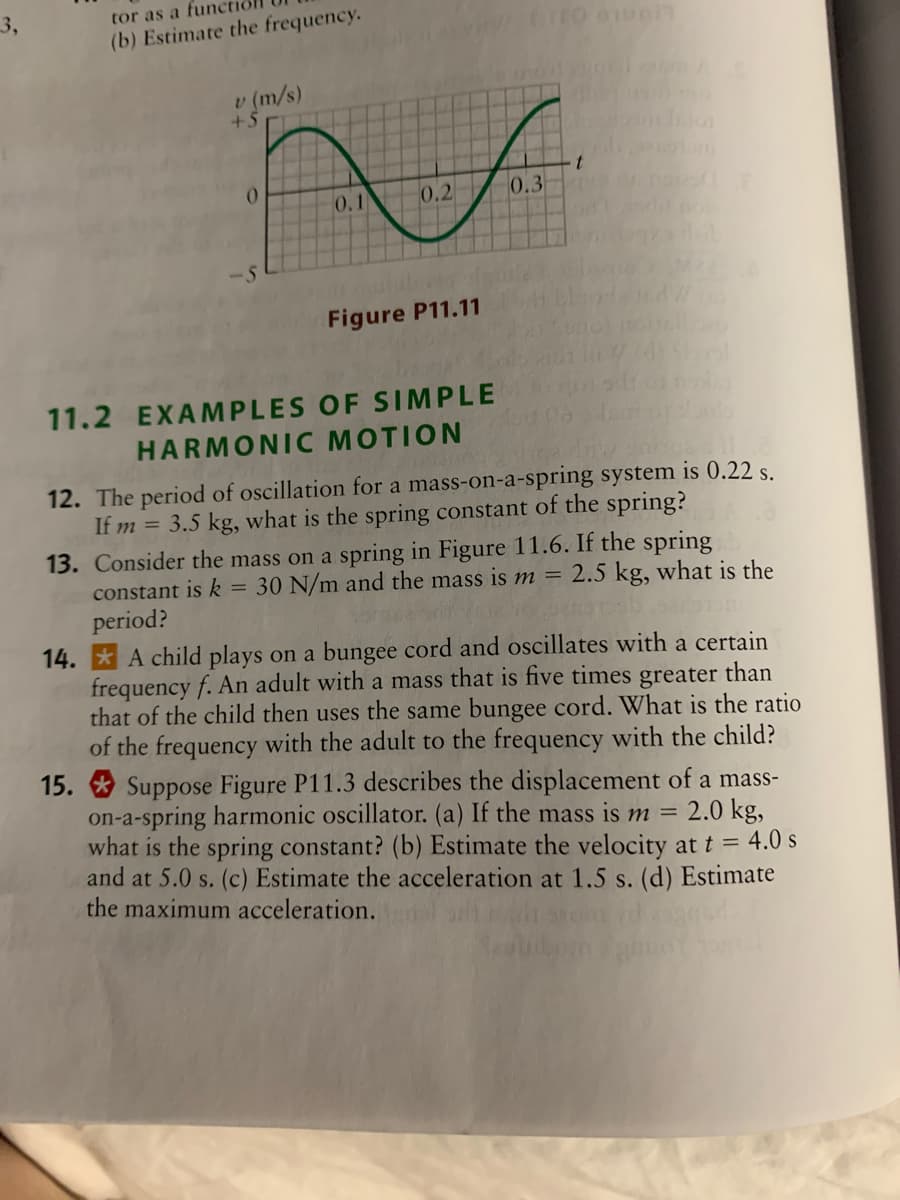
Transcribed Image Text:3,
tor as a fun
(b) Estimate the frequency.
m/s)
0.
0.2
0.3
0.1
-5
Figure P11.11
EXAMPLES OF SIMPLE
HARMONIC MOTION
11.2
12. The period of oscillation for a mass-on-a-spring system is 0.22 s.
If m = 3.5 kg, what is the spring constant of the spring?
13. Consider the mass on a spring in Figure 11.6. If the spring
constant is k
period?
14. * A child plays on a bungee cord and oscillates with a certain
frequency f. An adult with a mass that is five times greater than
that of the child then uses the same bungee cord. What is the ratio
of the frequency with the adult to the frequency with the child?
15. * Suppose Figure P11.3 describes the displacement of a mass-
on-a-spring harmonic oscillator. (a) If the mass is m =
what is the spring constant? (b) Estimate the velocity at t = 4.0 s
and at 5.0 s. (c) Estimate the acceleration at 1.5 s. (d) Estimate
the maximum acceleration.
= 30 N/m and the mass is m =
2.5 kg, what is the
2.0 kg,

Transcribed Image Text:Subscripts
volume ,no"u" use
MusH start wlone of These eguahions
use "v" for
Physics 104 Equation Sheet
k = 9.0 x 10° Nm²/C²
Ho = 4n x 107 N/A²
C = 3.00 x 10° m/s
e = 1.6 x 1019 C
E0 = 8.85 x 1012 C²/Nm?
"= 6.63 x 10 34 Js = 4.14 x 1015 eVs lo = 1012 w/m?
me = 9.11 x 10³1 kg
m, = 1.67 x 1027 kg
nair = 1.00
nsoap = 1.50
Wsilver = 4.74 eV
nwater = 1.33
Vsound = 340 m/s
1 eV = 1.6 x 10 19 J
F = kqıq2/r²
PE = kqı92/r
V = kQ/r
AV = -EAx
E = kQ/r?
F = qE
C = q/AV
AV = IR
R = pL/A
APEE = -WE = -qEd
APE = qAV
C = E0A/d
PE = ½ QAV
1/Reg = E, 1/R;
P = IAV
Reg = E; R,
| = Aq/At
F = qvB sino
F = ILB sino
B = Hol/2nr
OB = BA cosO
EMF = NA DB/At
B = Ho nl
IV1 = 12 V2
V1/V2 = N1/N2
EMF = NBAW sin(wt)
v = fA
n = c/v
An = Aair/n
f = 1/T
W = 2nf =
%3D
F = -kAx
PE = ½ kAx?
V =
ni sin1 = n2 sino2
fs
fo =
B = 10 log10 (1/lo)
12/l1 = r/r?
1/o + 1/i = 1/f
fo = fs(1 ± °o/p)
d sino = mA
m = -i/o
f = R/2
P = 1/f
d sino = (m + ½ )A
Am T = 2.90 x 10 mK
KEmax = hf – W
E = hf
En = -13.6eV/n?
L = nh/2n
Rn = (0.0529 nm) n²
A = h/mv = h/p
A-X' = (h/mc)(1 – cos©)
AxAp. 2 h/47
ΔΕΔt2 h/4π
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168000
Author:
Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning