3. A laser light is held at a height of 30cm above the surface of a block of glass, and forming an angle of 30 with such surface, as in Figure. The block of glass has a depth of 15cm. The laser is right above the edge of the block. The light is hitting the bottom surface of the glass at a distance of 63em from the edge of the glass block. (a) Caleulate the index of refraction of the glass. (b) Caleulate the total time it takes light to complete the trip from the laser to the bottom surface of the block. The same material is now used to mamafacture a comverging lens with spherical surfaces of equal radius. (e) Caleulate the radius of the curvature such that the resulting lens has a focal length of 50cm. A pencil of length 10cm is held at a distance of 60 cm from that lens. (d) Caleulate the size and position of the resulting image, highlighting whether it is real or virtual, erect or inverted. Include a drawing depicting all focal points, and rays you used to find the position and size of the image.
3. A laser light is held at a height of 30cm above the surface of a block of glass, and forming an angle of 30 with such surface, as in Figure. The block of glass has a depth of 15cm. The laser is right above the edge of the block. The light is hitting the bottom surface of the glass at a distance of 63em from the edge of the glass block. (a) Caleulate the index of refraction of the glass. (b) Caleulate the total time it takes light to complete the trip from the laser to the bottom surface of the block. The same material is now used to mamafacture a comverging lens with spherical surfaces of equal radius. (e) Caleulate the radius of the curvature such that the resulting lens has a focal length of 50cm. A pencil of length 10cm is held at a distance of 60 cm from that lens. (d) Caleulate the size and position of the resulting image, highlighting whether it is real or virtual, erect or inverted. Include a drawing depicting all focal points, and rays you used to find the position and size of the image.
College Physics
10th Edition
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Chapter22: Reflection And Refraction Of Light
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 18P: A ray of light strikes a flat, 2.00-cm-thick block of glass (n = 1.50) at ail angle of 30.0 with...
Related questions
Question
THIS IS THE FULL QUESTION
PLEASE HELP READ CAREFULLY
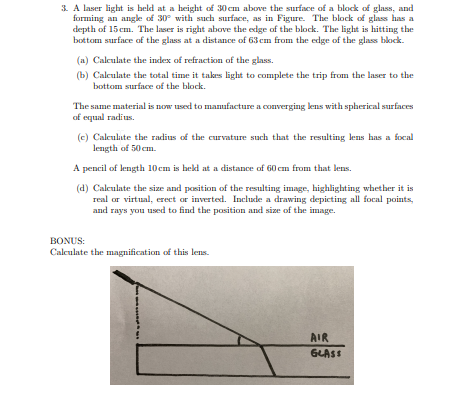
Transcribed Image Text:3. A laser light is held at a height of 30 cm above the surface of a block of glass, and
forming an angle of 30° with such surface, as in Figure. The block of glass has a
depth of 15 cm. The laser is right above the edge of the block. The light is hitting the
bottom surface of the glass at a distance of 63 cm from the edge of the glass block.
(a) Calculate the index of refraction of the glass.
(b) Calculate the total time it takes light to complete the trip from the laser to the
bottom surface of the block.
The same material is now used to manufacture a converging lens with spherical surfaces
of equal radius.
(c) Calculate the radius of the curvature such that the resulting lens has a focal
length of 50 em.
A pencil of length 10cm is hekd at a distance of 60 cm from that lens.
(d) Calculate the size and position of the resulting image, highlighting whether it is
real or virtual, erect or inverted. Include a drawing depicting all focal points,
and rays you used to find the position and size of the image.
BONUS:
Calculate the magnification of this lens.
AIR
GLASS
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168000
Author:
Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:
OpenStax College
