3. An interesting kind of one shot game is known as a “Prisoners' Dilemma.“ The payoffs in a Prisoners' Dilemma are such that rational actors end up at a Nash equilibrium solution that is in neither party's best interest. This type of game crops up in all kinds of places, from arms control to trade policy, as well as in business strategy situations. (a) Here below is a version of the original Prisoners' Dilemma. The premise is that two guilty suspects are arrested for a crime and held in separate cells so they cannot communicate; if neither confesses they will each get a small jail sentence; but if one confesses and implicates the other, while the other doesn't confess, the confessor goes free while the other gets a stiff sentence; if they both confess they both spend significant time in jail. The payoffs below are in years of prison time, so low values are better than high values. Prisoner 2 Confess Deny 1,1 Deny Confess 8,0 5,5 Prisoner 1 0,8 What's the solution to this game, and why? In what sense is the solution not the best outcome for the prisoners? (b) Here below is the first payoff matrix we saw in class today for the UA-SW game. Is it a Prisoners Dilemma? Explain why or why not (and note, here, higher values for the payoffs are good). SW High 60, 0 50, 50 Low 20, 20 0, 60 Low UA High
3. An interesting kind of one shot game is known as a “Prisoners' Dilemma.“ The payoffs in a Prisoners' Dilemma are such that rational actors end up at a Nash equilibrium solution that is in neither party's best interest. This type of game crops up in all kinds of places, from arms control to trade policy, as well as in business strategy situations. (a) Here below is a version of the original Prisoners' Dilemma. The premise is that two guilty suspects are arrested for a crime and held in separate cells so they cannot communicate; if neither confesses they will each get a small jail sentence; but if one confesses and implicates the other, while the other doesn't confess, the confessor goes free while the other gets a stiff sentence; if they both confess they both spend significant time in jail. The payoffs below are in years of prison time, so low values are better than high values. Prisoner 2 Confess Deny 1,1 Deny Confess 8,0 5,5 Prisoner 1 0,8 What's the solution to this game, and why? In what sense is the solution not the best outcome for the prisoners? (b) Here below is the first payoff matrix we saw in class today for the UA-SW game. Is it a Prisoners Dilemma? Explain why or why not (and note, here, higher values for the payoffs are good). SW High 60, 0 50, 50 Low 20, 20 0, 60 Low UA High
Chapter8: Game Theory
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 8.9P
Related questions
Question
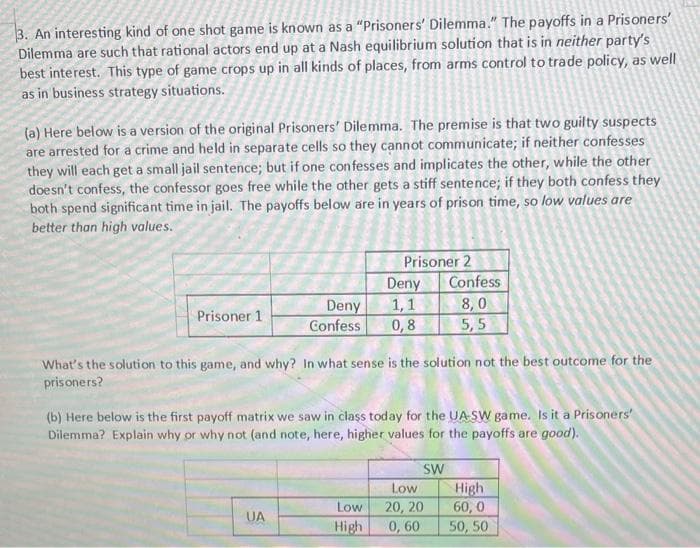
Transcribed Image Text:3. An interesting kind of one shot game is known as a "Prisoners' Dilemma." The payoffs in a Prisoners'
Dilemma are such that rational actors end up at a Nash equilibrium solution that is in neither party's
best interest. This type of game crops up in all kinds of places, from arms control to trade policy, as well
as in business strategy situations.
(a) Here below is a version of the original Prisoners' Dilemma. The premise is that two guilty suspects
are arrested for a crime and held in separate cells so they cannot communicate; if neither confesses
they will each get a small jail sentence; but if one con fesses and implicates the other, while the other
doesn't confess, the confessor goes free while the other gets a stiff sentence; if they both confess they
both spend significant time in jail. The payoffs below are in years of prison time, so low values are
better than high values.
Prisoner 2
Deny
Confess
8,0
5,5
1,1
Deny
Confess
Prisoner 1
0,8
What's the solution to this game, and why? In what sense is the solution not the best outcome for the
prisoners?
(b) Here below is the first payoff matrix we saw in class today for the UA-SW game. Is it a Prisoners'
Dilemma? Explain why or why not (and note, here, higher values for the payoffs are good).
SW
High
60, 0
50, 50
Low
Low
20, 20
0, 60
UA
High
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305585126
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781285165875
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305585126
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781285165875
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Microeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305971493
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Microeconomics
Economics
ISBN:
9781305156050
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506381
Author:
James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning