3. Run the simulation by clicking on the pause/play button. While the pendulum bob is oscillating, activate the Period Timer and note the period of oscillation. 4. Keeping the same parameters, make several trials, each time, increasing the acceleration due to gravity by 5 m/s² m until g = 25 m/s². Record your data in the table 3 below. 5. Note that for inverse gravity, all you must do is divide the value 1 by the gravity in column 1. Table 3 Acceleration due to gravity, g, (m/s²) 5 10 15 20 25 Period, T, of Oscillation (s) 2.8220 1.9925 1.6267 1.4081 1.2592 Period Squared (T²) (S²) 7.963684 3.970056 2.646153 1.982746 1.585585 Inverse Gravity (1/g) (s²/m)
3. Run the simulation by clicking on the pause/play button. While the pendulum bob is oscillating, activate the Period Timer and note the period of oscillation. 4. Keeping the same parameters, make several trials, each time, increasing the acceleration due to gravity by 5 m/s² m until g = 25 m/s². Record your data in the table 3 below. 5. Note that for inverse gravity, all you must do is divide the value 1 by the gravity in column 1. Table 3 Acceleration due to gravity, g, (m/s²) 5 10 15 20 25 Period, T, of Oscillation (s) 2.8220 1.9925 1.6267 1.4081 1.2592 Period Squared (T²) (S²) 7.963684 3.970056 2.646153 1.982746 1.585585 Inverse Gravity (1/g) (s²/m)
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology Update (No access codes included)
9th Edition
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Chapter39: Relativity
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 39.1CQ: In several cases, a nearby star has been found to have a huge planet orbiting about it, although...
Related questions
Question
100%
I need to add the inverse gravity to my chart. How do I calculate the inverse gravity?
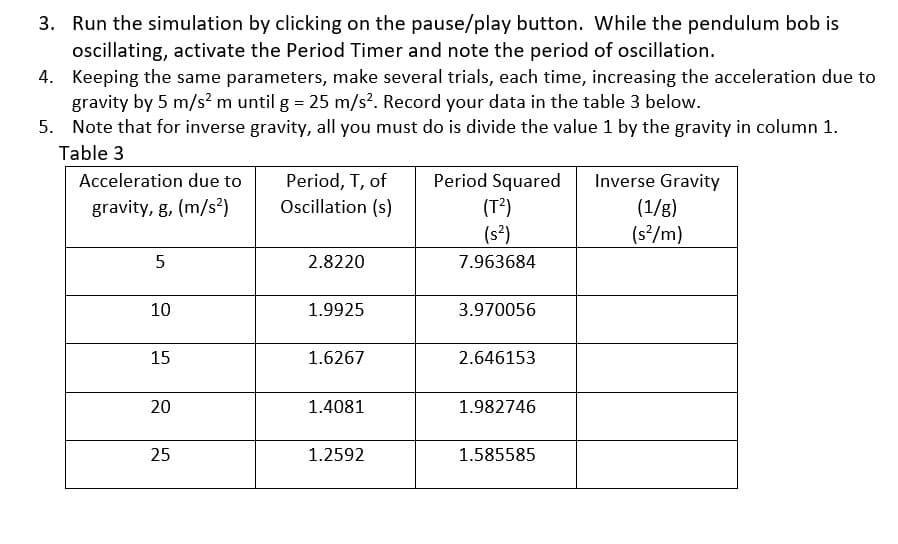
Transcribed Image Text:3. Run the simulation by clicking on the pause/play button. While the pendulum bob is
oscillating, activate the Period Timer and note the period of oscillation.
4. Keeping the same parameters, make several trials, each time, increasing the acceleration due to
gravity by 5 m/s² m until g = 25 m/s2. Record your data in the table 3 below.
5. Note that for inverse gravity, all you must do is divide the value 1 by the gravity in column 1.
Table 3
Acceleration due to
gravity, g, (m/s²)
5
10
15
20
25
Period, T, of
Oscillation (s)
2.8220
1.9925
1.6267
1.4081
1.2592
Period Squared
(T²)
(s²)
7.963684
3.970056
2.646153
1.982746
1.585585
Inverse Gravity
(1/g)
(s²/m)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168000
Author:
Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168284
Author:
Andrew Fraknoi; David Morrison; Sidney C. Wolff
Publisher:
OpenStax

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168000
Author:
Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168284
Author:
Andrew Fraknoi; David Morrison; Sidney C. Wolff
Publisher:
OpenStax

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Horizons: Exploring the Universe (MindTap Course …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305960961
Author:
Michael A. Seeds, Dana Backman
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

An Introduction to Physical Science
Physics
ISBN:
9781305079137
Author:
James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar Torres
Publisher:
Cengage Learning