3. Suppose that the charges in Sample Problems 1.4 item number 3 are situated as shown. Find the resultant electric force on the charge at A. +q b. 1.00 m A В 1.00 m D b. +9
3. Suppose that the charges in Sample Problems 1.4 item number 3 are situated as shown. Find the resultant electric force on the charge at A. +q b. 1.00 m A В 1.00 m D b. +9
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student Edition
1st Edition
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Chapter28: The Atom
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 60A
Related questions
Question
Suppose that the charges in Sample Problems 1.4 item number 3 are situated as shown, find the resultant electric force on the charge at A. The diagrams are attached herewith.
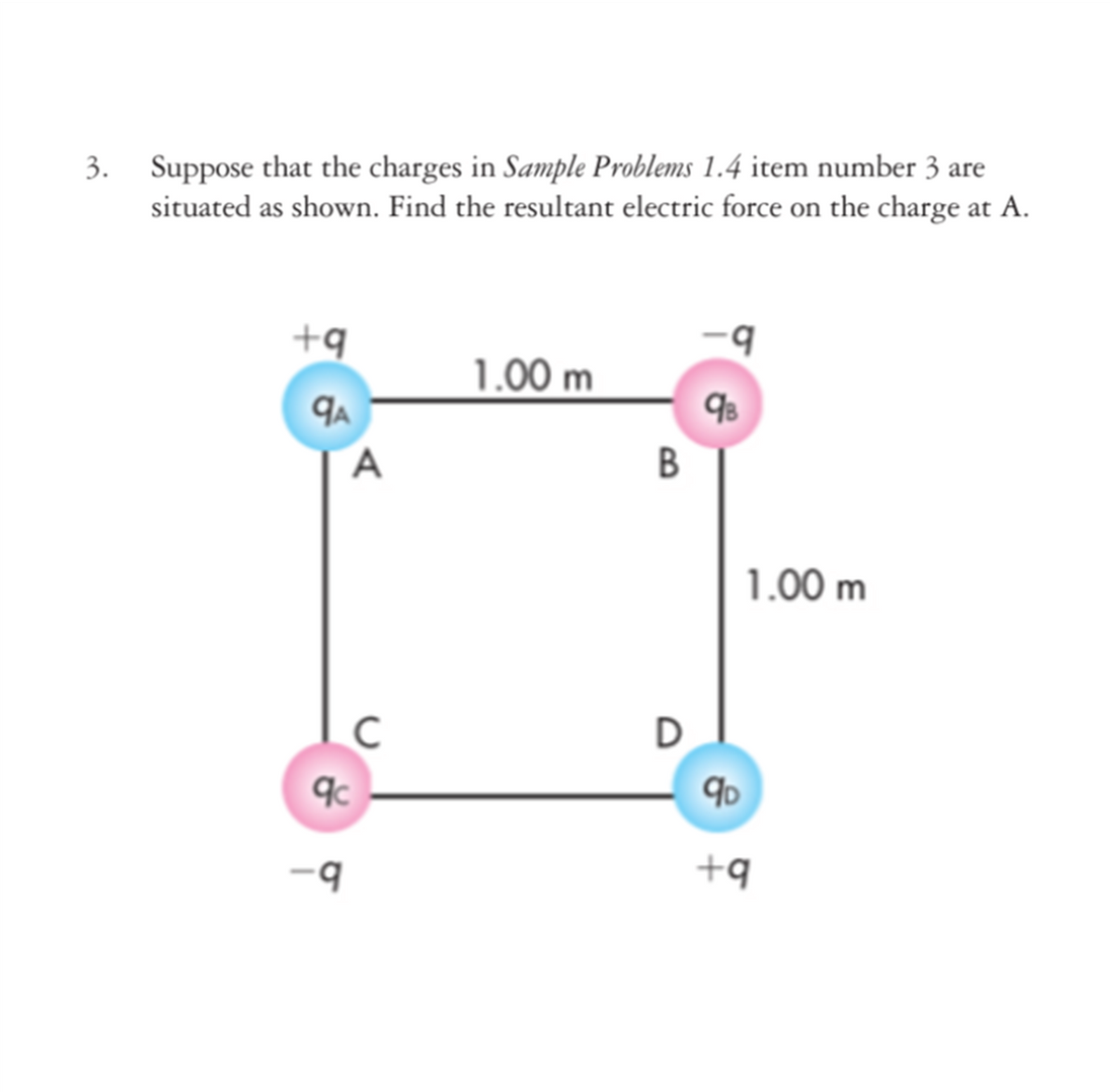
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose that the charges in Sample Problems 1.4 item number 3 are
situated as shown. Find the resultant electric force on the charge at A.
3.
+q
1.00 m
A
В
1.00 m
D
b.
+q
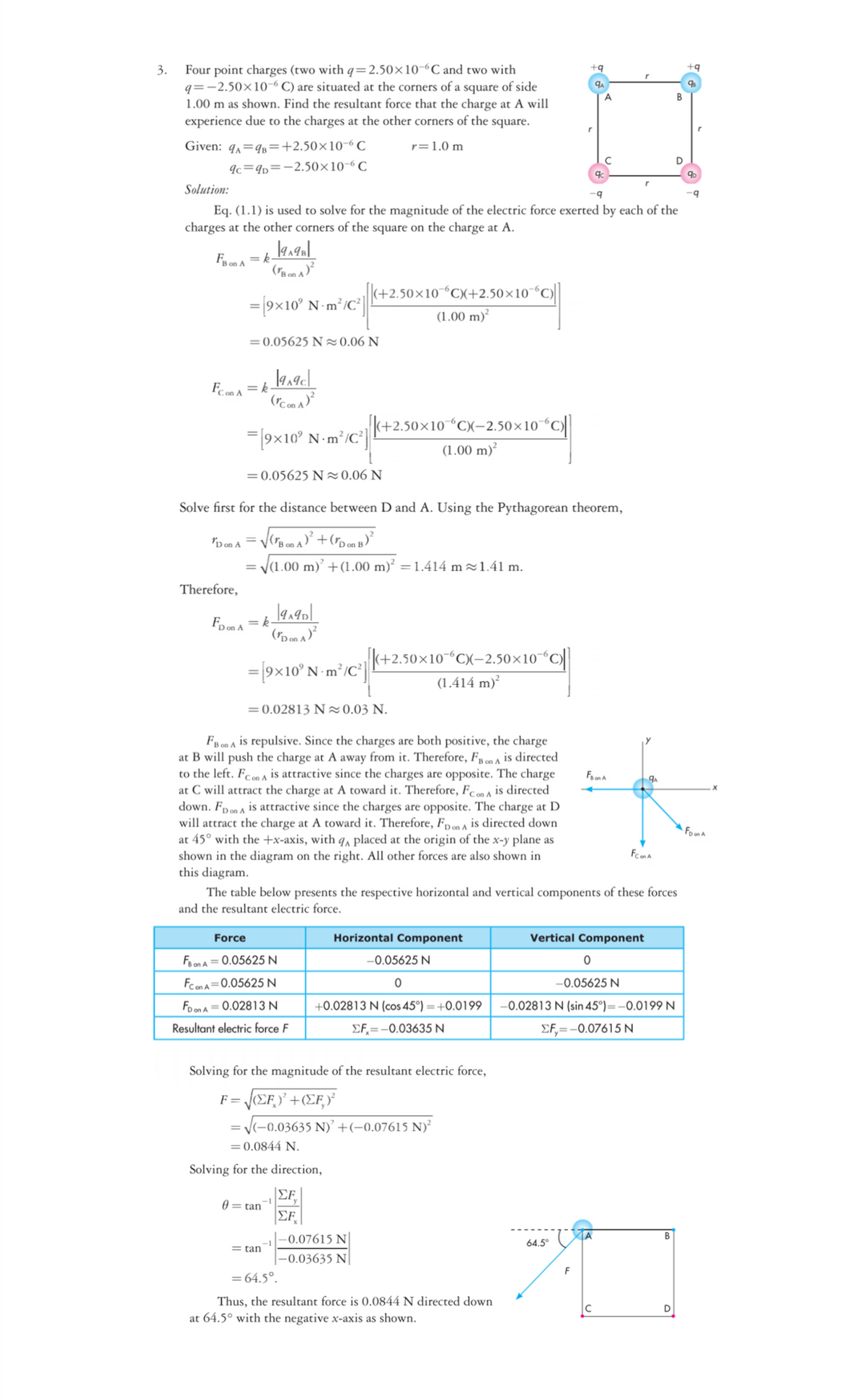
Transcribed Image Text:Four point charges (two with q=2.50×10-6C and two with
q=-2.50×10-6 C) are situated at the corners of a square of side
1.00 m as shown. Find the resultant force that the charge at A will
experience due to the charges at the other corners of the square.
+9
3.
+q
Given: 9,=9B=+2.50×10¬6 C
r=1.0 m
Ic=9p=-2.50×10-6C
Solution:
Eq. (1.1) is used to solve for the magnitude of the electric force exerted by each of the
charges at the other corners of the square on the charge at A.
Fs on A = k-
|(+2.50×10¬°C)(+2.50×10¯“C)|
= 19x10° N-m²/C"|
(1.00 m)²
= 0.05625 N20.06 N
Feom A = k
|(+2.50×10“CX-2.50×10°C
=19x10° N m²/C²|
(1.00 m)?
= 0.05625 N20.06 N
Solve first for the distance between D and A. Using the Pythagorean theorem,
'D on A =
("B on A
V(1.00 m)’ +(1.00 m)² = 1.414 m~1.41 m.
Therefore,
Fo on A = k-
=[9x10° N m²/C²| (+2.50×10°C)X-2.50×10°C||
(1.414 m)²
= 0.02813 N20.03 N.
FB on A is repulsive. Since the charges are both positive, the charge
at B will push the charge at A away from it. Therefore, FB on A is directed
to the left. Fcon A is attractive since the charges are opposite. The charge
at C will attract the charge at A toward it. Therefore, Fc on A is directed
down. Fpon A is attractive since the charges are opposite. The charge at D
will attract the charge at A toward it. Therefore, F on A is directed down
at 45° with the +x-axis, with q, placed at the origin of the x-y plane as
shown in the diagram on the right. All other forces are also shown in
this diagram.
Fooma
Foona
Fcon A
The table below presents the respective horizontal and vertical components of these forces
and the resultant electric force.
Force
Horizontal Component
Vertical Component
FoonA = 0.05625 N
–0.05625 N
FconA=0.05625 N
–0.05625 N
Foona = 0.02813 N
+0.02813 N (cos 45°) =+0.0199
-0.02813 N (sin 45°)=-0.0199 N
Resultant electric force F
EF,=-0.03635 N
EF,=-0.07615 N
Solving for the magnitude of the resultant electric force,
F =
V(-0.03635 N)' +(-0.07615 N)²
= 0.0844 N.
Solving for the direction,
|EF,
0 = tan
EF
TA
--0.07615 N
64,5°
= tan
|-0.03635 N
= 64.5°.
Thus, the resultant force is 0.0844 N directed down
at 64.5° with the negative x-axis as shown.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill