3. Suppose you have reason to believe that you can predict the value of some random variable Y from the values of another random variable X (e.g. X is the number of classes a student has missed, and Y is their score on the final exam). In the simplest scenario, the predicted value of Y would be Ý = aX +b for some constants a and b (this would be called a linear predictor). The quality of this predictor can be measured using the mean square error E((Y – Ý )²). (a) Show that the mean square error is minimized if we pick constants b = p, a= µY – bµx , where p is the correlation coefficient between X and Y. (b) Calculate the mean square error for this best linear predictor. How does the value of p affect the error?
3. Suppose you have reason to believe that you can predict the value of some random variable Y from the values of another random variable X (e.g. X is the number of classes a student has missed, and Y is their score on the final exam). In the simplest scenario, the predicted value of Y would be Ý = aX +b for some constants a and b (this would be called a linear predictor). The quality of this predictor can be measured using the mean square error E((Y – Ý )²). (a) Show that the mean square error is minimized if we pick constants b = p, a= µY – bµx , where p is the correlation coefficient between X and Y. (b) Calculate the mean square error for this best linear predictor. How does the value of p affect the error?
Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
4th Edition
ISBN:9781285463247
Author:David Poole
Publisher:David Poole
Chapter7: Distance And Approximation
Section7.3: Least Squares Approximation
Problem 31EQ
Related questions
Question
HWM-8(3)
Please help me with the below question needed with a clear step by step explanation, please
NEEDED ALL PARTS PLEASE
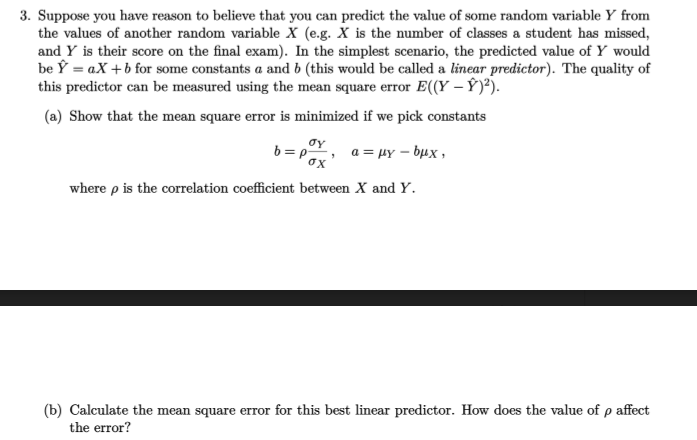
Transcribed Image Text:3. Suppose you have reason to believe that you can predict the value of some random variable Y from
the values of another random variable X (e.g. X is the number of classes a student has missed,
and Y is their score on the final exam). In the simplest scenario, the predicted value of Y would
be Ý = aX +b for some constants a and b (this would be called a linear predictor). The quality of
this predictor can be measured using the mean square error E((Y – Ý)²).
(a) Show that the mean square error is minimized if we pick constants
oy
b = pY, a = HY – bµx ,
ox
where p is the correlation coefficient between X and Y.
(b) Calculate the mean square error for this best linear predictor. How does the value of p affect
the error?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 5 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning